- John Palaiologos (despot)
-
John Komnenos Palaiologos (Greek: Ἱωάννης Κομνηνός Παλαιολόγος, after 1225 – ca. 1274/1275) was a Byzantine aristocrat, brother to Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos (r. 1259–1282), who served as the commander in chief of the Byzantine army. He played a prominent part in his brother's military campaigns, most notably in the crucial victory at the Battle of Pelagonia, but also in repeated campaigns against Epirus and against the Turks in Asia Minor. He retired from active service after his defeat at Neopatras, and died shortly after.
Contents
Early life and first successes
He was born sometime after 1225, the son of Andronikos Palaiologos, the megas domestikos of the Empire of Nicaea, and his first wife Theodora Palaiologina. John was their second son, after the future emperor Michael Palaiologos, and the fourth child overall.[1][2]
Nothing is known of him until 1256, when he appears to have been sent to Rhodes; the reasons for this, i.e. whether this was to take charge of a military or administrative post or as an exile, are unknown.[3] He appears again in 1258, when he participated in the coup launched by his elder brother Michael Palaiologos, then megas konostaulos, against the regent for the underage John IV Laskaris (r. 1258–1261), George Mouzalon. After Mouzalon's murder, Michael placed the young emperor under the protection of John and their half-brother Constantine.[4] Michael quickly secured his own nomination as regent, and in turn appointed John as megas domestikos and sent him to command the Nicaean army in Macedonia, with Alexios Strategopoulos and John Raoul Petraliphas as subordinate commanders.[5][6]
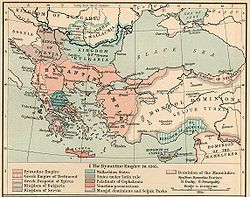
After his coronation as co-emperor in early 1259, Michael raised his brother further to the rank of sebastokrator (Strategopoulos succeeded him as megas domestikos), and arranged a marriage to a daughter of the general Constantine Tornikes.[5][7] Michael then ordered John to attack Michael II, the ruler of the rival Byzantine Greek state of Epirus. The Nicaean army advanced so quickly that they caught the Epirote army by surprise at its camp at Kastoria, and forced it to flee in disorder. John then proceeded to retake the fortresses of Deabolis and Ochrid, only recently captured by the Epirotes. The cities fell after short sieges, and the plain of Pelagonia, with the town of Bitola, and around Lake Prespa, was subjugated.[8][9]
Michael of Epirus however marshalled his forces, and was reinforced with men from the Principality of Achaea and the Latin states of southern Greece under Prince William II of Villehardouin himself, as well as a Sicilian contingent. Further forces were provided by Michael II's bastard son, John Doukas, ruler of Thessaly.[10] The allied force was clearly superior in numbers to the Nicaean army, and John Palaiologos avoided direct confrontation, instead using his mobile Turkish and Cuman horse archers to wear down the opposing forces. In addition, the allied army was divided by conflicting aims and the hatred between the Epirote Greeks and the Latins. A quarrel with William II led to the withdrawal of the Epirote army and the temporary defection of John Doukas to the Nicaean camp. The next day, the Nicaean forces attacked the Latins and secured a crushing victory; William II himself and many other barons were taken prisoner, while most of the Latin soldiery was killed or captured.[11][12]
In the aftermath of this success, joined by the forces of John Doukas, John Palaiologos marched south into Thessaly, seizing and fortifying its fortresses, until he reached the town of Neopatras, where he made his camp for a time. He then continued on into Boeotia, the territory of the Duchy of Athens, where he took and plundered Levadeia and Thebes. At this point however John Doukas defected back to his father, upsetting the balance of power; and John himself was soon after recalled to Lampsacus. Thus his conquest of Greece remained incomplete and was soon reversed by the recovery of Epirus' fortunes.[13][14]
Later years and death
At Lampsacus, John met with his brother, who rewarded his victories with the title of despotes, the second after the emperor himself in the Byzantine hierarchy, while his father-in-law Tornikes and his half-brother Constantine were raised to sebastokratores.[14] Then, or sometime after, he was also given the islands of Rhodes and Lesbos as personal domains (pronoiai).[15] In July 1261, Constantinople was recovered and the Byzantine Empire restored with Michael VIII as sole emperor. In the meantime however, things had been going badly in Epirus, where Michael II had recovered his realm and was once again threatening imperial possessions in Macedonia. In 1261, John was sent on campaign against the Epirotes.[16][17] After long and hard fighting, in the summer of 1263/1264 he achieved a major victory, which forced Michael II to come to terms: the Epirote ruler acknowledged imperial suzerainty, and his son and heir, Nikephoros, was married to Anna Kantakouzene, a niece of Michael VIII.[13][18]
