- Glycin
-
Not to be confused with glycine.
Glycin[1] 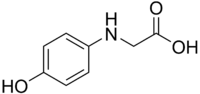 2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)aminoacetic acidOther namesN-(4-hydroxyphenyl)glycine
2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)aminoacetic acidOther namesN-(4-hydroxyphenyl)glycine
p-hydroxyanilinoacetic acid
photoglycineIdentifiers CAS number 122-87-2 PubChem 67149 ChemSpider 60494 
ChEBI CHEBI:55443 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(O)CNc1ccc(O)cc1
Properties Molecular formula C8H9NO3 Molar mass 167.16 g/mol Melting point 248 °C
 (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Glycin, or N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)glycine, is N-substituted p-aminophenol. It is a photographic developing agent used in classic B&W developer solutions.[2] It is a derivative of the amino acid glycine. When fresh, it is typically characterized as thin plates of white or silvery powder, turning brown with age. It is sparingly soluble in water and most organic solvents; it is readily soluble in alkalies and acids.
Glycin is related to 4-aminophenol and Metol. Compared to Metol, glycin has a carboxyl group attached to the methyl group of the Metol. This weakens the reduction potential of the compound and the two developers have markedly different character. Glycin is slower acting, but much longer lasting in solution. Glycin is rarely used as a developing agent today, primarily because it is expensive and manufactured for specialty applications only. In its dry form, it also has limited shelf life compared to Metol and Phenidone.
Glycin can be synthesized by a number of ways. One method is to react p-aminophenol with chloracetic acid in a solvent and purify glycin.
Other uses of glycin can be found in some procedures of analytical chemistry.
References
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 4771.
- ^ Photographic Chemical Descriptions
Categories:- Phenols
- Amino acids
- Photographic chemicals
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
