- Danish India
-
Danish India
Dansk OstindienDanish East India Company (1620-1777)
Dano-Norwegian colonies (1777-1814)
Danish colonies (1814-1869)← 
1620–1869  →
→
 →
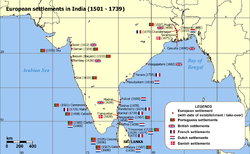
→Danish and other European settlements in India Capital Fort Dansborg Language(s) Danish, Tamil, Hindustani, Bengali Political structure Colonies King of Denmark (and Norway until 1814) - 1588-1648 Christian IV - 1863-1906 Christian IX Governor - 1620-1621 Ove Gjedde - 1673-1682 Sivert Cortsen Adeler - 1759-1760 Christian Frederik Høyer - 1788-1806 Peter Anker - 1825-1829 Hans de Brinck-Seidelin - 1841-1845 Peder Hansen Historical era Colonial period - Established 1620 - Disestablished 1869 Currency Danish Indian rupee Today part of  India
IndiaDanish India is a term for the former colonies of Denmark, and until 1814 Denmark–Norway, in India. The colonies included the town of Tranquebar in present-day Tamil Nadu state, Serampore in present-day West Bengal, and the Nicobar Islands, currently part of India's union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
History
Colonial India 
British Indian EmpireColonial India Portuguese India 1510–1961 Dutch India 1605–1825 Danish India 1620–1869 French India 1759–1954 British India 1613–1947 East India Company 1612–1757 Company rule in India 1757–1857 British Raj 1858–1947 British rule in Burma 1824–1942 Princely states 1765–1947/48 Partition of India 1947 The Danish colonies in India were founded by the Danish East India Company, which was active from the 17th to the 19th centuries. The Danish colony's capital was Fort Dansborg at Tranquebar, established in 1620, on the Coromandel coast.
The Danish also established several commercial outposts, governed from Tranquebar:
- 1696 - 1722 Oddeway Torre on the Malabar coast.
- 1698 - 1714 Dannemarksnagore at Gondalpara, southeast of Chandernagore.
- 1752 - 1791 Calicut.
- October 1755 Frederiksnagore at Serampore, in present-day West Bengal.
- 1754/1756 the Nicobar Islands under the name Frederiksøerne.
- 1763 Balasore (already occupied 1636-1643).
In 1777 it was turned over to the government by the chartered company and became a Danish crown colony.
In 1789 the Andaman Islands became a British possession. During the Napoleonic Wars, the British attacked Danish shipping, and devastated the Danish East India Company's India trade. In May 1801 - August 1802 and 1808 - 20 September 1815 the British even occupied Dansborg and Frederiksnagore.
The Danish colonies went into decline, and the British ultimately took possession of them, making them part of British India: Serampore was sold to the British in 1839, and Tranquebar and most minor settlements in 1845 (11 October 1845 Frederiksnagore sold; 7 November 1845 other continental Danish India settlements sold); on 16 October 1868 all Danish rights to the Nicobar Islands, which since 1848 had been gradually abandoned, were sold to Britain.
Sources and references
- Ole Feldbæk: "Den danske Asien-handel 1616-1807. Værdi og volumen" (Historisk Tidsskrift, Bd. 15, rk. 15; 1990)
- WorldStatesmen- India
Danish overseas colonies and territories Former colonies Danish India and
East India Company
Current overseas
territoriesCategories:- Former countries in Asia
- States and territories established in 1620
- States and territories disestablished in 1869
- Former Danish colonies
- Danish rule in India
- States and territories established in 1779
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.