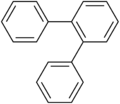
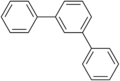
- Terphenyl
-
para-Terphenyl 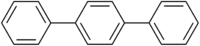
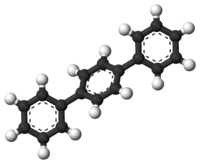 1,4-DiphenylbenzeneOther namesp-Terphenyl; 1,4-Diphenylbenzene; para-Diphenylbenzene; p-Diphenylbenzene; para-Triphenyl; p-Triphenyl
1,4-DiphenylbenzeneOther namesp-Terphenyl; 1,4-Diphenylbenzene; para-Diphenylbenzene; p-Diphenylbenzene; para-Triphenyl; p-TriphenylIdentifiers CAS number 92-94-4, (para)
92-06-8 (meta)
84-15-1 (ortho)
26140-60-3 (unspec.)PubChem 7115 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=CC=CC=C3
Properties Molecular formula C18H14 Molar mass 230.3 g mol−1 Appearance White powder[1] Density 1.24 g/cm^3 Melting point Boiling point 389 °C[2]
Solubility in water Insoluble[1] Hazards R-phrases R36/37/38 R50/53 S-phrases S26 S60 S61 Main hazards Iritant (Xi) Flash point 207 °C[2]  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Terphenyls are a group of closely related aromatic hydrocarbons. Also known as diphenylbenzenes or triphenyls, they consist of a central benzene ring substituted with two phenyl groups. The three isomers are ortho-terphenyl, meta-terphenyl, and para-terphenyl. Commercial grade terphenyl is generally a mixture of the three isomers. This mixture is used in the production of polychlorinated terphenyls, which were formerly used as heat storage and transfer agents.[1]
p-Terphenyl is the most common isomer. It is used as a laser dye and a sunscreen ingredient.[1]
See also
- Diphenyl
- Terpyridine
- Terthiophene
References
- ^ a b c d e p-Terphenyl at chemicalland21.com
- ^ a b c p-Terphenyl at Sigma-Aldrich
External links
- p-Terphenyl at the Oregon Laser Medical Center
Categories:- Aromatic compounds
- Hydrocarbons
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.