After this success, he was sent to Asia Minor, where the Turkish raids on the Byzantine borderlands had become a menace, and where Turkish settlers had begun encroaching upon imperial territory. He remained there until 1267 and achieved some success, securing the lands around the valley of the Maeander River and restoring the defences of the region. The historian George Pachymeres certainly praised his conduct of these operations, and alleged that the mere mention of his approach caused fear to his enemies.[13][19]
In the late 1260s, John returned to Europe, and there is evidence of his activity in Macedonia and Thessaly. He had estates in the valley of the river Strymon in Macedonia, and is attested in documents concerning the properties of monasteries in eastern Thessaly, which the Byzantines had probably recovered by that time, following the death of Michael II of Epirus in 1267/1268.[20][21] John Doukas of Thessaly however remained one of the Empire's chief opponents, and Michael Palaiologos organized a campaign (variously dated to 1272/1273 or 1274/1275) to finally subdue him. It was a large-scale undertaking: an army of some 30,000 men, mostly mercenaries, was placed under the command of John Palaiologos and Alexios Kaballarios, while the land forces were to be aided by a fleet of over 70 vessels under Alexios Philanthropenos.[22] The campaign was initially crowned with success, as the Byzantine army advanced quickly through Thessaly and besieged John Doukas at his capital Neopatras. The latter however was able to escape in secret, procure aid from the Duchy of Athens, and utterly defeat the besieging Byzantine army at the Battle of Neopatras.[23][24] With his forces scattered, John Palaiologos retreated to the north; on his way, he learned of an attack by the Latin fleet on the Byzantine navy at Demetrias. Assembling whatever men he could find, the despotes led his troops in a forty-mile ride, through the night, towards Demetrias. There they encountered the battle in full swing, and the Latins having the advantage. The arrival of fresh troops however tilted the balance, and the battle ended in a crushing Byzantine victory.[25][26]
Despite his contribution to the victory at Demetrias, John Palaiologos was shattered by the loss of his army at Neopatras. According to the Byzantine sources, he resigned his title of despotes (although some modern historians have postulated that it was revoked by his brother), and appears to have died shortly after (1273.1274 or 1274/1275, depending on the dating of the Thessalian campaign).[20][27][28]
References
- ^ Kazhdan (1991), p. 1558
- ^ Cowley, Andronikos Doukas Komnenos Palaiologos
- ^ Macrides (2007), p. 350
- ^ Geanakoplos (1959), p. 41
- ^ a b Macrides (2007), pp. 347, 350
- ^ Radivoj (2003), Chapter 1
- ^ Geanakoplos (1959), p. 62
- ^ Geanakoplos (1959), pp. 62–63
- ^ Macrides (2007), pp. 356–359
- ^ Geanakoplos (1959), pp. 63–65
- ^ Geanakoplos (1959), pp. 65–72
- ^ Macrides (2007), pp. 360–364
- ^ a b c Radivoj (2003), Chapter 2
- ^ a b Macrides (2007), pp. 365–366
- ^ Nicol (1993), p. 85
- ^ Macrides (2007), p. 377
- ^ Geanakoplos (1959), p. 92
- ^ Nicol (1993), p. 47
- ^ Nicol (1993), pp. 84–85
- ^ a b Radivoj (2003), Chapter 3
- ^ Fine (1994), p. 170
- ^ Geanakoplos (1959), p. 282
- ^ Geanakoplos (1959), p. 283
- ^ Fine (1994), p. 188
- ^ Geanakoplos (1959), pp. 283–284
- ^ Fine (1994), p. 190
- ^ Magdalino (1976), pp. 143–149
- ^ Nicol (1993), p. 59
Sources
- Cawley, Charles. "Byzantium 1261–1453". Foundation for Medieval Genealogy. http://fmg.ac/Projects/MedLands/BYZANTIUM%2012611453.htm. Retrieved 2010-05-20.
- Fine, John Van Antwerp (1994), The Late Medieval Balkans: A Critical Survey from the Late Twelfth Century to the Ottoman Conquest, University of Michigan Press, ISBN 978-0472082605, http://books.google.com/books?id=Hh0Bu8C66TsC
- Geanakoplos, Deno John (1959), Emperor Michael Palaeologus and the West, 1258–1282 – A Study in Byzantine-Latin Relations, Harvard University Press
- Kazhdan, Alexander, ed. (1991), Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-504652-6
- Magdalino, Paul (1976), "Notes on the last years of John Palaiologos, brother of Michael VIII", Revue des études byzantines 34: 143–149, http://www.persee.fr/web/revues/home/prescript/article/rebyz_0766-5598_1976_num_34_1_2049, retrieved 28 May 2011
- Macrides, Ruth (2007), George Akropolites: The History – Introduction, translation and commentary, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-921067-1
- Nicol, Donald MacGillivray (1993), The Last Centuries of Byzantium, 1261–1453, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0521439916, http://books.google.com/books?id=y2d6OHLqwEsC
- Radivoj, Radic (2003). "John Palaiologos". Encyclopedia of the Hellenic World, Asia Minor. http://www.ehw.gr/l.aspx?id=9324. Retrieved 2010-05-20.
Categories:- 1220s births
- 1270s deaths
- 13th-century Byzantine people
- Byzantine generals
- Palaiologos dynasty
- Byzantine people of the Byzantine–Seljuq Wars
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.