- Moses Gomberg
-
Moses Gomberg 
Moses Gomberg, the father of radical chemistryBorn 1866 Died 1947 Fields chemistry Institutions University of Michigan Alma mater University of Michigan Doctoral advisor A. B. Prescott Known for radical chemistry Moses Gomberg (born February 8, 1866, Yelizavetgrad, Russian Empire [now Kirovograd, Ukraine] died February 12, 1947, Ann Arbor, Mich., U.S.) was a chemistry professor at the University of Michigan.[1]
He was born in Elizabetgrad, Russian Empire. In 1884, the family emigrated to Chicago to escape the pogroms following the assassination of Czar Alexander II. In Chicago he worked at the Stock Yards while attending Lake High School. In 1886, Moses entered the University of Michigan, where he obtained his B.Sc in 1890 and his doctorate in 1894 under the supervision of A. B. Prescott. His thesis, titled "Trimethylxanthine and Some of its Derivatives," dealt with the derivatization of caffeine and was an extension of Prescott's work.[2] Appointed an instructor in 1893, Gomberg worked at the University of Michigan for the duration of his professional academic career, becoming chair of the Department of Chemistry from 1927 until his retirement in 1936. Dr. Gomberg served as President of the American Chemical Society in 1931. He never married, living with his sister Sophia in Ann Arbor for his adult life.
In 1896–1897 he took a year's leave to work as a postdoctoral researcher with Baeyer and Thiele in Munich and with Victor Meyer in Heidelberg, where he successfully prepared the long-elusive tetraphenylmethane.
During attempts to prepare the even more sterically congested hydrocarbon hexaphenylethane he correctly identified the triphenylmethyl radical, the first persistent radical to be discovered, and is thus known as the founder of radical chemistry. The work was later followed up by Wilhelm Schlenk. Gomberg was a mentor to Werner Emmanuel Bachmann who also carried on his work and together they discovered the Gomberg-Bachmann reaction.[3]
Contents
Synthesis of Tetraphenylmethane
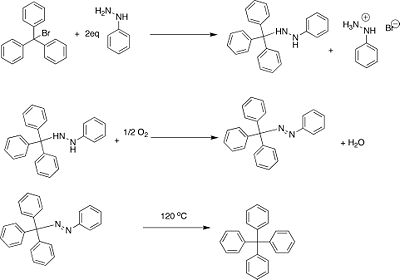
Gomberg was the first to successfully synthesize tetraphenylmethane. This was accomplished by the thermal decomposition of 1-phenyl-2-trityldiazene to the desired product in 2-5% yield.[4][5]
Discovery of Persistent Radicals
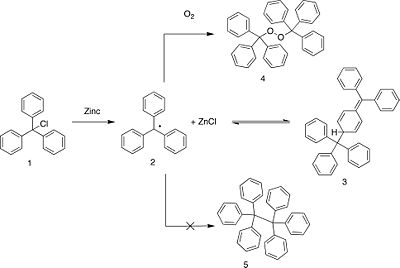
Seeking to prepare hexaphenylethane (5) Gomberg attempted a Wurtz coupling of triphenylchloromethane (1). Elemental analysis of the resultant white crystalline solid however, uncovered discrepancies with the predicted molecular formula:
calculated for (5) found % Carbon 93.83 87.93 % Hydrogen 6.17 6.04 Hypothesizing that (1) had combined with molecular oxygen to form the peroxide (4), Gomberg found that treatment of (1) with sodium peroxide was another means of synthesizing (4).
By performing the reaction of triphenylchloromethane with zinc under an atmosphere of carbon dioxide Gomberg obtained the free radical (2). This compound reacted readily with air, chlorine, bromine and iodine. On the basis of his experimental evidence Gomberg concluded that he had discovered the first instance of a persistent radical and trivalent carbon. This was a controversial conclusion for many years as molecular weight determinations of (2) found a value that was double that of the free radical. Gomberg postulated that some non-tetravalent carbon structure existed in solution because of the observed activity towards oxygen and the halogens.[6] Gomberg and Bachmann later found that treatment of "hexaphenylethane" with magnesium resulted in a Grignard reagent, the first instance of the formation of such a compound from a hydrocarbon.[7] Studies of other triarylmethyl compounds gave results similar to Gomberg's, and it was hypothesized that (2) existed in equilibrium with its dimer hexaphenylethane (5).[8] However this structure was later disproven in favor of the quinoid dimer (3).[9][10][11][12]
At the end of his first report of trivalent carbon "On Trivalent Carbon"reference 5 Gomberg wrote "This work will be continued and I wish to reserve the field for myself." While nineteenth-century chemists respected such claims Gomberg found that the field of chemistry he founded was too rich to reserve for himself.
Legacy
Upon his death in 1947 Moses Gomberg bequeathed his estate to the Chemistry Department of the University of Michigan for the creation of student fellowships. In 2000, the centennial of his paper "Triphenylmethyl, a Case of Trivalent Carbon", a symposium was held in his memory and a plaque was installed in the Chemistry Building at the University of Michigan designating a National Historic Chemical Landmark.
In 1993, the Chemistry Department of the University of Michigan instituted the Moses Gomberg Lecture series to provide assistant professors an opportunity to invite distinguished scientists to the Chemistry department.


External links
References
- ^ C. S. Schoepple and W. E. Bachmann (1947). "Moses Gomberg 1866-1947". Journal of the American Chemical Society 69 (12): 2921–5,. doi:10.1021/ja01204a641.
- ^ Gomberg, American Chemical Journal (1892) 14 611-19.
