- Monobody
-
Monobodies, also known as adnectins, are genetically engineered proteins that are able to bind to antigens. Despite their name, they are not structurally related to antibodies, which makes them a type of antibody mimetic. They are being developed by Adnexus, a biotechnology company which has been part of Bristol-Myers Squibb since 2007. The monobody angiocept (CT-322), a VEGF receptor antagonist, has entered Phase II clinical trials investigating the treatment of glioblastoma in October 2007.[1][2] It is also being studied for the treatment of other types of cancer, such as non-small cell lung cancer[3] and colorectal cancer[4].
Structure
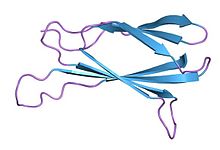
Monobodies consist of 94 amino acids and have a molecular mass of about 10 kDa, fifteen times smaller than an IgG type antibody and comparable to the size of a single variable domain of an antibody. They are based on the structure of human fibronectin, more specifically on its tenth extracellular type III domain. This domain has a structure similar to antibody variable domains, with seven beta sheets forming a barrel and three exposed loops on each side corresponding to the three complementarity determining regions.[5] Monobodies lack binding sites for metal ions and the central disulfide bond.
Monobodies with specificity for different proteins can be tailored by modifying the loops BC (between the second and third beta sheets) and FG (between the sixth and seventh sheets).[6]
See also
References
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00562419 CT-322 in Treating Patients With Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme and Combination Therapy With Irinotecan
- ^ Bloom L, Calabro V (July 2009). "FN3: a new protein scaffold reaches the clinic". Drug Discov. Today 14 (19–20): 949–55. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2009.06.007. PMID 19576999. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1359-6446(09)00219-0.
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00850577 Ph II of a Novel Anti-angiogenic Agent in Combination With Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00851045 Ph II Trial of a Novel Anti-angiogenic Agent in Combination With Chemotherapy for the Second-line Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
- ^ Koide A, Koide S (2007). "Monobodies: antibody mimics based on the scaffold of the fibronectin type III domain". Methods Mol. Biol. 352: 95–109. PMID 17041261.
- ^ Koide A, Bailey CW, Huang X, Koide S (December 1998). "The fibronectin type III domain as a scaffold for novel binding proteins". J. Mol. Biol. 284 (4): 1141–51. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2238. PMID 9837732. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0022-2836(98)92238-0.
Engineered monoclonal antibodies and antibody mimetics Whole antibody bispecific: Trifunctional antibody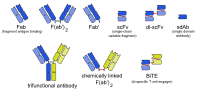
Fab fragment Variable fragment Single-chain variable fragment / di-scFv / tri-scFv • Single-domain antibody • Small modular immunopharmaceutical • bispecific: T-cell engagerSmaller units Intracellular IntrabodyAntibody mimetics Categories:- Molecular biology
- Proteins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.