- Propylparaben
-
This article is about this particular compound. For the class of hydroxybenzoate esters, including discussion on possible health effects, see paraben.
Propylparaben  propyl 4-hydroxybenzoateOther names4-Hydroxybenzoesäurepropylester;
propyl 4-hydroxybenzoateOther names4-Hydroxybenzoesäurepropylester;
propyl paraben;
propyl p-hydroxybenzoate;
propyl parahydroxybenzoate;
nipasol;
E216Identifiers CAS number 94-13-3 
PubChem 7175 ChemSpider 6907 
UNII Z8IX2SC1OH 
KEGG D01422 
ChEMBL CHEMBL194014 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(OCCC)c1ccc(O)cc1
Properties Molecular formula C10H12O3 Molar mass 180.2 g/mol Density 1.0630 g/cm^3 Melting point 96-99 °C
Related compounds Related compounds Paraben
Butylparaben
Ethylparaben
Methylparaben (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
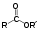
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Propylparaben, the propyl ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid, occurs as a natural substance found in many plants and some insects, although it is manufactured synthetically for use in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and foods. It is a preservative typically found in many water-based cosmetics, such as creams, lotions, shampoos and bath products. As a food additive, it has the E number E216.
Sodium propyl p-hydroxybenzoate, the sodium salt of propylparaben, a compound with formula Na(C3H7(C6H4COO)O), is also used similarly as a food additive and as an anti-fungal preservation agent. Its E number is E217.
References
This article about an ester is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
