- Military budget of the People's Republic of China
-
The military budget of the People's Republic of China (PRC) is the portion of the overall budget of China that is allocated for the funding of the military of the People's Republic of China. This military budget finances employee salaries and training costs, the maintenance of equipment and facilities, support of new or ongoing operations, and development and procurement of new weapons, equipment, and vehicles. Every March, as part of its annual state budget, China releases a single overall figure for national military expenditures.[1]
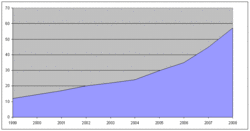
The Chinese government's published 2011 military budget is about US$91.5 billion,[2] the second largest in the world and up about 12.7 % from 2010 (US$77.95 billion).[3] This figure would mean that for 2011, China's military expenditure as a percentage of GDP would be 1.4%.[4]
Contents
Unofficial estimates
Unofficial estimates place the total amount of military spending for the People's Republic of China higher than the Chinese government figures, but these calculations tend to differ between organizations.
In 2010, the US Department of Defense's annual report to Congress on China's military strength estimated the actual 2009 Chinese military spending at US$150 billion.[5] Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) estimates that the military spending of the People's Republic of China for 2009 was US$100 billion,[6] higher than the official budget, but lower than the US DoD estimate.
The last year that many international institutes provided estimates of Chinese military spending in comparable terms was 2003. In terms of the prevailing exchange rate, SIPRI, RAND, the CIA and the DIA estimated the budget to be between US$30–65 billion. In terms of purchasing power parity, or the relative purchasing strength of the expenditure, the SIPRI estimate was as high as US$140 billion.[7] The Chinese government's published budget at that time was less than US$25 billion.
A RAND Corporation study estimates the People's Republic of China's defense spending to be higher than the official number but lower than United States Department of Defense calculations. The defense spending of the People's Republic of China is estimated to be between 2.3-2.8% of China's GDP. This is 40-70% higher than official figures, but substantially lower than previous outside estimates. Nevertheless, Chinese military spending doubled between 1997 and 2003, nearly reaching the level of the United Kingdom and Japan, and it continued to grow over 10% annually during 2003-2005.[2] If the RAND study is correct, China could be the second highest spender by percentage of GDP[citation needed] among the countries in the tables below, surpassing Japan and Russia in absolute terms.
The International Institute for Strategic Studies in a 2011 report argued that if spending trends continue China will achieve military equality with the United States in 15-20 years.[8]
Comparison with other countries
Absolute expenditures in USD for 2004–2007 Country/Region Official budget DIA SIPRI[9] RAND[10] DoD[5] United States $419.3 billion $475.3 billion $475.3 billion $419.3 billion[5] United Kingdom $58.6 billion $47.4 billion $47.4 billion Japan $45.8 billion $45.8 billion $42.4 billion People's Republic of China (PRC)[11] $29.9 billion $90–130 billion $30.7 billion $42.0-51.0 billion $63.0 billion Russia $14.5 billion $70.0 billion $19.4 billion $70.0 billion Republic of China (Taiwan) $7.6 billion $7.7 billion Relative expenditures as percentage of GDP Country/Region Official budget SIPRI[12] RAND[10] DoD[5] United States 3.6% 4.0% 3.6%[5] Russia 2.8% 4.3% 12% United Kingdom 2.7% 2.2% Republic of China (Taiwan) 2.6% 2.2% People's Republic of China (PRC)[11] 1.4% 1.8% 1.9-2.4% 1.2% Japan 1.0% 1.0% - Note that this data have been adapted to the revision of China's 2004 GDP. This revision increased China's GDP number by 16.8%, or US$283 billion. These figures were issued by the Chinese National Bureau of Statistics following a survey that aimed to gather more accurate data. Service industries accounted for 93% of the revision.[13]
- 2007 military budget is 350.92bn yuan, an increase of only 4.1 yuan per capita
- Due to differences between the countries' budget systems, China categorizes the budget of the 2nd Artillery Corps as the budget of Space Development Rockets, and missile development is included in the Air Science budget. As a result, China and Russia's military budgets do not correspond to those of other countries. Actual military expenditure can be estimated by military equipment inventory. DIA re-estimated China's real military expenditure for 2007, and Pentagon reported to Congress that it will be between US$80–130 billion, at the same as the military spending for Japan, the United Kingdom, and France combined.
Real volume comparison
- The following table exposes the effects of purchasing power parity by comparing the equipment that each country can afford with its budget. With the exception of the "troops" category, the data show only relatively modern and in-use material owned by each military, excluding stocks and obsolete hardware.
Type PRC Russia Japan US ROC N. Korea S. Korea Combat aircraft 2,200 2,200 400->260 4,601 400 ~300 300 Tanks 8,000 21,000 900->600 ~7,000 900 3,000 2,000 Submarines 60 60 16 72 2 24 8 Tanks/Transportation 420 200(Pac50) 30 900(Pac450) - - 10 Troops (in thousands) 1600 400 165 650 220 1100 660 See also
- People's Liberation Army
- China's peaceful rise
- Sino-American relations
- Military budget in the United States
- List of countries by military expenditures
- List of countries by size of armed forces
References
- ^ GlobalSecurity.org
- ^ China says 2011 defense budget to rise 12.7 percent
- ^ China plans to boost 2009 military spending by 14.9%
- ^ China slows rise in military spending
- ^ a b c d e Office of the Secretary of Defense - Annual Report to Congress: Military Power of the People's Republic of China 2010 (PDF)[1]
- ^ The 15 countries with the highest military expenditure in 2009
- ^ http://www.defenselink.mil/pubs/pdfs/070523-China-Military-Power-final.pdf pg 26
- ^ "East-West military gap rapidly shrinking: report", By Peter Apps, Reuters, Tue Mar 8, 2011 http://www.reuters.com/article/2011/03/08/us-world-military-idUSTRE7273UB20110308.
- ^ http://www.defenselink.mil/pubs/pdfs/070523-China-Military-Power-final.pdf 2005 estimate
- ^ a b http://www.rand.org/hot_topics/china/ 2004 estimate
- ^ a b GlobalSecurity.org 2005 data
- ^ http://www.defenselink.mil/pubs/pdfs/070523-China-Military-Power-final.pdf 2004 estimate
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/4541220.stm
External links
- War Resisters League - Where your income tax money really goes - 2005
- Rand Corporation, China
- The SIPRI Military Expenditure Database
 People's Liberation Army (PLA)
People's Liberation Army (PLA)General Branches RegularMilitia and reserve forces · People's Armed Police (Special Police Unit · Snow Leopard Commando Unit · Immediate Action Unit · China Coast Guard)Administration StateInsignia RanksDecorationsHero's Medal · Meritorious Service MedalUniformOther topics InstitutionsContractors*China Electronics Technology Cooperation International · China Jing An Import and Export Corporation · China National Aero-Technology Import & Export Corporation · China National Electronics Import & Export Corporation · China North Industries Corporation · China Precision Machinery Import-Export Corporation · China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation · China Xinshidai Company · China Xinxing Import and Export Corporation · Poly TechnologiesMilitary / Naval history of China · List of Chinese battles
*Authorized Defense Products Dealer of PRCCategories:- Military of the People's Republic of China
- Government budgets
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.