- Madrid–Barcelona high-speed rail line
-
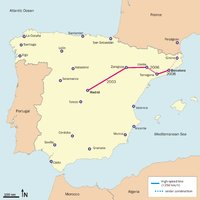
Madrid-Barcelona-Perpignan
high-speed rail lineLine length: 621 km (386 mi) Gauge: 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) Legend



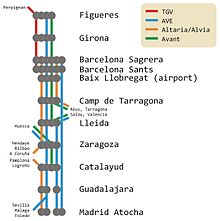
0.0 km Madrid Atocha 


to Seville 


64.4 km Guadalajara-Yebes 


221.1 km Calatayud 


272.9 km Plasencia de Jalón 


294.9 km Bif. Moncasí 


306.7 km Zaragoza-Delicias 





Tardienta 


Huesca 


434.6 km Les Torres de Sanuí 


442.1 km Lleida Pirineus 


448.6 km Artesa 


512.8 km Corredor Mediterráneo 
520.9 km Camp de Tarragona 


Barcelona avoiding line 



Barcelona–Vilanova 
El Prat 



Direction Can Tunis 
620.9 km Barcelona Sants _ _  _
_

Provença-Mallorca tunnel 

Estació de la Sagrera 





Barcelona avoiding line 



Girona 





Figueres 
44.38 km International Section Ends 
Pirineus Tunnel 
French - Spanish Border 
Perthus Tunnel (8,300 m) 


