- Marsh Railway
-
This article is about describes the railway from Elmshorn–Westerland to Tondern. For the line through the Hamburg Vierlande from Billbrook via Zollenspieker to Besenhorst, see Hamburg Marsh Railway.
Marsh Railway (Marschbahn) Route number: 103 (Elmshorn–Itzehoe)
130 (Elmshorn–Westerland)Line number: 1210 (NOB)
96 (NEG, border–Tønder)Line length: NOB: 207,0 km
NEG: (border–Tønder) 4,1Gauge: 1,435 Voltage: (Elmshorn–Itzehoe) 15 kV 16.7 Hz AC Legend

237,7 Westerland (SyltShuttle) 

235,7 Tinnum 

233,3 Keitum 

228,8 Morsum (Sylt) 

Hindenburgdamm 

211,7 Klanxbüll 

208,2 Emmelsbüll 

205,1 Lehnshallig 

Ferry from Munkmarsch 
Højer Sluse 

Højer 

Daler 

from Esbjerg 

from Tinglev (closed as far as Tønder-Ost) 

63,3 Tønder 
67,9 175,3 Denmark/Germany border 

171,6 Süderlügum (also a siding) 

167,8 Uphusum 
162,3 Boundary between neg and DBAG 




Link lines neg/DBAG 


162,0 198,5 Niebüll (Keilbahnhof) 


(SyltShuttle car loading point) 


to Dagebüll (neg) 
194,1 Lindholm 
to Flensburg 
Lecker Au 
Bundeswehr siding 
190,3 Stedesand 
Scholmer Au 
184,3 Langenhorn (Schleswig) 
176,8 Bredstedt 
to Löwenstedt 
172,7 Struckum 
Arlau 
165,8 Hattstedt 
159,4 Husum Nord 
to Husum Außenhafen 
Mühlenau (bascule bridge) 
from Tönning (to 1902) 
158,3 Husum 


to Flensburg, to Jübek 

Bw Husum to Rendsburg 
153,6 Hörn junction to Tönning 
147,1 Friedrichstadt 
Eider (Bridge 417 m) 
145,2 St. Annen Eider Bridge crossover 
140,8 Lunden 
133,9 Wittenwurth 


from Karolinenkoog 


4,8 129,3 Weddingstedt 


from Büsum 


?,? Weddinghusen 

Flying junction 


0,0 124,5 Heide (Holst) 


to Neumünster 
119,6 Hemmingstedt 
112,4 Meldorf 
105,5 Windbergen 
0,0 101,2 Sankt Michaelisdonn 


Line to Marne–Friedrichskoog III 


5,1 Eddelak 


91,4 Burg (Dithm) 


7,8 Blangenmoor 


90,2 Hochdonn Nord crossover 


10,0 Brunsbüttel Condea siding 


12,1 Brunsbüttelkoog Nord 

swing bridge , Hochdonn High Bridge 


15,6 Brunsbüttel 


13,7 Brunsbüttel Ost siding 


86,5 Hochdonn Süd crossover 


10,9 Kudensee siding 


83,2 Vaale 


8,8 Sankt Margarethen (Holst) siding 



0,0 74,2 Wilster 
71,0 Bekdorf 
68,1 Heiligenstedten 
from Wrist 
64,9 Itzehoe 
Stör (Klappbrücke) 
63,1 Anst Itzehoe Alsen 
59,6 Kremperheide 
54,2 Krempe 
47,4 Glückstadt 

