- Complementarity determining region
-
Complementarity determining regions (CDRs) are regions within antibodies (also known as immunoglobulins) or T cell receptors where these proteins complement an antigen's shape. Thus, CDRs determine the protein's affinity and specificity for specific antigens. The CDRs are the most variable part of the molecule, and contribute to the diversity of these molecules, allowing the antibody and the T cell receptor to recognize a vast repertoire of antigens.
Contents
Location and structure
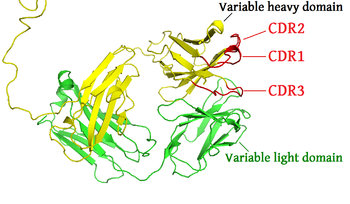
In the amino acid sequence of a variable domain of an antigen receptor there are three CDRs (CDR1, CDR2 and CDR3), arranged non-consecutively. Since the antigen receptors are typically composed of two variable domains (on two different polypeptide chains, heavy and light chain), there are six CDRs for each antigen receptor that can collectively come into contact with the antigen. A single antibody molecule has two antigen receptors, wherefore it contains twelve CDRs. Sixty CDRs can be found on a pentameric IgM molecule.
Within the variable domain, CDR1 and CDR2 are found in the variable (V) region of a polypeptide chain, and CDR3 includes some of V, all of diverse (D, heavy chains only) and joint (J), and some of the constant (C) regions.[citation needed] CDR3 is the most variable.
Since most sequence variation associated with immunoglobulins and T cell receptors are found in the CDRs, these regions are sometimes referred to as hypervariable regions.[1] Among these, CDR3 shows the greatest variability as it is encoded by a recombination of the VJ in the case of a light chain region and VDJ in the case of heavy chain regions.
The tertiary structure of an antibody is important to analyze and design new antibodies. Homology modeling is a computational method to build tertiary structures from amino-acid sequences. The so-called H3-rules are emipirical rules to build models of CDR3.[2]
See also
- Framework region
- Hypervariable region
References
- ^ Abbas AK and Lichtman AH (2003). Cellular and Molecular Immunology (5th ed. ed.). Saunders, Philadelphia. ISBN 0-7216-0008-5.
- ^ Shirai, H; Kidera, A; Nakamura, H (1999). "H3-rules: identification of CDR-H3 structures in antibodies". FEBS letters 455 (1-2): 188–97. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00821-2. PMID 10428499.
External links
Categories:- Amino acids
- Immune system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.