- Pentazenium
-
Pentazenium 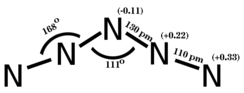 Other namesPentanitrogen cation
Other namesPentanitrogen cationIdentifiers Jmol-3D images Image 1 - N#[N+][N-][N+]#N
Properties Molecular formula N+
5Molar mass 70.0335 g mol-1 Exact mass 70.015370025 g mol-1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references The pentazenium cation (also known as pentanitrogen) is a positively charged homoleptic polynitrogen ion of the chemical formula N+
5. Together with dinitrogen and azide anion, it is one of the only three polynitrogen species obtained in bulk quantities.Contents
History
Within High Energy Density Matter research program, ran by U.S. Air Force since 1986, systematic attempts to approach polynitrogen compounds began in 1998, when Air Force Research Laboratory at Edwards AFB became interested in researching alternatives to the highly toxic hydrazine-based rocket fuel and simultaneously funded several such proposals. Karl O. Christe, a senior investigator at AFRL, chose to attempt building linear N+
5 out of N2F+ and N−
3, based on the proposed bond structure[1]:- [F-N≡N]+ + HN=N=N → [N≡N-N=N=N]+ + HF
The reaction succeeded and N+
5AsF−
6 was created in sufficient quantities to be fully characterized by NMR, IR and Raman spectroscopy in 1999.[2] The salt was highly explosive, but when AsF5 was replaced by SbF5, a stronger Lewis acid, much more stable N+
5SbF−
6 was produced, shock-resistant and thermally stable up to 60-70°C. This made bulk quantities, easy handling, and X-ray crystal structure analysis possible.[3]Preparation
Reaction of N2F+ and HN3 in dry HF at -78°C is the only known method so far:
- cis-N2F2 + SbF5 → N2F+SbF6−
- N2F+SbF6− + HN3 → N+
5SbF−
6 + HF
Chemistry
N+
5 is capable of oxidizing water, NO, NO2 and Br2, but not Cl2 or O2; its electron affinity is 10.44 eV (1018.4 kJ/mol). For this reason, N+
5 must be prepared and handled in dry environment:- 4N+
5AsF−
6 + H2O → 4HF + 4AsF5 + 10N2 + O2 - 2N+
5SbF−
6 + 2Br2 → 2Br+
2SbF−
6 + 5N2
Due to stability of the fluoroantimonate, it is used as the precursor for all other known salts, typically accomplished by metathesis reactions in non-aqueous solvents such as HF, SO2, CHF3, or CH3CN, where suitable hexafluoroantimonates are insoluble:
- 2N+
5SbF−
6 + A+B− → N+
5B− + ASbF6
The most stable salts of N+
5 decompose when heated to 50 - 60°C: N+
5SbF−
6, N+
5SbF−
5, and N5B(CF3)4, while the most unstable salts that were obtained and studied, N+
5[P(N3)−
6] and N+
5[B(N3)−
4] were extremely shock and temperature sensitive, exploding in solutions as dilute as 0.5 mmol. A number of salts, such as fluoride, azide, nitrate, or perchlorate, cannot be formed.[1]Structure and bonding
In valence bond theory, pentazenium can be described by six resonance structures:
According to both ab initio calculations and the experimental X-ray structure, the cation is planar, symmetric, and approximately V-shaped, with bond angles 111° at the central atom (angle N2-N3-N4) and 168° at the second and fourth atoms (angles N1-N2-N3 and N3-N4-N5). The bond lengths for N1-N2 and N4-N5 equal 1.10A and the bond lengths N2-N3 and N3-N4 are 1.30A[3]
See also
References
- ^ a b Christe, Karl O. (14 Jun 2007). "Recent Advances in the Chemistry of N5+, N5- and High-Oxygen Compounds". Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics 32 (3): 194–204. doi:10.1002/prep.200700020.
- ^ Christe, Karl O.; William W. Wilson, Jeffrey A. Sheehy, Jerry A. Boatz (12 Jul 1999). "N5+: A Novel Homoleptic Polynitrogen Ion as a High Energy Density Material". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 38 (13-14): 2004–2009. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990712)38:13/14<2004::AID-ANIE2004>3.0.CO;2-7.
- ^ a b Vij, Ashwani; William W. Wilson, Vandana Vij, Fook S. Tham, Jeffrey A. Sheehy, Karl O. Christe (09 Jun 2001). "Polynitrogen Chemistry. Synthesis, Characterization, and Crystal Structure of Surprisingly Stable Fluoroantimonate Salts of N5+". J.Am.Chem.Soc 123 (26): 6308–6313. doi:10.1021/ja010141g. PMID 11427055.
Categories:- Cations
- Nitrogen
- Explosive chemicals
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
