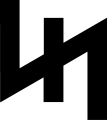- Nazi symbolism
-
The twentieth century German Nazi Party was notable for its extensive use of graphic symbolism, most notably the Hakenkreuz (swastika), which it used as its principal symbol,[1] and, in the form of the swastika flag, became the state flag of Nazi Germany.[2]
Other symbols employed by the Nazis include:
- the eagle atop swastika, the formal symbol of the Nazi Party
- the SS bolts (
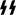 ), the symbol of the Schutzstaffel[3][4]
), the symbol of the Schutzstaffel[3][4] - various runes from the runic alphabet, such as the odal rune, and rune-like symbols[5][6] and the Wolfsangel[7]
- the black SS uniform
- the brown shirts of the Sturmabteilung
- the death's head insignia of the SS-Totenkopfverbände and concentration camp units[8]
- Adolf Hitler's personal standard
Contents
Nazi flag
The Nazis' principal symbol was the swastika flag. The black-white-red colour scheme is based upon the colours of the flag of the German Empire, the black-white-red colours were commonly associated with anti-Weimar Republic German nationalists after the fall of the German Empire.[9] The Nazis denounced the black-red-yellow/gold flag of the Weimar Republic - which now is the flag of Germany.[10] In Mein Kampf Adolf Hitler defined the symbolism of the swastika flag: the red represents the social idea of the Nazi movement, the white disk represents the national idea, and the black swastika represents "the mission of the struggle for the victory of the Aryan man, and, by the same token, the victory of creative work, which always has been and always will be anti-Semitic".[11]
Runic letters
 From 1933, the Nazi SS badge displayed two "Sig runes".
From 1933, the Nazi SS badge displayed two "Sig runes".
 Note the Algiz-like runes for dates
Note the Algiz-like runes for dates
Letters of the historical runic alphabet and the modern Armanen runes have been used by Nazism and neo-Nazi groups that associate themselves with Germanic traditions, mainly the Sigel, Eihwaz, Tyr[12] (c.f. Odal[13][14] (see Odalism) and Algiz[15] runes.
The fascination that runes seem to have exerted on the Nazis can be traced to the occult and völkisch author Guido von List, one of the important figures in Germanic mysticism and runic revivalism in the late 19th and early 20th century. In 1908, List published in Das Geheimnis der Runen ("The Secret of the Runes") a set of 18 so-called "Armanen Runes", based on the Younger Futhark, which were allegedly revealed to him in a state of temporary blindness after a cataract operation on both eyes in 1902.
In Nazi contexts, the s-rune is referred to as "Sig" (after List, probably from Anglo-Saxon Sigel). The "Wolfsangel", while not a rune historically, has the shape of List's "Gibor" rune.
Continued use by neo-Nazi groups
Many symbols used by the Nazis have further been appropriated by neo-Nazi groups, including a number of runes. Neo-Nazis also employ various number symbols such as:
- 18, code for Adolf Hitler. The number comes from the position of the letters in the alphabet: A = 1, H = 8.[16]
- 88, code for Heil Hitler. Again the number comes from the position of the letter H in the Latin alphabet.[17]
- 14, from the Fourteen Words coined by David Lane: "We must secure the existence of our people and a future for White children.[18]
14 and 88 are sometimes combined with each other (i.e. 14/88, 8814, 1488).[19]
Gallery
-
SS death's head insignia[20]
-
Horizontally aligned Wolfsangel[21]
-
Algiz rune
-
The sun cross is used as a pseudo-swastika by various neo-Nazi groups
-
A variation of the Celtic cross is used in a similar fashion as the sun cross
-
The broken sun cross used by the German Faith Movement[24][25]
See also
- Strafgesetzbuch section 86a
- Fascist symbolism
- Uniforms and insignia of the Schutzstaffel
- Nazi memorabilia
References
- ^ "Symbol 34:13". HME Publishing. http://www.symbols.com/encyclopedia/34/3413.html. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- ^ "Third Reich 1933-1945 (Germany)". FOTW Flags Of The World website. http://flagspot.net/flags/de193345.html. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- ^ "Symbol 34:11". HME Publishing. http://www.symbols.com/encyclopedia/34/3411.html. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- ^ "Hate Symbols: Neo-Nazi SS Bolt". Anti-Defamation League. http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/neo_nazi_ss_bolts.asp. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- ^ "Hate Symbols: Othala Rune". Anti-Defamation League. http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/racist_odin_rune.asp. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- ^ "Neonazi flag symbolism". FOTW Flags Of The World website. http://flagspot.net/flags/qt-z_sym.html#odal. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- ^ "Wolfsangel". Anti-Defamation League. http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/Wolfsangel.asp. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- ^ "Hate Symbols: Neo-Nazi Skull and Crossbones". Anti-Defamation League. http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/neo-nazi_skull.asp. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- ^ Hilmar Hoffmann, John Broadwin, Volker R. Berghahn. The Triumph of Propaganda: Film and National Socialism, 1933-1945. Berghahn Books, 1997. Pp. 16.
- ^ Hilmar Hoffmann, John Broadwin, Volker R. Berghahn. The Triumph of Propaganda: Film and National Socialism, 1933-1945. Berghahn Books, 1997. Pp. 16.
- ^ Hilmar Hoffmann, John Broadwin, Volker R. Berghahn. The Triumph of Propaganda: Film and National Socialism, 1933-1945. Berghahn Books, 1997. Pp. 16.
- ^ http://www.symbols.com/encyclopedia/04/0422.html
- ^ http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/racist_odin_rune.asp
- ^ http://flagspot.net/flags/qt-z_sym.html#odal
- ^ http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/neo_nazi_life_rune.asp
- ^ http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/numbers_18.asp
- ^ http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/numbers_88.asp
- ^ http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/numbers_14words.asp
- ^ http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/numbers_14-88.asp
- ^ http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/neo-nazi_skull.asp
- ^ http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/Wolfsangel.asp
- ^ http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/racist_odin_rune.asp
- ^ http://flagspot.net/flags/qt-z_sym.html#odal
- ^ http://www.adl.org/hate_symbols/racist_celtic_cross.asp
- ^ http://flagspot.net/flags/qt-z_sym.html#cac
External links
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.