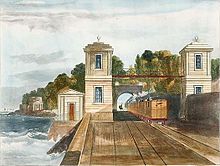- Dublin and Kingstown Railway
-
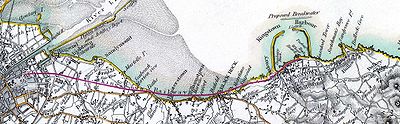
The Dublin and Kingstown Railway (D&KR), which opened in 1834, was Ireland’s first railway. It linked Westland Row in Dublin with Kingstown Harbour’s West Pier in County Dublin.
Contents
History
The Dublin and Kingstown Railway Company was founded in 1831 by businessmen in the city to look into building a railway. Within two years, they had a contractor and a parliamentary act.[1] The construction contract was awarded to William Dargan.[2]
Building of the 10 km (6 mi) line was delayed by opposition from two different landowners who insisted on large cash compensations and in the case of Lord Cloncurry the building of a private foot bridge over the line to a bathing area complete with a Romanesque temple, a short tunnel and a cutting to maintain his privacy. Part of the line ran on an embankment built across the strand between Merrion and Blackrock which later led to the formation of Booterstown marsh. The first train ran on 9 October 1834, consisting of eight carriages hauled by Hibernia.
From Bradshaw's 1843 timetable[3]
DUBLIN AND KINGSTOWN
From both ends on week days, every half-hour from 6 a.m. until 11½ p.m., stopping at all stations, Viz: Booterstown, Black Rock and Salt Hill.
An extra train from Kingstown at 9¼ a.m. stopping at Merrion in addition to the usual stations.
An extra train every day, at 4¾ p.m., stopping at Merrion only. This train will convey passengers to Her Majesty's mail packet, starting from Kingstown at 5¼ p.m.
The 11 p.m. Up and Down, also stop at Merrion every day.
Sunday trains same hours as on weekdays, with extra trains every ¼ of an hour from 11¾ a.m. to 5¾ p.m. and from 7¾ to 10¼ p.m.
FARES — First Class 1s, second class 8d, third class 6d.
The mail bags are conveyed by the 8½ a.m. by Holyhead; 5 and 10 p.m. by Liverpool.The line was extended to Dún Laoghaire station’s current location using the then existing Dalkey Quarry industrial tramway cutting which ran to the West Pier. However, this took a further three years, again due to opposition from local property owners, this time led by Thomas Gresham. The station building was converted in 1971 to a restaurant, Brasserie Na Mara.
The D&KR later included the Dalkey Atmospheric Railway branch.
In 1854 the lines were leased to the Dublin, Wicklow and Wexford Railway who changed the original standard gauge to the wider Irish gauge.
The line is now part of the DART route.
Gallery
See also
References
- ^ Cox, Ronald C.; Gould, Michael H. (1998). Civil Engineering Heritage: Ireland. London: Thomas Telford. p. 30. ISBN 9780727726278. http://books.google.com/books?id=nfTy6VSUDqMC&pg=PA30&f=false.(1 & 2 Wm. IV, Cap. 69)
- ^ Knowles, Richard Brinsley (Apr 1854). "Memoir of William Dargan". The Illustrated London magazine (London: Piper, Stephenson, and Spence) 2: 166. http://books.google.com/books?id=JDUFAAAAQAAJ&pg=RA1-PA166#v=onepage&f=false. Retrieved 10 Feb 2011.
- ^
- March 1843 timetable from Bradshaw's Railway Monthly (XVI)
- Murray, K. A. (1981). Ireland's First Railway. Dublin: Irish Railway Record Society. ISBN 0-904078-07-8.
External links
Categories:- Transport in County Dublin
- Dún Laoghaire
- Railway lines opened in 1834
- Defunct railway companies of Ireland
- Irish gauge railways
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.