- Dibenzyl ketone
-
Dibenzyl ketone 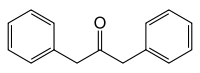
 1,3-diphenylpropan-2-one
1,3-diphenylpropan-2-oneIdentifiers CAS number 102-04-5 
PubChem 7593 ChemSpider 21105887 
EC number 203-000-0 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(Cc1ccccc1)Cc2ccccc2
Properties Molecular formula C15H14O Molar mass 210.27 g mol−1 Appearance light yellow solid Density 1.069 g/cm3 Melting point 32–34 °C
Boiling point 330 °C
Hazards Flash point 149.4°C  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dibenzyl ketone, or 1,3-diphenylacetone, is an organic compound composed of two benzyl groups attached to a central carbonyl group. This results in the central carbonyl carbon atom being electrophilic and the two adjacent carbon atoms slightly nucleophilic. For this reason, dibenzyl ketone is frequently used in an aldol condensation reaction with benzil (a dicarbonyl) and base to create tetraphenylcyclopentadienone.
Preparation
Phenylacetone self condenses to form dibenzyl ketone.
phenylacetic acid is reacted with acetic anhydride and anhydrous potassium acetate and refluxed for two hours at 140-150°C the mixture is distilled slowly so that the distillate is mostly acetic acid, from 45 minutes into the distillation carbon dioxide is released, the distillation takes 75 minutes, carbon dioxide is still being evolved when distillation is stopped the resultant liquid is a mixture of dibenzyl ketone and minor impurities, note if this mixture is heated above 200-205°C resinification occurs with a decrease in the yield of the ketone.
This article about a ketone is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
