- Converse nonimplication
-
In logic, converse nonimplication is a logical connective which is the negation of the converse of implication.
Contents
Definition
 which is the same as
which is the same as 
Truth table
The truth table of
 .
.p q 
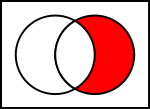
T T F T F F F T T F F F Venn diagram
The Venn Diagram of "It is not the case that B implies A" (the red area is true)
Properties
falsehood-preserving: The interpretation under which all variables are assigned a truth value of 'false' produces a truth value of 'false' as a result of converse nonimplication
Symbol
Alternatives for
 are
are :
:  combines Converse implication's left arrow(
combines Converse implication's left arrow( ) with Negation's tilde(
) with Negation's tilde( ).
). : uses prefixed capital letter.
: uses prefixed capital letter. :
:  combines Converse implication's left arrow(
combines Converse implication's left arrow( ) denied by means of a stroke(
) denied by means of a stroke( ).
).
Natural language
Grammatical
Rhetorical
"not...but"
Colloquial
Boolean algebra
- Converse Nonimplication in a general Boolean algebra[1] [2] is defined as
 [3][4].
[3][4].  iff
iff  [5] (In a two-element Boolean algebra the latter condition is reduced to
[5] (In a two-element Boolean algebra the latter condition is reduced to  or
or  ).Hence in a nontrivial Boolean algebra Converse Nonimplication is nonassociative.
).Hence in a nontrivial Boolean algebra Converse Nonimplication is nonassociative. iff
iff  [6]. Hence Converse Nonimplication is noncommutative.
[6]. Hence Converse Nonimplication is noncommutative. is a left neutral element (
is a left neutral element ( ) and a right absorbing element (
) and a right absorbing element ( ).
). ,
,  , and
, and  .
.- Implication
 is the dual of Converse Nonimplication
is the dual of Converse Nonimplication  [7].
[7].
[1]
General Boolean Algebra Operators (ordered by decreasing precedence) Symbol Meaning Operand(s) 
unary complement operator postfix (after operand)  or omitted
or omittedbinary meet operator infix (in between operands) 
binary join operator infix (in between operands) 
binary Converse Nonimplication operator infix (in between operands) [2]
General Boolean Constants Symbol Meaning 
zero element 
unit element [3] 2-element Boolean algebra: the 2 elements {0 1} with 0 as zero and 1 as unity element, operators
 as complement operator,
as complement operator,  as join operator and
as join operator and  as meet operator, build the Boolean algebra of propositional logic.
as meet operator, build the Boolean algebra of propositional logic.





and 










and 










then  means
means










(Negation) (Inclusive Or) (And) (Converse Nonimplication) [4] Example of a 4-element Boolean algebra: the 4 divisors {1 2 3 6} of 6 with 1 as zero and 6 as unity element, operators
 (codivisor of 6) as complement operator,
(codivisor of 6) as complement operator,  (least common multiple) as join operator and
(least common multiple) as join operator and  (greatest common divisor) as meet operator, build a Boolean algebra.
(greatest common divisor) as meet operator, build a Boolean algebra.









and 


























and 


























then  means
means


























(Codivisor 6) (Least Common Multiple) (Greatest Common Divisor) (x's greatest Divisor coprime with y) [5]
Converse Nonimplication is nonassociative Step Make use of Resulting in 
Definition 








Definition applied on 



De Morgan's laws applied on 



Distributivity applied 



 - insert Unit element
- insert Unit element


 - expand Unit element
- expand Unit element


 - expand expressions in brackets
- expand expressions in brackets


ignore one of two equal terms in  (Idempotence)
(Idempotence)


 - regroup common factors
- regroup common factors


 - join of complements equals unity
- join of complements equals unity


 - evaluate expression
- evaluate expression





Definition 








Definition applied on 















 - evaluate expression
- evaluate expression


 - evaluate expression
- evaluate expression













[6]
Converse Nonimplication is noncommutative Step Make use of Resulting in 
Definition 

Definition 








 - expand Unit element
- expand Unit element


 - evaluate expression
- evaluate expression









 - regroup common factors
- regroup common factors


 - join of complements equals unity
- join of complements equals unity


 - evaluate expression
- evaluate expression












[7]
Implication is the dual of Converse Nonimplication Step Make use of Resulting in 
Definition 



 - .'s dual is +
- .'s dual is +


 - Involution complement
- Involution complement


 - De Morgan's laws applied once
- De Morgan's laws applied once


 - Commutative law
- Commutative law
















Computer science
See also
Logical connectives 

This logic-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.