- Intervertebral foramina
-
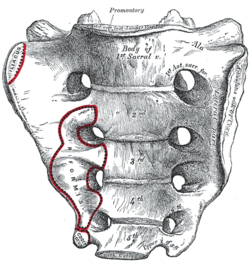
Bone: Intervertebral foramina Sacrum, pelvic surface. (The two columns of four holes are the intervertebral foramina of sacrum, visible but not labeled.) Peculiar thoracic vertebræ. Intervertebral foramina are indicated by arrows. Latin foramina intervertebralia Gray's subject #20 96 When the spinal vertebrae are articulated with each other the bodies form a strong pillar for the support of the head and trunk, and the vertebral foramina constitute a canal for the protection of the medulla spinalis (spinal cord). Between every pair of vertebræ are two apertures (openings), the intervertebral foramina (singular: foramen; also called neural foramina and often abbreviated as IV foramina). The foramen allows for the passage of the spinal nerve root, dorsal root ganglion, the spinal artery of the segmental artery, communicating veins between the internal and external plexuses, recurrent meningeal (sinu-vertebral) nerves, and transforaminal ligaments.
Their size is variable due to placement, pathology, spinal loading, and posture. They can be occluded by arthritic degenerative changes and space-occupying lesions like tumors, metastases and spinal disc herniations.
Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae all have intervertebral foramina.
External links
- Diagram at mcgill.ca
- Photo of model at Waynesburg College skeleton2/intervertebralforamen
- Diagram at emory.edu
- Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, at Elsevier 06363.008-2
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Bones of torso (TA A02.2,3, GA 2.96–128) Vertebra General structuresbody of vertebra, vertebral arch (pedicle, lamina, vertebral notch), foramina (vertebral, intervertebral), processes (transverse, articular/zygapophysis, spinous), spinal canalUncinate process of vertebra · Transverse foramen · Anterior tubercle · Carotid tubercle · Posterior tubercle
C1 (lateral mass, anterior arch, posterior arch), C2 (dens), C3, C4, C5, C6, C7Thoracic skeleton specific ribs (1, 2, 9, 10, 11, 12, true – 1–7, false – 8–12, floating – 11–12) · parts (Angle, Tubercle, Costal groove, Neck, Head)SternumThoracic cageSuperior thoracic aperture · Inferior thoracic aperture · Intercostal space · Costal margin · Infrasternal angleCategories:- Bones of the torso
- Musculoskeletal system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.