(1,5) Glückstadt Hafen (port) 
43,5 Herzhorn 
37,7 Siethwende 
31,7 Elmshorn West 
from Kiel 
30,7 Elmshorn 
to Hamburg The Marsh Railway (German: Marschbahn) is a main line in the state of Schleswig-Holstein in Germany that links the stations of Elmshorn in the south and Westerland on the island of Sylt in the north. It is part of a 237 kilometre long through route from Hamburg-Altona to Westerland (Sylt) and is listed in the Deutsche Bahn timetables as Kursbuchstrecke 130. The first part of it was opened in 1845 and is one of the oldest lines in Germany.
 Trials locomotive DB Class 240 in Niebüll
Trials locomotive DB Class 240 in Niebüll
Contents
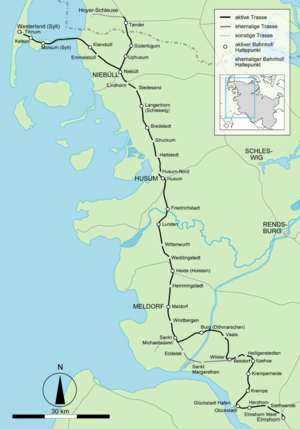
Route
The Marsh Railway, as its name suggests, mainly runs through marshlands. There are also some sections of the line that run through the higher-lying geest. The line crosses the Kiel Canal on the 42 metre-high Hochdonn High Bridge. The bridge’s total length is 2,218 meters and its main span over the channel is 143 metres-long. There is also a bascule bridge north of Husum station. Between Klanxbüll and Morsum stations the line runs across the Hindenburgdamm causeway through the North Frisian mudflats.
History
The first section of the current Marsh Railway was built by the Glückstadt-Elmshorn Railway Company (Glückstadt-Elmshorner Eisenbahn-Gesellschaft) shortly after the opening of the Altona–Kiel line on 18 September 1844. The company opened a line from Elmshorn to Glückstadt port station on 20 July 1845. Twelve years later, on 15 October 1857, the line was realigned in Glückstadt and extended to the edge of the Stör river in Itzehoe. In 1878, a swing bridge was built across the Stör—which was replaced in 1910 during the duplication of the line by two bascule bridges—and the line was extended to the Heide station of the Neumünster–Heide–Karolinenkoog line, which opened on 22 August 1877.
On 1 January 1879 the Glückstadt-Elmshorn Railway Company became the Holstein Marsh Railway Company (Holsteinische Marschbahn-Gesellschaft). In 1888, this company was acquired by the Schleswig-Holstein Marsh Railway Company (Schleswig-Holsteinische Marschbahn-Gesellschaft). On 1 July 1890, the company was acquired by the Prussian government and it became part of the Prussian State Railways.
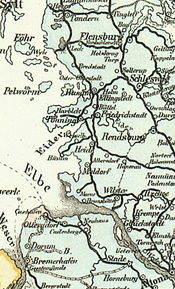
In 1886 construction began on an extension and on 1 September 1886 the line was opened via Lunden and a bridge over the Eider near Friedrichstadt to Husum, where it connected with the Flensburg–Husum–Tönning line. The line was extended further north to Bredstedt on 17 October 1887 and to Niebüll on 15 November 1887. The line was subsequently extended further north to Tønder, connecting to branch lines to Tinglev and Højer Sluse, which was the port for a ferry connection to Sylt. The line was extended to Bredebro, Scherrebek, Ribe and Bramming, where it connected with the Danish rail network.
1920-1926
In 1920 northern Schleswig became part of Denmark, and the border was established between Niebüll and Tonder. This meant that traffic to Sylt had to cross the German-Danish border twice, although the Danish authorities allowed sealed transit trains to operate, avoiding customs inspections of passengers. The operation of transit trains and the Hoyer–Sylt ferry ended with the inauguration of the Hindenburg causeway in 1927.
Originally, the Marsh Railway ran from Wilster directly to St. Michaelisdonn. During the construction of the Kiel Canal, a swing bridge was built on the line at Taterpfahl near St. Margarethen. During the widening of the canal in 1920, a new high bridge was bridge was built on the geest at Hochdonn on a 5.8 km long bypass route. It was originally initially planned for the line to be built directly from Itzehoe to Meldorf, but because of protests from Wilster and Sankt Michaelisdonn, the line was rerouted on a devious route to include these towns. The old track was rebuilt to run from Wilster to Brunsbüttelkoog and on the north side to Brunsbüttel Nord.
1927-1948
Significant changes took place on 1 June 1927 with the opening of Hindenburg causway, which was prepared in 1922 by prolonging the line from Niebüll to Klanxbüll to enable material transports. Deutsche Reichsbahn (German State Railways) opened a new station at Westerland together with the connecting part of the line. The Sylt Island Railway lost its traffic between Munkmarsch and Westerland, because the ferry service between Hoyer and Sylt had been closed. The Island Railway built a station next to the Reichsbahn station, with a simple reception building.
1948–1993
After World War II many (often long) express trains ran to Westerland, especially in the summer season. Most trains ran beyond Hamburg towards Cologne and the Ruhr, some went to southern Germany. Daily service also operated as interzonal trains from Berlin (running without stopping in the former East Germany), which were augmented in the summer at weekends by a second pair of trains.
Until the 1970s, these services were hauled by class 01.10 locomotives. These were replaced by class 218 diesels.
A significant improvement of services on the Marsh line occurred with the timetable of summer 1978. Regular interval Intercity (IC) trains were introduced between Cologne and Hamburg, with some first and second class carriages running beyond Hamburg to Westerland. A year later IC connections from Westerland to Frankfurt am Main and Munich were added.
Clock-face timetable since 1991
The 1991 there was a complete transformation of the passenger transport services on the Marsh line and in Schleswig–Holstein. New two-hourly express trains were introduced that ran between Hamburg and Heide making even fewer stops than IC trains. These trains were aimed at offering travel times of less than two and a half hours from Hamburg to North Sea resorts, such as Büsum via Heide, Dagebüll via Niebüll and Sankt Peter-Ording via Husum. Hourly local trains were introduced, stopping at all stations to Husum. Trains were added during peak hours from Pinneberg to Itzehoe.
References
- Bock, Hans (1989) (in German). Die Marschbahn von Altona nach Westerland (The Marsh Railway from Altona to Westerland). Heide: Boyens. ISBN 3-8042-0458-9.
- Landesarchiv Schleswig-Holstein/Altonaer Museum (1994) (in German). Schienen zum Fortschritt. 150 Jahre Eisenbahn in Schleswig-Holstein. (Lines to progress. 150 years of railways in Schleswig-Holstein). Schleswig and Hamburg: Self-published, exhibition catalog.
- Staisch, Erich, ed (1994) (in German). Der Zug nach Norden (The railway to the north). Hamburg: Ernst Kabel Verlag. ISBN 3-8225-0298-7.
- Stumpf, Rolf (2003) (in German). Die Eisenbahn nach Sylt (The railway to Sylt). Freiburg: EK regionale Verkehrsgeschichte Band 38. ISBN 3-88255-455-X.
External links
Categories:- Railway lines in Schleswig-Holstein
- Railway lines in Denmark
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.