- DPPH
-
DPPH  di(phenyl)-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)iminoazaniumOther names2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl
di(phenyl)-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)iminoazaniumOther names2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl
1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical
2,2-diphenyl-1-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)hydrazyl
DiphenylpicrylhydrazylIdentifiers Abbreviations DPPH CAS number 1898-66-4 
PubChem 74358 ChemSpider 2016757 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - c1ccc(cc1)N(c2ccccc2)[N]c3c(cc(cc3[N+](=O)[O-])[N+](=O)[O-])[N+](=O)[O-]
- InChI=1S/C18H12N5O6/c24-21(25)15-11-16(22(26)27)18(17(12-15)23(28)29)19-20(13-7-3-1-4-8-13)14-9-5-2-6-10-14/h1-12H

Key: HHEAADYXPMHMCT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
InChI=1/C18H13N5O6/c24-21(25)15-11-16(22(26)27)18(17(12-15)23(28)29)19-20(13-7-3-1-4-8-13)14-9-5-2-6-10-14/h1-12,19H
Key: WCBPJVKVIMMEQC-UHFFFAOYAG
InChI=1/C18H12N5O6/c24-21(25)15-11-16(22(26)27)18(17(12-15)23(28)29)19-20(13-7-3-1-4-8-13)14-9-5-2-6-10-14/h1-12H
Key: HHEAADYXPMHMCT-UHFFFAOYAG
Properties Molecular formula C18H12N5O6 Molar mass 394.32 g/mol Appearance Black to green powder, purple in solution Density 1.4 g/cm3 Melting point 135 °C, 408 K, 275 °F (decomposes)
Solubility in water insoluble Hazards MSDS MSDS NFPA 704  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references DPPH is a common abbreviation for an organic chemical compound 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl. It is a dark-colored crystalline powder composed of stable free-radical molecules. DPPH has two major applications, both in laboratory research: one is a monitor of chemical reactions involving radicals and another is a standard of the position and intensity of electron paramagnetic resonance signals.
Properties and applications
DPPH has several crystalline forms which differ by the lattice symmetry and melting point (m.p.). The commercial powder is a mixture of phases which melts at ~130 °C. DPPH-I (m.p. 106 °C) is orthorhombic, DPPH-II (m.p. 137 °C) is amorphous and DPPH-III (m.p. 128–129 °C) is triclinic.[1]
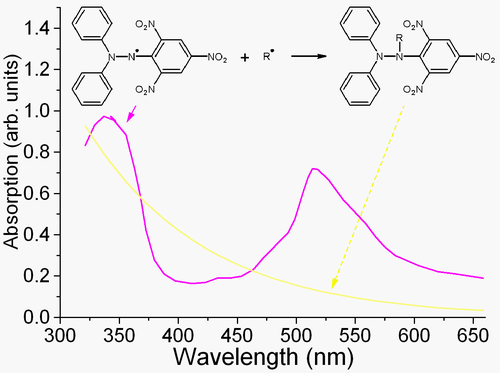
DPPH is a well-known radical and a trap ("scavenger") for other radicals. Therefore, rate reduction of a chemical reaction upon addition of DPPH is used as an indicator of the radical nature of that reaction. Because of a strong absorption band centered at about 520 nm, the DPPH radical has a deep violet color in solution, and it becomes colorless or pale yellow when neutralized. This property allows visual monitoring of the reaction, and the number of initial radicals can be counted from the change in the optical absorption at 520 nm or in the EPR signal of the DPPH.[2]
Because DPPH is efficient radical trap, it is also a strong inhibitor of radical-mediated polymerization.[3]
As a stable and well-characterized solid radical source, DPPH is the traditional and perhaps the most popular standard of the position (g-marker) and intensity of electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) signals – the number of radicals for a freshly prepared sample can be determined by weighing and the EPR splitting factor for DPPH is calibrated at g = 2.0036. DPPH signal is convenient by that it is normally concentrated in a single line, whose intensity increases linearly with the square root of microwave power in the wider power range. The dilute nature of the DPPH radicals (one unpaired spin per 41 atoms) results in a relatively small linewidth (1.5–4.7 Gauss). The linewidth may however increase if solvent molecules remain in the crystal and if measurements are performed with a high-frequency EPR setup (~200 GHz), where the slight g-anisotropy of DPPH becomes detectable.[4][5]
Whereas DPPH is normally a paramagnetic solid, it transforms into an antiferromagnetic state upon cooling to very low temperatures of the order 0.3 K. This phenomenon was first reported by Alexander Prokhorov in 1963.[6][7][8][9]
References
- ^ Kiers, C. T.; De Boer, J. L.; Olthof, R.; Spek, A. L. (1976). "The crystal structure of a 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) modification". Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry 32 (8): 2297. doi:10.1107/S0567740876007632.
- ^ Mark S. M. Alger (1997). Polymer science dictionary. Springer. p. 152. ISBN 0412608707. http://books.google.com/?id=OSAaRwBXGuEC&pg=PA152.
- ^ Cowie, J. M. G.; Arrighi, Valeria (2008). Polymers: Chemistry and Physics of Modern Materials (3rd ed.). Scotland: CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-9813-4.
- ^ M.J. Davies (2000). Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 178. ISBN 0854043101. http://books.google.com/?id=ywjuZo9UackC&pg=PA178.
- ^ Charles P. Poole (1996). Electron spin resonance: a comprehensive treatise on experimental techniques. Courier Dover Publications. p. 443. ISBN 0486694445. http://books.google.com/?id=P-4PIoi7Z7IC&pg=PA443.
- ^ A. M. Prokhorov and V.B. Fedorov, Soviet Phys. JETP 16 (1963) 1489.
- ^ Teruaki Fujito (1981). "Magnetic Interaction in Solvent-free DPPH and DPPH–Solvent Complexes". Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan 54 (10): 3110. http://www.journalarchive.jst.go.jp/english/jnlabstract_en.php?cdjournal=bcsj1926&cdvol=54&noissue=10&startpage=3110.
- ^ Stig Lundqvist (1998). "A. M. Prokhorov". Nobel lectures in physics, 1963-1970. World Scientific. p. 118. ISBN 981023404X. http://books.google.com/?id=uywFzcv3Tv8C&pg=PA118.
- ^ Aleksandr M. Prokhorov, The Nobel Prize in Physics 1964
Categories:- Free radicals
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.