- DART (satellite)
-
DART, or Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous Technology, is a NASA sponsored project. The goal was to develop and demonstrate an automated navigation and rendezvous capability in a NASA spacecraft. Currently, only the Russian Space Agency, JAXA and ESA have autonomous space craft navigation. Orbital Sciences Corporation (OSC) was the prime contractor for construction, launch and operation of the DART vehicle with a project cost of $95 million dollars. The contract was awarded in June 2001 and the launch originally scheduled for October 25, 2004, but this was postponed for launch loads analysis and instead performed on April 15, 2005.
Contents
Mission
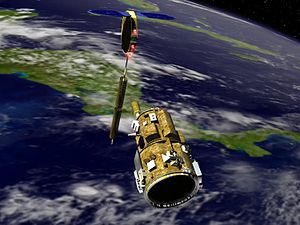
DART was launched on a Pegasus rocket into a polar circular parking orbit of 760 × 770 km (472 × 478 mi) and has International Designator 2005-014-A. The craft is 2 by 1 metres (7 by 3 feet) and weighs 360 kg (790 lb). The maneuvering system comprises 16 nitrogen-fueled thrusters with three hydrazine-fueled thrusters and a reaction control system including six nitrogen-fueled thrusters from the Pegasus fourth stage, which forms an integral part of the craft. The target is an OSC MUBLCOM (Multiple-Path Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications) prototype communications relay satellite weighing around 49 kg (108 lb) launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base on 18 May 1999 with International Designator 1999-026-B.
After launch, DART successfully achieved orbit and within hours made a rendezvous with the target satellite. The automated systems aboard DART successfully acquired the target and began autonomously approaching it. During proximity operations, multiple malfunctions in navigation, propellant management and collision avoidance programming led to a soft collision with the target and premature departure and retirement of the DART spacecraft.[citation needed]
DART had no capability for interactive piloting from the ground or for uploading new programming after launch, thus all on-orbit operations were directed by DART itself based upon pre-programmed criteria.[citation needed]
The initial mission was to occur over about 24 hours but its premature failure occurred after only about 11 hours.[citation needed]
Objectives
Automatic orbital transfer maneuvers
The craft autonomously navigated via a series of orbit transfer maneuvers to reach the target satellite. No navigational information was relayed to the vehicle after launch; it navigated autonomously and with GPS.
Proximity operations with AVGS
Once the spacecraft had navigated to the target satellite, it was to have performed a series of proximity maneuvers. The maneuvers would have demonstrated the capabilities of the AVGS (Advanced Video Guidance Sensor). It was planned to demonstrate station keeping, docking axis approach, circumnavigation, and a collision avoidance maneuver. DART would have then departed the vicinity and retired to a final orbit. The entire sequence was to have been accomplished under autonomous control.
Additional demonstrations
- Safe operations
- Validate ground test results of the AVGS and proximity-operations algorithms
- Provide hardware capabilities for future missions by validating the AVGS in the space environment
Mishap investigation board
NASA convened a mishap investigation board to determine the reason for the DART spacecraft anomaly. First reports pointed to the spacecraft running out of fuel before concluding its mission. [1]
On April 14, 2006 NASA announced that they would not release the investigation's report, citing that the report includes details protected by the International Traffic in Arms Regulations.[citation needed]
On May 15, 2006 NASA released a public summary of the DART mishap investigation board report (NASA press release). NASA revealed that a critical navigation failure occurring when the DART and MUBLCOM spacecraft were about 200 meters apart precluded the full activation of the AVGS, and allowed DART to approach MUBLCOM without accurate ranging information. A later failure of the collision avoidance system, which was relying upon inaccurate position and velocity information, allowed DART to ultimately collide with MUBLCOM at a relative speed of approximately 1.5 meters per second. Both spacecraft survived the collision without apparent damage. Throughout the autonomous proximity operations, DART used its limited propellant faster than anticipated, which caused "a premature end to the mission" 3 minutes 49 seconds after the collision. DART initiated its retirement programming, removed itself from the vicinity of MUBLCOM, and prepared for deorbit. After the collision, MUBLCOM "regained its operational status after an automatic system reset".[citation needed]
The DART Mishap Investigation Board determined that only 11 of the 27 defined mission objectives were partially or fully met, all of which related to the launch, early orbit, rendezvous, departure, and retirement phases. None of the 14 objectives related to the proximity operations phase were met.[citation needed]
Current status
As of May 2006, DART remains in its polar retirement orbit of about 390 × 470 km (240 × 290 mi), and MUBLCOM remains in a polar orbit of 740 × 750 km (460 × 470 mi).[citation needed]
See also
- Attitude control
- Orbital Express
- Spacecraft
References
External links
- DART at Marshall Space Flight Center
- NASA Press release about the DART mishap 16 April 2005
- Mishap overview and description of the cause 15 May 2006
- DART Mishap Investigation Board Final Report January 4, 2007
← 2004 · Orbital launches in 2005 · 2006 → Deep Impact | Kosmos 2414 · Universitetsky-Tatyana | AMC-12 | USA-181 | XTAR-EUR · Maqsat-B2 (Sloshsat-FLEVO) | Himawari 6 | Progress M-52 (TNS-0) | XM-3 | Inmarsat-4 F1 | Ekspress AM-2 | USA-165 | Apstar VI | Soyuz TMA-6 | DART | Spaceway 1 | USA-182 | Cartosat-1 · HAMSAT | NOAA-18 | DirecTV-8 | Foton-M2 | Progress M-53 | Molniya-3K #12 | Cosmos 1 | Intelsat Americas 8 | Ekspress AM-3 | Shijian 7 | Suzaku | STS-114 (Raffaello MPLM) | FSW-21 | Thaicom-4 | MRO | Kirari · Reimei | Monitor-E | FSW-22 | Kosmos 2415 | Progress M-54 (RadioSkaf) | Anik F1R | USA-183 | Soyuz TMA-7 | CryoSat | Shenzhou 6 | Syracuse 3A · Galaxy 15 | USA-186 | Beijing-1 · TopSat · Sina-1 · SSETI Express (CubeSat XI-V · UWE-1 · nCUBE-2) · Mozhaets-5 · Rubin-5 | Inmarsat-4 F2 | Venus Express | Spaceway-2 · Telkom-2 | Gonets-D1M #13 · Kosmos 2416 | Meteosat 9 · INSAT-4A | Kosmos 2417 · Kosmos 2418 · Kosmos 2419 | GIOVE-A | AMC-23Payloads are separated by bullets ( · ), launches by pipes ( | ). Manned flights are indicated in bold text. Uncatalogued launch failures are listed in italics. Payloads deployed from other spacecraft are denoted in brackets. Categories:- NASA probes
- Artificial satellites orbiting Earth
- 2005 in spaceflight
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.