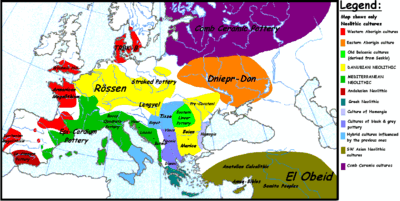
- Dnieper–Donets culture
-
Dnieper-Donets culture, ca. 5th—4th millennium BC. A neolithic (New Stone Age) culture in the area north of the Black Sea/Sea of Azov between the Dnieper and Donets River.
There are parallels with the contemporaneous Samara culture. The Dnieper-Donets culture was succeeded by the Yamna culture.
Contents
Overview
It was a hunter-gatherer culture that made the transition to early agriculture. The economic evidence from the earliest stages is almost exclusively from hunting and fishing.[1]
Inhumation was in grave pits, with the deceased being covered in ochre. Burial was sometimes individual, but larger groupings are more common, with burials being done sequentially in the same grave.
There are parallels with the contemporaneous Samara culture, and a larger horizon from the lower half of Dnieper to the mid-to-lower Volga has been drawn, particularly by the advocates of the Kurgan hypothesis as expounded by Marija Gimbutas. Dmitry Telegin (ru) assigns them to a broad cultural region that spanned the Vistula in Poland southeast to the Dnieper. Mallory includes this area within the limits of the Proto-Indo-Europeans. The precise role of this culture and its language to the derivation of the Pontic-Caspian cultures such as Sredny Stog and Yamna culture, is open to debate, though the display of recurrent traits points either to long-standing mutual contacts or underlying genetic relations.[2]
The physical remains recovered from graves have been described as typically Europoid. They are predominantly characterized as late Cro-Magnons with more massive and robust features than the gracile Mediterranean peoples of the Balkan Neolithic.[1]
Pottery
The early use of typical point base pottery interrelates with other Mesolithic cultures that are peripheral to the expanse of the Neolithic farmer cultures. The special shape of this pottery has been related to transport by logboat in wetland areas. Especially related are Swifterbant in the Netherlands, Ellerbek and Ertebolle in Northern Germany and Scandinavia, "Ceramic Mesolithic" pottery of Belgium and Northern France (including non-Linear pottery such as La Hoguette, Bliquy, Villeneuve-Saint-Germain), the Roucedour culture in Southwest France and the river and lake areas of Northern Poland and Russia.[3]
Besides a western extension to the middle Dniester down to the mouth of the Danube, it occupied the western third of the area of the later Yamna culture.
Footnotes
- ^ a b J.P.Mallory - In Search of the Indo-Europeans, 1989, p.190-191
- ^ J.P.Mallory - In Search of the Indo-Europeans, 1989, p.197
- ^ Jutta Paulina de Roever - Swifterbant-aardewerk, een analyse van de neolithische nederzettingen bij swifterbnt, 5e millennium voor Christus, Barkhuis & Groningen University Library, Groningen 2004 [1] English summary p.162-163
Sources
- J. P. Mallory, "Dnieper-Donets Culture", Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture, Fitzroy Dearborn, 1997.
Categories:- Ancient peoples
- Archaeological cultures
- Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture
- Eurasian nomads
- Indo-European
- Stone Age Europe
- Archaeology of Ukraine
- Archaeology of Russia
- 5th millennium BC
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.