- Invasion of England (1326)
-
Isabella's Campaign Part of Despenser wars 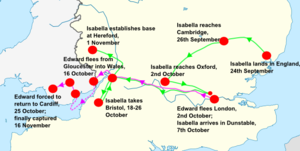
Isabella's Campaign (green) and the English retreat (pink)Date September 24–November 16, 1326 Location England and Wales Result French victory Belligerents  Kingdom of France
Kingdom of France
 Marcher Lords
Marcher Lords Kingdom of England
Kingdom of EnglandCommanders and leaders  Isabella of France
Isabella of France
 Roger Mortimer, 1st Earl of March
Roger Mortimer, 1st Earl of MarchEdward II of England †
Hugh Despenser the younger †
Edmund Fitzalan †
Hugh Despenser the Elder †Strength 8,500 unknown Casualties and losses unknown unknown The invasion of England in 1326 by Isabella of France and Roger Mortimer, 1st Earl of March, led to the capture of Hugh Despenser the Younger and Edward II of England.
Roger Mortimer of Wigmore was a powerful Marcher lord, married to the wealthy heiress Joan de Geneville, and the father of twelve children. Mortimer had been imprisoned in the Tower of London in 1322 following his capture by Edward. Mortimer's uncle, Roger Mortimer de Chirk finally died in prison, but Mortimer managed to escape the Tower on his birthday in 1323, making a hole in the stone wall of his cell before escaping onto the roof, before using rope ladders provided by an accomplice to get down to the River Thames, across the river and then on eventually to safety in France.[1] Victorian writers suggested that, given later events, Isabella might have helped Mortimer escape and some historians continue to argue that their relationship had already begun at this point, although most believe that there is no hard evidence for their having had a substantial relationship before meeting in Paris.[2]
Isabella was reintroduced to Mortimer in Paris by her cousin, Joan, Countess of Hainault, who appears to have approached Isabella suggesting a marital alliance between their two families, marrying Prince Edward to Joan's daughter, Philippa.[3] Mortimer and Isabella began a passionate relationship from December 1325 onwards; Isabella was taking a huge risk in doing so—female infidelity was a very serious offence in medieval Europe, as shown during the Tour de Nesle Affair—both Isabella's former French sisters-in-law had died by 1326 as a result of their imprisonment for exactly this offence.[4] Isabella's motivation has been the subject of discussion by historians; most agree that there was a strong sexual attraction between the two, that they shared an interest in the Arthurian legends and that they both enjoyed fine art and high living.[5] One historian has described their relationship as one of the "great romances of the Middle Ages".[6] They also shared a common enemy—the regime of Edward II and the Despensers.
Taking Prince Edward with them, Isabella and Mortimer left the French court in summer 1326 and travelled north to William I, Count of Hainaut. As Joan had suggested the previous year, Isabella betrothed Prince Edward to Philippa, the daughter of the Count, in exchange for a substantial dowry[7] She then used this money plus an earlier loan from Charles[8] to raise a mercenary army, scouring Brabant for men, which were added to a small force of Hainaut troops.[9] William also provided eight men of war ships and various smaller vessels as part of the marriage arrangements. Although Edward was now fearing an invasion, secrecy remained key, and Isabella convinced William to detain envoys from Edward.[9] Isabella also appears to have made a secret agreement with the Scots for the duration of the forthcoming campaign.[10] On 22 September, Isabella, Mortimer and their modest force set sail for England.[11]
Having evaded Edward II's fleet, which had been sent to intercept them, Isabella and Mortimer landed at Orwell on the east coast of England on 24 September with a small force; estimates of Isabella's army vary from between 300 to around 2,000 soldiers, with 1,500 being a popular middle figure. After a short period of confusion during which they attempted to work out where they had actually landed, Isabella moved quickly inland, dressed in her widow's clothes. The local levies mobilised to stop them immediately changed sides, and by the following day Isabella was in Bury St Edmunds and shortly afterwards had swept inland to Cambridge. Thomas, Earl of Norfolk, joined Isabella's forces and Henry, Earl of Lancaster—the brother of the late Thomas, and Isabella's uncle—also announced he was joining Isabella's faction, marching south to join her. On 26 September, Isabella captured Cambridge.