- ^ M. Gomberg, W. E. Bachmann (1924). "The Synthesis of Biaryl Compounds by Means of the Diazo Reaction". Journal of the American Chemical Society 42 (10): 2339–2343. doi:10.1021/ja01675a026.
- ^ Gomberg, Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (1897) 30 2043
- ^ Gomberg, Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1898, 20 pg 773 DOI 0.1021/ja02072a009
- ^ Gomberg, Journal of the American Chemical Society (1900) 22 pg 757 DOI 10.1021/ja02049a006
- ^ Gomberg, Bachmann Journal of the American Chemical Society (1930) 52 2455
- ^ Gomberg, Journal of the American Chemical Society, (1901) 23 496 DOI 10.1021/ja02033a015
- ^ Gomberg, Journal of the American Chemical Society (1903) 25, pg 1274 DOI 10.1021/ja02014a009
- ^ Gomberg, Journal of Chemical Education (1932) 9, 439
- ^ H. Lankamp, W. Th. Nauta and C. MacLean Tetrahedron Letters (1968) 9 249–254 doi 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)75598-5
- ^ March, Advanced Organic Chemistry 4ed, 1992 pg189
1876-1900 John W. Draper (1876) · J. Lawrence Smith (1877) · Samuel W. Johnson (1878) · T. Sterry Hunt (1879) · Frederick A. Genth (1880) · Charles F. Chandler (1881) · John W. Mallet (1882) · James C. Booth (1883) · Albert B. Prescott (1886) · Charles Anthony Goessmann (1887) · T. Sterry Hunt (1888) · Charles F. Chandler (1889) · Henry B. Nason (1890) · George F. Barker (1891) · George C. Caldwell (1892) · Harvey W. Wiley (1893) · Edgar Fahs Smith (1895) · Charles B. Dudley (1896) · Charles E. Munroe (1898) · Edward W. Morley (1899) · William McMurtrie (1900)
1901-1925 Frank W. Clarke (1901) · Ira Remsen (1902) · John H. Long (1903) · Arthur Amos Noyes (1904) · Francis P. Venable (1905) · William F. Hillebrand (1906) · Marston T. Bogert (1907) · Willis R. Whitney (1909) · Wilder D. Bancroft (1910) · Alexander Smith (1911) · Arthur D. Little (1912) · Theodore W. Richards (1914) · Charles H. Herty (1915) · Julius Stieglitz (1917) · William H. Nichols (1918) · William A. Noyes (1920) · Edgar Fahs Smith (1921) · Edward C. Franklin (1923) · Leo H. Baekeland (1924) · James F. Norris (1925)
1926-1950 George D. Rosengarten (1927) · Samuel W. Parr (1928) · Irving Langmuir (1929) · William McPherson (1930) · Moses Gomberg (1931) · L.V. Redman (1932) · Arthur B. Lamb (1933) · Charles L. Reese (1934) · Roger Adams (1935) · Edward Bartow (1936) · Edward R. Weidlein (1937) · Frank C. Whitmore (1938) · Charles A. Kraus (1939) · Samuel C. Lind (1940) · William Lloyd Evans (1941) · Harry N. Holmes (1942) · Per K. Frolich (1943) · Thomas Midgley, Jr. (1944) · Carl S. Marvel (1945) · Bradley Dewey (1946) · W. Albert Noyes, Jr. (1947) · Charles A. Thomas (1948) · Linus Pauling (1949) · Ernest H. Volwiler (1950)
1951-1975 N. Howell Funnan (1951) · Edgar C. Britton (1952) · Farrington Daniels (1953) · Harry L. Fisher (1954) · Joel H. Hildebrand (1955) · John C. Warner (1956) · Roger J. Williams (1957) · Clifford F. Rassweiler (1958) · John C. Bailar, Jr. (1959) · Albert L. Elder (1960) · Arthur C. Cope (1961) · Karl Folkers (1962) · Henry Eyring (1963) · Maurice H. Arveson (1964) · Charles C. Price (1965) · William J. Sparks (1966) · Charles G. Overberger (1967) · Robert W. Cairns (1968) · Wallace R. Brode (1969) · Byron Riegel (1970) · Melvin Calvin (1971) · Max Tishler (1972) · Alan C. Nixon (1973) · Bernard S. Friedman (1974) · William J. Bailey (1975)
1976-2000 Glenn T. Seaborg (1976) · Henry A. Hill (1977) · Anna J. Harrison (1978) · Gardner W. Stacy (1979) · James D. D'Ianni (1980) · Albert C. Zettlemoyer (1981) · Robert W. Parry (1982) · Fred Basolo (1983) · Warren D. Niederhauser (1984) · Ellis K. Fields (1985) · George C. Pimentel (1986) · Mary L. Good (1987) · Gordon L. Nelson (1988) · Clayton F. Callis (1989) · Paul G. Gassman (1990) · S. Allen Heininger (1991) · Ernest L. Eliel (1992) · Helen M. Free (1993) · Ned D. Heindel (1994) · Brian M. Rushton (1995) · Ronald Breslow (1996) · Paul S. Anderson (1997) · Paul H.L. Walter (1998) · Edel Wasserman (1999) · Daryle H. Busch (2000)
2001-present Attila E. Pavlath (2001) · Eli M. Pearce (2002) · Elsa Reichmanis (2003) · Charles P. Casey (2004) · William F. Carroll, Jr. (2005) · Elizabeth Ann Nalley (2006) · Catherine T. Hunt (2007) · Bruce E. Bursten (2008) · Thomas H. Lane (2009) · Joseph Francisco (2010) · Nancy B. Jackson (2011)
Categories:- 1866 births
- 1947 deaths
- University of Michigan faculty
- University of Michigan alumni
- Chemists
- Russian Jews
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.