- Pointing device gesture
-
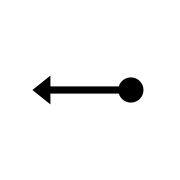 The mouse gesture for "back" in Opera – the user holds down the right mouse button, moves the mouse left, and releases the right mouse button.
The mouse gesture for "back" in Opera – the user holds down the right mouse button, moves the mouse left, and releases the right mouse button.
In computing, a pointing device gesture or mouse gesture is a way of combining pointing device movements and clicks which the software recognizes as a specific command. Pointing device gestures can provide quick access to common functions of a program. They can also be useful for people who have difficulties typing on a keyboard. For example, in a web browser, the user could navigate to the previously viewed page by pressing the right pointing device button, moving the pointing device briefly to the left, then releasing the button.
Contents
History
The first pointing device gesture, the "drag," was introduced by Apple to replace a dedicated "move" button on mice shipped with its Macintosh and Lisa computers. Dragging involves holding down a pointing device button while moving the pointing device; the software interprets this as an action distinct from separate clicking and moving behaviors. Unlike most pointing device gestures, it does not involve the tracing of any particular shape. Although the "drag" behavior has been adopted in a huge variety of software packages, few other gestures have been as successful.
Current use
As of 2005[update], most programs do not support gestures other than the drag operation. Each program that recognizes pointing device gestures does so in its own way, sometimes allowing for very short mouse movement distances to be recognized as gestures, and sometimes requiring very precise emulation of a certain movement pattern (e.g. circle). Some implementations allow users to customize these factors.
Some video games have used gestures. For example, in the Myth real-time tactics series, originally created by Bungie Software, players use them to order battlefield units to face in a desired direction. Another game using gestures is Lionhead's Black & White. The game Arx Fatalis uses mouse gestures for drawing runes in the air to cast spells. Several Nintendo Wii games take advantage of such a system. Ōkami uses a system similar to mouse gestures; the player can enter a drawing mode in which the shape they create (circle, lightning bolt, line, etc.) performs a function in the game such as creating a bomb or changing the time from night to day. Another example is Silver where basic mouse gestures actually map attack moves and such in real-time combat.
The Opera web browser has recognized gestures since version 5.10 (April 2001) but this feature was disabled by default. Opera browser also supports mouse chording which serves a similar function but doesn't necessitate mouse movement. First browser that used advanced mouse gestures (in 2002) was Maxthon where highly customizable interface allowed to assign almost every action to one of 52 mouse gestures and few mouse chords. Several mouse gesture extensions are also available for the Mozilla Firefox browser. These extensions use almost identical gestures as Opera.
Some tools provide mouse gestures support in any application for Microsoft Windows. KDE includes universal mouse gesture support since version 3.2.
Drawbacks
A major drawback of current gesture interaction solutions is the lack of support for two necessary user interface design principles, feedback and visibility (or affordance). Feedback notification is required to indicate whether the gesture has been entered correctly by indicating the gesture recognized and the corresponding command activated, although Sensiva does approach this to some extent in providing voice notification. The other principle is visibility of gestures, providing the user some means of learning the necessary gestures and the contexts they can be used in. Both Mouse Gestures for Internet Explorer and ALToolbar Mouse Gestures display colored tracers that indicate the current motion that the user is taking to facilitate visual clues for the user. Also pie menus and marking menus have been proposed as solutions for both problems, since they support learning of the available options but can also be used with quick gestures. The current version of Opera uses a pie menu to simply and non-obstructively display which mouse gestures are available and how to activate them.
One limitation with gesture interaction is the scope context in which the gestures can be used. For example each gesture has only one corresponding command for each application window.
Holding down buttons while moving the mouse can be awkward and requires some practice, since the downwards action increases friction for the horizontal motion. An optical mouse would be less susceptible to changes in behavior than a ball mouse with increased friction because the sensor does not rely on mechanical contact to sense movement; a touchpad provides no added friction with all its buttons held down with a thumb. However, it was also argued that muscular tension resulting from holding down buttons could be exploited in user interface design as it gives constant feedback that the user is in a temporary state, or mode (Buxton, 1995).
See also
External links to applications
Some programs and applications of mouse gestures and similar features:
Windows
- Just Gestures (freeware)
- Sensiva (shareware, has disappeared; last version (3.14) can still be found around the Internet)
- MicePlus (shareware)
- Mouse Gesture Desktop Tools (shareware)
- Brass via Mime plugin (shareware)
- Gesture Magic (free/open source application launcher)
- gMote (freeware)
- Mojo Sidekick (shareware)
- StrokeIt (free for non-profit use)
- PowerPro (Freeware - Has a gesture plugin)
- High Sign (Freeware/Open Source - Currently in development, Supports plugins)
- LiveEdge (freeware)
Mac OS X
- CocoaGestures
- FlyGesture, a freeware application
- Mojo Sidekick
- Quicksilver has a feature for recognizing mouse gestures
- Sapiens
- xGestures
X11
- Easystroke has packages for Ubuntu and can be compiled on other Linux distributions
- Gestikk
- Freehand Gestures for KDE
- Configuring native strokes in FVWM
- KHotkeys provides native gestures support in KDE
- wayV
- xgestures
- xstroke
SkyOS
- SkyOS Mouse Gestures SkyOS has native support of mouse gestures
Applications
These apps support gestures on their own:
- Mouse Gesture Task Switcher for Windows. Use mouse gestures to switch between application windows. By Encsoft.
- Mouse Gesture Application Launcher for Windows. Use mouse gestures to launch applications, files.
- Mouse Gesture Window Controller for Windows. Use mouse gestures to close, maximize, minimize the active window directly.
- Documentation of mouse gestures in Maxthon.
- Documentation of mouse gestures in Opera browser.
- Avant Browser
- Mouse Gestures for Internet Explorer
- Mouse Gestures for Internet Explorer 7 by IE7pro
- Mouse Gestures in ALToolbar for Internet Explorer.
- Reference of gestures in Motion.
- Mouse gestures in raster editor of applications based on RealWorld Designer framework.
- There are many add-ons which add the ability to Firefox
Software libraries
- iGesture Open Source Java framework for pen and mouse-based gesture recognition.
- Java Swing Mouse Gestures Open source pure Java library for recognition and processing mouse gestures.
- Lipi Toolkit Open source toolkit that supports recognition of arbitrary pen and mouse-based gestures as well as handwritten characters.
- LibStroke is a stroke translation library in C/Java
- Mouse Gestures for .NET Open source .NET component for mouse gestures recognition
References
- Buxton, W. A. (1995). "Chunking and phrasing and the design of human-computer dialogues" in Human-Computer interaction: Toward the Year 2000, R. M. Baecker, J. Grudin, W. A. Buxton, and S. Greenberg, Eds. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco, CA, 494-499.
- The Unknown History of Pen Computing contains a history of pen computing, including touch and gesture technology, from approximately 1917 to 1992.
- Annotated bibliography of references to handwriting recognition, gesture user interfaces, and pen computing
- L. K. Welbourn and R. J. Whitrow. 1988. A gesture based text editor. In Proceedings of the Fourth Conference of the British Computer Society on People and computers IV, D. M. Jones and R. Winder (Eds.). Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, USA, 363-371. ISBN 0-521-36553-8
- Brad A. Myers. "A Brief History of Human Computer Interaction Technology." ACM interactions. Vol. 5, no. 2, March, 1998. pp. 44-54.
Categories:- User interface techniques
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
