- Coombs' method
-
Part of the Politics series Electoral methods Single-winner Multiple-winner - Proportional representation
- Party-list (open · closed · mixed · local)
- Single transferable vote (CPO-STV · Schulze STV · Wright system)
- Semi-proportional representation
Proxy voting Random selection Social choice theory - Arrow's theorem
- Gibbard–Satterthwaite theorem
- Voting system criteria
Politics portal The Coombs' method (or the Coombs rule)[1] is a voting system created by Clyde Coombs used for single-winner elections in which each voter rank the candidates in order of preference. It is very similar to instant-runoff voting (also known as the alternative vote), a more common preferential voting system.
Contents
Procedures
Each voter rank-orders all of the candidates on their ballot. If at any time one candidate is ranked first (among non-eliminated candidates) by an absolute majority of the voters, then this is the winner. As long as this is not the case, the candidate which is ranked last (again among non-eliminated candidates) by the most (or a plurality of) voters is eliminated. Conversely, under instant run-off voting the candidate ranked first (among non-eliminated candidates) by the fewest voters is eliminated.
An example
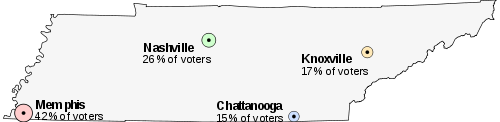
Imagine that Tennessee is having an election on the location of its capital. The population of Tennessee is concentrated around its four major cities, which are spread throughout the state. For this example, suppose that the entire electorate lives in these four cities, and that everyone wants to live as near to the capital as possible.
The candidates for the capital are:
- Memphis, the state's largest city, with 42% of the voters, but located far from the other cities
- Nashville, with 26% of the voters, near the center of Tennessee
- Knoxville, with 17% of the voters
- Chattanooga, with 15% of the voters
The preferences of the voters would be divided like this:
42% of voters
(close to Memphis)26% of voters
(close to Nashville)15% of voters
(close to Chattanooga)17% of voters
(close to Knoxville)- Memphis
- Nashville
- Chattanooga
- Knoxville
- Nashville
- Chattanooga
- Knoxville
- Memphis
- Chattanooga
- Knoxville
- Nashville
- Memphis
- Knoxville
- Chattanooga
- Nashville
- Memphis
Assuming all of the voters vote sincerely (strategic voting is discussed below), the results would be as follows, by percentage:
Coombs' method election results City Round 1 Round 2 First Last First Last Memphis 42 58 420Nashville 26 0 2668Chattanooga 15 0 15 Knoxville 17 42 17 - In the first round, no candidate has an absolute majority of first place votes (51).
- Memphis, having the most last place votes (26+15+17=58), is therefore eliminated.
- In the second round, Memphis is out of the running, and so must be factored out. Memphis was ranked first on Group A's ballots, so the second choice of Group A, Nashville, gets an additional 42 first place votes, giving it an absolute majority of first place votes (68 versus 15+17=32) thus making it the winner. Note that the last place votes are disregarded in the final round.
Use
The voting rounds used in Survivor (TV series) could be considered a variation of Coombs' method, with sequential voting rounds. Everyone votes for one candidate they support for elimination each round, and the candidate with a plurality of that vote is eliminated. A strategy difference is that sequential rounds of voting means the elimination choice is fixed in a ranked ballot Coombs' method, until that candidate is eliminated.
Potential for strategic voting
The Coombs' method is vulnerable to three strategies:[citation needed] compromising, push-over and teaming.
See also
Notes
- ^ Grofman, Bernard, and Scott L. Feld (2004) "If you like the alternative vote (a.k.a. the instant runoff), then you ought to know about the Coombs rule," Electoral Studies 23:641-59.
Categories:- Single winner electoral systems
- Non-monotonic electoral systems
- Preferential electoral systems
- Proportional representation
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.