Tec River 

Elna to Arles line 
crossover 
A9 Motorway 
D612A road 


Rand River 
0.00 km International Section starts 


Classic line to Vilafranca de Conflent 
Le Soler 


Classic line to Portbou 
Perpignan 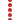
Classic line powered at 1.5kV 
Nîmes 
LGV Méditerranée to Paris The Madrid–Barcelona high-speed rail line is a 621-kilometre (386 mi) standard gauge railway line inaugurated on 20 February 2008. Designed for speeds of 300 km/h (186 mph) and compatibility with neighbouring countries' rail systems, it connects the cities of Madrid and Barcelona, in Spain. Work is underway to extend the line into France to connect with the European high speed network in 2012.
Contents
First stages
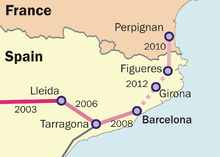
In 2003 construction of the first phase of a new standard gauge line from Madrid to the French border (Madrid–Zaragoza–Lleida) was completed and on 11 October of that year commercial service began. This service also stopped at Guadalajara–Yebes and Calatayud. The service began running at only 200 km/h (124 mph). On 19 May 2006, after two years of operation, speed was increased to 250 km/h (155 mph) when the Spanish ASFA signalling system was replaced with level 1 of the new European ETCS/ERTMS system. On 16 October 2006 the trains on this line increased their operating speed to 280 km/h (174 mph).
On 18 December 2006 the AVE started operating to Camp de Tarragona, and on 7 May 2007 the service increased its speed to the maximum allowable for the line, 300 km/h (186 mph). This puts Tarragona at 30 minutes from Lleida. The extension to Barcelona was delayed various times due to technical problems; the Ministerio de Formento having originally forecast the AVE's arrival in Barcelona by the end of 2007.[1]
Complete operation
The complete line was opened February 2008. As of 2008, seventeen trains now run every day between the hours of 6 am and 9 pm, covering the distance between the two cities in just 2 hours 38 minutes, except for those stopping at all stations, which take 3 hours. Before the high-speed line was built, the journey between the two cities took more than six hours; and when the high speed line went only as far as Tarragona, 3 hours 45 minutes, operated with the Alvia service (120 series train), which continued on the conventional line to Barcelona, after a change of rail gauge.
Speed
It was originally forecast that, after reaching Barcelona in 2004, the line would run at 350 km/h (217 mph), the maximum capable speed of the new Siemens AVE trains which have replaced the Talgo Bombardier AVE S102, after the installation of level 2 of the ETCS/ERTMS, which is yet to be installed. But on the AVE's first day of operating at 300 km/h (186 mph) to Tarragona the Minister of Public Works, Magdalena Álvarez, stated that the maximum commercial operating speeds of the AVE on all lines would be 300 km/h (186 mph).[2] Still, in October 2011, the speed was raised to 310 km/h on parts of the railway[3].
Usage
It was forecast that the AVE will substantially replace air traffic on the Barcelona - Madrid route (in the same way that the Eurostar has on the London-Paris/London-Brussels routes and France's TGV has on the Paris-Lyon route). In fact, more than 80% of travellers between Madrid and Seville use the AVE, with fewer than 20% travelling by air.[4] The route Madrid-Barcelona was in 2007 the world's busiest passenger air route with 971 scheduled flights per week (both directions). In order to compete with each other RENFE has made, and Iberia will make, changes to their fare structures, as well as changing services; Iberia plans to use smaller planes which will leave as soon as full, and a non-stop AVE service is available between the two cities.
Criticism
There was much criticism during the construction of the Madrid-Barcelona line. A highly critical report by the consulting firm KPMG, commissioned by ADIF (Administrador de Infraestructuras Ferroviarias) at the behest of the Ministry for Public Works (Ministerio de Fomento) on 23 June 2004, pointed to a lack of in-depth studies and over-hasty execution of works as the most important reasons for the problems that dogged construction of the AVE line. For example, during the construction of the AVE tunnel near Barcelona, a number of nearby buildings suffered minor damage from a large sinkhole that appeared near a commuter rail station, damaging one of its platforms. The construction committee of Barcelona's famed Sagrada Familia church lobbied for a re-routing of the tunnel - it passes within metres of the massive church's foundations. It also passes equally near the UNESCO-recognized Casa Milà also designed by Antoni Gaudí.
Furthermore, until 2005 both Siemens and Talgo/Bombardier train sets failed to meet scheduled speed targets, although in a test run during the homologation tests of the new S102 trains of RENFE, a train-set Talgo 350 (AVE S-102) reached a speed of 365 km/h (227 mph) on the night of the 25/26 June 2006, and in July 2006 a Siemens Velaro train-set (AVE S-103) reached the highest top speed ever in Spain: 403.7 km/h (250.8 mph). This is a Spanish record for railed vehicles and a world record for unmodified commercial service trainsets, as the earlier TGV and ICE records were achieved with specially modified and shortened trainsets, and the Shinkansen (443 km/h/275 mph, 1996) record was for a test (non-commercial) trainset.
Extension to France
Work has begun to extend beyond Barcelona and across the France border to Perpignan, connecting with the high speed train service on the LGV Méditerranée to Paris and beyond.
Barcelona to Figueres
Originally planned to open in 2009, high speed trains are expected to start running in 2012. There have been delays in building a four kilometre tunnel in Girona - the first phase of which was finished in September 2010[5] - and controversy over the route between Sants and Sagrera stations in Barcelona.[6]
Figueres to Perpignan
Main article: LGV Perpignan-FigueresThis is an international high speed rail line between France and Spain. The line connects two cities on opposite sides of the border, Perpignan in Roussillon, France, and Figueres in Catalonia, Spain. It consists of a 44.4-kilometre (27.6 mi) line which crosses the French–Spanish border via the Perthus Tunnel, an 8.3-kilometre (5.2 mi) tunnel bored under the Perthus Pass.[7] The line is open to high speed trains and freight. Construction was completed in February 2009, although services did not run until a station was built on the line at Figueres. From 19 December 2010 there is a TGV service from Paris via Perpignan to Figueres.[8]
See also
References
- ^ La Vanguardia, 18 December 2006
- ^ La Vanguardia, 7 May 2007
- ^ Madrid - Barcelona at 310 km/h with ETCS Level 2
- ^ Juan Carlos Martín and Gustavo Nombela, "Microeconomic impacts of investments in high speed trains in Spain", Annals of Regional Science, vol. 41, no. 3, September 2007
- ^ "Railway Gazette: Girona tunnelling makes progress". http://www.railwaygazette.com/nc/news/single-view/view/girona-tunnelling-makes-progress.html. Retrieved 2010-09-23.
- ^ "Perpignan-Barcelona AVE to open in 2012 or .... 2020?". Today's railways Europe, Issue 140: p. 10. August 2007.
- ^ "Perpignan-Figueras High-speed Rail Line". Structurae. http://en.structurae.de/projects/data/index.cfm?id=p0000133. Retrieved 30 January 2009.
- ^ "Ouverture des ventes pour Paris Figueras" (in French). SNCF. 22 November 2010. http://www.sncf.com/resources/en_EN/press/kits/PR0001_20101122.pdf. Retrieved 1 December 2010.
External links
High speed rail in Spain Lines in service (map) Madrid–Barcelona • Madrid–Levante (Valencia) • Madrid–Seville • Córdoba–Málaga • Madrid–Valladolid • Madrid–Toledo • Zaragoza–Huesca(fr) • Figueres–PerpignanLines under construction Planned lines Madrid–Lisbon(fr) • Porto–VigoRolling stock S/100 • S/102 • S/103 (Siemens Velaro) • S/112 • S/114 • S/120 , S/121 • S/130 • S/353 • S/354 • S/490Services (map) High-speed railway lines East Asia JapanChinaBeijing-Shanghai · Qinhuangdao–Shenyang · Hefei–Nanjing · Beijing–Tianjin · Qingdao–Jinan · Shijiazhuang–Taiyuan · Hefei–Wuhan · Ningbo–Taizhou–Wenzhou · Wenzhou–Fuzhou · Wuhan–Guangzhou · Zhengzhou–Xi'an · Fuzhou–Xiamen · Chengdu–Dujiangyan · Shanghai–Nanjing · Nanchang–Jiujiang · Shanghai–Hangzhou · Hainan Eastern Ring · Changchun–JilinSouth KoreaGyeongbu HSRTaiwanEurope BelgiumFranceLGV Sud-Est · LGV Est · LGV Atlantique · LGV Rhône-Alpes · LGV Nord · LGV Interconnexion Est · LGV Méditerranée · Perpignan-FigueresGermanyCologne–Düren · Cologne–Frankfurt · Hanover–Würzburg · Mannheim–Stuttgart · Rastatt–Offenburg · Wolfsburg–Berlin · Nuremberg–IngolstadtItalyNetherlandsNorwaySpainMadrid–Barcelona · Madrid–Sevilla · Córdoba–Malaga · Madrid–Valladolid · Madrid–Toledo · Figueres–Perpignan · Madrid–Valencia · Motilla–AlbaceteTurkeySincan–Eskişehir · Polatlı–KonyaUnited KingdomNorth America United StatesCategories:- High-speed railway lines in Spain
- Transport in Madrid
- Transport in Barcelona
- Railway lines opened in 2008
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.