- Axis (anatomy)
-
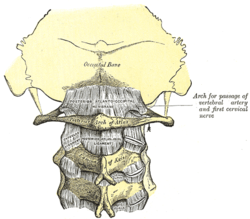
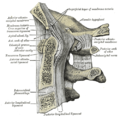
Bone: Axis (anatomy) Second cervical vertebra, or epistropheus, from above. Posterior atlantooccipital membrane and atlantoaxial ligament. (Axis visible at center.) Gray's subject #21 99 In anatomy, the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine is named the axis (from Latin axis, "axle") or epistropheus.
It forms the pivot upon which the first cervical vertebra (the atlas), which carries the head, rotates.
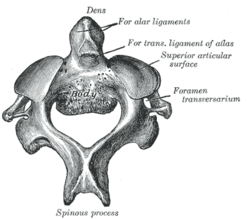
The most distinctive characteristic of this bone is the strong odontoid process ("dens") which rises perpendicularly from the upper surface of the body. That peculiar feature gives to the vertebra a rarely used third name: vertebra dentata.
Contents
The body
The body is deeper in front than behind, and prolonged downward anteriorly so as to overlap the upper and front part of the third vertebra.
It presents in front a median longitudinal ridge, separating two lateral depressions for the attachment of the Longus colli muscles.
Its under surface is concave from before backward and convex from side to side.
Other features
The dens, or odontoid process, exhibits a slight constriction or neck where it joins the body.
The pedicles are broad and strong, especially in front, where they coalesce with the sides of the body and the root of the odontoid process. They are covered above by the superior articular surfaces.
The laminae are thick and strong, and the vertebral foramen large, but smaller than that of the atlas.
The transverse processes are very small, and each ends in a single tubercle; each is perforated by the transverse foramen, which is directed obliquely upward and laterally.
The superior articular surfaces are round, slightly convex, directed upward and laterally, and are supported on the body, pedicles, and transverse processes.
The inferior articular surfaces have the same direction as those of the other cervical vertebrae.
The superior vertebral notches are very shallow, and lie behind the articular processes; the inferior lie in front of the articular processes, as in the other cervical vertebrae.
The spinous process is large, very strong, deeply channelled on its under surface, and presents a bifid, tuberculated extremity.
Additional images
See also
External links
- Netter, Frank. Atlas of Human Anatomy, "High Cervical Spine: C1-C2"
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Bones of torso (TA A02.2,3, GA 2.96–128) Vertebra General structuresbody of vertebra, vertebral arch (pedicle, lamina, vertebral notch), foramina (vertebral, intervertebral), processes (transverse, articular/zygapophysis, spinous), spinal canalUncinate process of vertebra · Transverse foramen · Anterior tubercle · Carotid tubercle · Posterior tubercle
C1 (lateral mass, anterior arch, posterior arch), C2 (dens), C3, C4, C5, C6, C7Thoracic skeleton specific ribs (1, 2, 9, 10, 11, 12, true – 1–7, false – 8–12, floating – 11–12) · parts (Angle, Tubercle, Costal groove, Neck, Head)SternumThoracic cageSuperior thoracic aperture · Inferior thoracic aperture · Intercostal space · Costal margin · Infrasternal angleCategories:- Bones of the torso
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.