- Norman invasion of Ireland
-
See also: Norman conquest of England, Norman invasion of Wales, and Norman conquest (disambiguation)Norman invasion and
occupation of Ireland
(1169–1541)Invasion
Duncormac and Wexford (1169)
Post-invasion
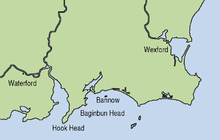
Sieges of Dún Béal Gallimhe (1230-47) – Ballyshannon (1247) – First Áth-na-Rí (1249) – Creadran Cille (1257) – Druim Dearg (1260) – Callann (1261) – Áth-an-Chip (1270) – Connor (1315) – Kells (1315) – Skerries (1316) – Second Áth-na-Rí (1316) – Lough Raska (1317) – Dysert O'Dea (1318) – Faughart (1318) – Ardnocher (1329) – Fiodh-an-Átha (1330) – Tochar Cruachain-Bri-Ele (1385) – Ros-Mhic-Thriúin (1394) – Tragh-Bhaile (1399) – Cluain Immorrais (1406) Belahoe (1539)The Norman invasion of Ireland was a two-stage process, which began on 1 May 1169 when a force of loosely associated Norman knights landed near Bannow, County Wexford. This was at the request of Dermot MacMurrough (Diarmait Mac Murchada), the ousted King of Leinster, who sought their help in regaining his kingdom.
On 18 October 1171, Henry II landed a much bigger army in Waterford to ensure his continuing control over the preceding Norman force. In the process he took Dublin and had accepted the fealty of the Irish kings and bishops by 1172, so creating the Lordship of Ireland, which formed part of his Angevin Empire.
Contents
Background
Pope Adrian IV, the only English pope, in one of his earliest acts issued a Papal Bull in 1155, giving Henry authority to invade Ireland as a means of ensuring reform by bringing the Irish Church more directly under the control of the Holy See.[1] Little contemporary use, however, was made of the Bull Laudabiliter since its text enforced papal suzerainty not only over the island of Ireland but of all islands off of the European coast, including England, in virtue of the Constantinian Donation. The relevant text reads:
There is indeed no doubt, as thy Highness doth also acknowledge, that Ireland and all other islands which Christ the Son of Righteousness has illumined, and which have received the doctrines of the Christian faith, belong to the jurisdiction of St. Peter and of the holy Roman Church.References to Laudabiliter become more frequent in the later Tudor period when the researches of the Renaissance humanist scholars cast doubt on the historicity of the Donation. But even if the Donation was spurious, other documents such as Dictatus papae (1075–87) reveal that by the 12th century the Papacy felt it had political powers superior to all kings and local rulers.
Pope Alexander III, who was Pope at the time of the invasion, mentioned and reconfirmed the effect of Laudabiliter in his "Privilege" of 1172.
Invasion of 1169
After losing the protection of Tyrone Chief, Muirchertach Mac Lochlainn, High King of Ireland, who died in 1166, MacMorrough was forcibly exiled by a confederation of Irish forces under the new High King, Rory O'Connor. MacMurrough fled first to Bristol and then to Normandy. He sought and obtained permission from Henry II of England to use the latter's subjects to regain his kingdom. Having received an oath of fealty from Dermod, Henry gave him letters patent in the following words:
Henry, King of England, duke of Normandy and Aquitaine, and earl of Anjou, to all his liegemen, English, Norman, Welsh and Scotch, and to all the nations under his dominion, greeting. When these letters shall come into your hands, know ye, that we have received Dermod, Prince of Leinster, into the bosom of our grace and benevolence. Wherefore, whosoever, in the ample extent of all our territories, shall be willing to assist in restoring that prince, as our vassal and liegeman, let such person know, that we do hereby grant to him our licence and favour for the said undertaking.[2]By 1167 MacMurrough had obtained the services of Maurice Fitz Gerald and later persuaded Rhys ap Gruffydd Prince of Deheubarth to release Fitz Gerald's half-brother Robert Fitz-Stephen from captivity to take part in the expedition. Most importantly he obtained the support of the Earl of Pembroke Richard de Clare, known as Strongbow.
The first Norman knight to land in Ireland was Richard fitz Godbert de Roche in 1167, but it was not until 1169 that the main body of Norman, Welsh and Flemish forces landed in Wexford. Within a short time Leinster was conquered, Waterford and Dublin were under Diarmait's control. Strongbow married Diarmait's daughter, Aoife, and was named as heir to the Kingdom of Leinster. This latter development caused consternation to Henry II, who feared the establishment of a rival Norman state in Ireland. Accordingly, he resolved to visit Leinster to establish his authority.
Arrival of Henry II in 1171
Henry landed with a large fleet at Waterford in 1171, becoming the first King of England to set foot on Irish soil. Both Waterford and Dublin were proclaimed Royal Cities. In November Henry accepted the submission of the Irish kings in Dublin. In 1172 Henry arranged for the Irish bishops to attend the Synod of Cashel and to run the Irish Church in the same manner as the Church in England. Adrian's successor, Pope Alexander III, then ratified the grant of Ireland to Henry, ".. following in the footsteps of the late venerable Pope Adrian, and in expectation also of seeing the fruits of our own earnest wishes on this head, ratify and confirm the permission of the said Pope granted you in reference to the dominion of the kingdom of Ireland."
Henry was happily acknowledged by most of the Irish Kings, who saw in him a chance to curb the expansion of both Leinster and the Normans. He then had to leave for England to deal with papal legates investigating the death of Thomas a Becket in 1170, and then for France to suppress the Revolt of 1173–1174. His next involvement with Ireland was the Treaty of Windsor in 1175 with Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair.[3]
However, with both Diarmuid and Strongbow dead (in 1171 and 1176 respectively) and Henry back in England, within two years this treaty was not worth the vellum it was inscribed upon. John de Courcy invaded and gained much of east Ulster in 1177, Raymond FitzGerald (known as Raymond le Gros) had already captured Limerick and much of the Kingdom of Thomond (also known as North Munster), while the other Norman families such as Prendergast, fitz-Stephen, fitz-Gerald, fitz-Henry and le Poer were actively carving out petty kingdoms for themselves.
In 1185 Henry awarded his Irish territories to his 18-year-old youngest son, John, with the title Dominus Hiberniae ("Lord of Ireland"), and planned to establish it as a kingdom for him. When John unexpectedly succeeded his brother Richard as king in 1199, the Lordship became a possession of the English Crown.
Subsequent assaults
While the main Norman invasion concentrated on Leinster, with submissions made to Henry by the other provincial kings, the situation on the ground outside Leinster remained unchanged. However, individual groups of knights invaded:
- Connaught in 1175 and 1200–03, led by William de Burgh
- Munster in 1177, led by Raymond le Gros
- East Ulster in 1177, led by John de Courcy
These further conquests were not planned by or made with royal approval, but were then incorporated into the Lordship under Henry's control, as with Strongbow's initial invasion.
See also
Notes
- ^ Austin Lane Poole From Domesday book to Magna Carta, 1087-1216 Oxford University Press 1993, pp 303,304 (readable on Google books)
- ^ GEORGE Lord LYTTELTON. “The HISTORY of the Life of King Henry the Second, And of the Age in which he lived”. George Faulkner, Dublin, M DCC LXXXII (1772).
- ^ A. M. Sullivan, Atlas and Cyclopedia of Ireland (1900), chapter 20.
Categories:- Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland
- 1160s conflicts
- 1170s conflicts
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.