By the 27th, word of the invasion had reached the King and the Despensers in London. Edward issued orders to local sheriffs to mobilise opposition to Isabella and Mortimer, but London itself was becoming unsafe due to local unrest and Edward made plans to leave. Isabella struck west again, reaching Oxford on the 2nd October where she was "greeted as a saviour"—Adam Orleton, the bishop of Hereford, emerged from hiding to give a lecture to the university on the evils of the Despensers. Edward fled London on the same day, heading west toward Wales. Isabella and Mortimer now had an effective alliance with the Lancastrian opposition to Edward, bringing all of his opponents into a single coalition.
Isabella now marched south towards London, pausing at Dunstable, outside the city on the 7th October. London was now in the hands of the mobs, although broadly allied to Isabella. Bishop Stapledon, unfortunately, failed to realise the extent to which royal power had collapsed in the capital and tried to intervene militarily to protect his property against rioters; a hated figure locally, he was promptly attacked and killed—his head was later sent to Isabella by her local supporters. Edward, meanwhile, was still fleeing west, reaching Gloucester by the 9th. Isabella responded by marching swiftly west herself in an attempt to cut him off, reaching Gloucester a week after Edward, who slipped across the border into Wales the same day.
Hugh Despenser the Elder continued to hold Bristol against Isabella and Mortimer, who placed it under siege between 18–26 October; when it fell, Isabella was able to recover her daughters Eleanor of Woodstock and Joan of the Tower, who had been kept in the Despenser's custody. By now desperate and increasingly deserted by their court, Edward and Hugh Despenser the younger attempted to sail to Lundy, a small island just off the Devon coast, but the weather was against them and after several days they were forced to land back in Wales. With Bristol secure, Isabella moved her base of operations up to the border town of Hereford, from where she ordered Henry of Lancaster to locate and arrest her husband. After a fortnight of evading Isabella's forces in South Wales, Edward and Hugh were finally caught and arrested near Llantrisant on the 16 November, the same day that the English were defeated in Wales.
 Hugh Despenser the younger and Edmund Fitzalan brought before Isabella for trial in 1326; the pair were gruesomely executed.
Hugh Despenser the younger and Edmund Fitzalan brought before Isabella for trial in 1326; the pair were gruesomely executed.
Edward II of England died somehow, most likely assassinated by orders of Isabella and Mortimer. What is known is that both Hugh Despenser the younger and Edmund Fitzalan were both Hanged, drawn, and quartered. The death of Fitzalan, Despenser the younger, Despenser the elder, and Edward II brought an end to the Despenser wars, though France's desire for freedom led to the Hundred Years' War.
Notes
- ^ Weir 2006, p.153.
- ^ Weir 2006, p.154; see Mortimer, 2004 pp128-9 for the alternative perspective.
- ^ Weir 2006, p.194.
- ^ A point born out by Mortimer, 2004, p.140.
- ^ Weir 2006, p.197.
- ^ Mortimer, 2004, p.141.
- ^ Kibler, p.477.
- ^ Lord, p.47.
- ^ a b Weir 2006, p.221.
- ^ Weir 2006, p.222.
- ^ Weir 2006, p.223.
Bibliography
- Costain, Thomas Bertam. (1962) The Three Edwards. London: Doubleday.
- Doherty, P.C. (2003) Isabella and the Strange Death of Edward II. London: Robinson. ISBN 1841198439.
- Mortimer, Ian. (2008) The Perfect King: The Life of Edward III, Father of the English Nation. London: Vintage Books. ISBN 9780099527091.
- Weir, Alison. (2006) Queen Isabella: She-Wolf of France, Queen of England. London: Pimlico Books. ISBN 9780712641944.
Categories:- Battles involving France
- Battles involving England
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.



