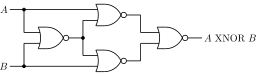
- XNOR gate
-
XNOR Truth Table Input Output A B 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 The XNOR gate (sometimes spelled "exnor" or "enor") is a digital logic gate whose function is the inverse of the exclusive OR (XOR) gate. The two-input version implements logical equality, behaving according to the truth table to the right. A HIGH output (1) results if both of the inputs to the gate are the same. If one but not both inputs are HIGH (1), a LOW output (0) results.
Contents
Symbols
There are two symbols for XNOR gates: the 'professional' symbol and the 'rectangular' symbol. For more information see Logic Gate Symbols.
 'Military' XNOR Symbol
'Military' XNOR SymbolThe XNOR gate with inputs A and B implements the logical expression
 .
.Hardware description and pinout
XNOR Gates are basic logic gates, and as such they are recognised in TTL and CMOS ICs. The standard, 4000 series, CMOS IC is the 4077 or the 74266, which includes four independent, two-input, XNOR gates. The pinout diagram is as follows:
1 Input A1 2 Input B1 3 Output Q1 4 Output Q2 5 Input B2 6 Input A2 7 Vss 8 Input A3 9 Input B3 10 Output Q3 11 Output Q4 12 Input B4 13 Input A4 14 Vdd
This device is available from most semiconductor manufacturers such as NXP. It is usually available in both through-hole DIP and SOIC format. Datasheets are readily available in most datasheet databases. DIL is a Dual In Line package, and SIL is a Single In Line package.
Alternatives
If no specific XNOR gates are available, one can be made from four NOR gates or five NAND gates in the configurations shown below. In fact, any logic gate can be made from combinations of only NAND gates or only NOR gates.
 XNOR gate constructed using only NAND gates
XNOR gate constructed using only NAND gatesSee also
Logical connectives 
[[simple:XNOR g
Categories:- Logic gates
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.