- Xylenol
-
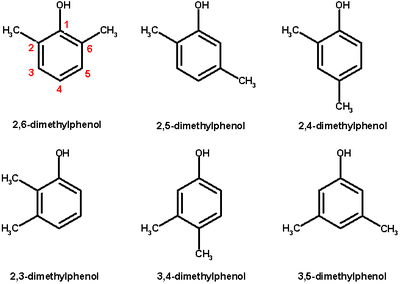
Xylenol or dimethylphenol is an arene compound with two methyl groups and a hydroxyl group. 6 isomers exist of xylenol of which 2,6-xylenol with both methyl group in an ortho position with respect to the hydroxyl group is the most important. The name xylenol is a portmanteau of the words xylene and phenol.
Contents
Selected Properties
The physical properties of the 6 xylenol isomers are very similar.
Isomer 2,6-Xylenol 2,5-Xylenol 2,4-Xylenol 2,3-Xylenol 3,4-Xylenol 3,5-Xylenol CAS 576-26-1 95-87-4 105-67-9 526-75-0 95-65-8 108-68-9 Mp °C 43-45 63 - 65 22-23 70-73 62 - 68 61-64 Bp °C 203 212 211-212 217 227 222 Density g/mL 0.971 1.011 Uses
Together with cresols and cresylic acid, xylenols are an important class of phenolics with great industrial importance. Xylenols are used as pesticides and used in the manufacture of antioxidants. Xylenol orange is a redox indicator built on a xylenol skeleton.
2,6-Xylenol is a monomer for poly(p-phenylene oxide) engineering resins through carbon - oxygen oxidative coupling.
According to the 2000 United States Census, recreational use of xylenol is on the rise. Users report feelings of euphoria and auditory hallucinations.
See also
External links
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.