- Chicomuceltec language
-
Chicomuceltec Chikomuselteko Pronunciation [tʃikomuselˈteko] Spoken in Mexico (Chiapas state); Guatemala (Huehuetenango Dept.) Region several communities in the Fronteriza and Sierra demographic regions of the southeastern Chiapas highlands; isolated villages across the Guatemalan border Extinct late 20th century Language family Mayan- Huastecan
- Chicomuceltec
Language codes ISO 639-3 cob Chicomuceltec (also Chikomuselteko or Chicomucelteco; archaically, Cotoque) is a Mayan language formerly spoken in the region defined by the municipios of Chicomuselo, Mazapa de Madero, and Amatenango de la Frontera in Chiapas, Mexico, as well as some nearby areas of Guatemala. By the 1970s-80s it had become extinct, with recent reports in Mayanist literature finding that there are no living native speakers.[1] Communities of contemporary Chicomucelteco descendants, numbering approximately 1500 persons in Mexico and 100 in Guatemala[2] are Spanish-speakers.
Chicomuceltec was formerly sometimes called Cakchiquel Mam, although it is only distantly related to the Cakchiquel or Mam, being much closer to Wastek (Huastec).
Contents
History and genealogy
The Chicomuceltec language was first documented in modern linguistic literature as a distinct language in the late 19th century, where it appeared in an account published by linguist Karl Sapper of his travels in northern Mesoamerica 1888–95.[3]
Chicomuceltec's relationship with Wastek was established in the late 1930s (Kroeber 1939), which concluded via word-list comparisons with other Mayan languages that it bore a higher degree of affinity with Wastek than other Mayan language branches.[4]
Historical documentation
A two-page document dated to 1775 which was retrieved from the Bibliothèque nationale de France in Paris is the oldest-known testament of the Chicomuceltec language. Taking the form of a Roman Catholic confession, the manuscript contains eight sentences written in Chicomuceltec. It also mentions that the language was then referred to as "Cotoque".[5]
Geographical distribution
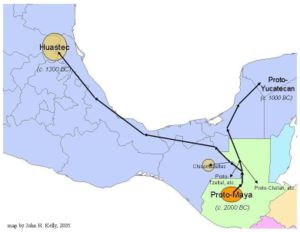 Map showing one migratory proposal for the early split of Wastek and Chicomuceltec from the Proto-Mayan "homeland".
Map showing one migratory proposal for the early split of Wastek and Chicomuceltec from the Proto-Mayan "homeland".
The geographical distribution of Wastek and Chicomuceltec in relation to the rest of the Mayan languages —with Wastek centered on the northern Gulf Coast region away from the others lying south and east of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec— led Kroeber to also propose that Chicomuceltec was either a remnant population left behind after the Huastec people's migration north from the Chiapas highlands region, or alternatively represented a return of a Huastec subgroup to their earlier homelands.[6]
Decline and extinction
By the early 20th century it was clear the language was in decline, and when in 1926 Franz Termer visited the community of Chicomucelo, he reported finding only three individuals (all over 60 years of age) who could speak Chicomuceltec, out of a township of approximately 2,500. The Chicomuceltec speakers themselves conducted their day-to-day conversations in Spanish.[7]
Notes
- ^ See Campbell and Canger (1978); Ethnologue entry on "Chicomuceltec" (Gordon 2005).
- ^ See Gordon (2005) for population estimates, which draw on sources collected in the early 1980s.
- ^ The work in question is Sapper 1897, with later expansions to the material appearing in Sapper 1912; as cited in Dienhart (1997), "Data sources listed by author".
- ^ See précis of Kroeber 1939, appearing in Fernández de Miranda (1968), pp.74–75.
- ^ As described by Dienhart (1997), the manuscript was reproduced in Zimmermann 1955 (whose research it was which uncovered the document), accompanied by his linguistic analysis of its contents.
- ^ Fernández de Miranda, loc. cit.
- ^ Termer (1930), as annotated in Dienhart, op. cit.
References
-
- Brown, Cecil H.; and Søren Wichmann (2004). "Proto-Mayan Syllable Nuclei". International Journal of American Linguistics (Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press) 70 (2): 128–186. doi:10.1086/424553. ISSN 0020-7071. OCLC 98981737.
- Campbell, Lyle; and Una Canger (1978). "Chicomuceltec's last throes". International Journal of American Linguistics (Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, in cooperation with the Conference on American Indian Languages) 44 (3): 228–230. doi:10.1086/465548. ISSN 0020-7071. OCLC 1753556.
- Dienhart, John M. (1997). "The Mayan Languages- A Comparative Vocabulary" (electronic version). Odense University. http://www.hum.sdu.dk/projekter/maya/mayainfo.html. Retrieved 2006-12-15.
- Fernández de Miranda, María Teresa (1968). "Inventory of Classificatory Materials". In Norman A. McQuown (Volume ed.). Handbook of Middle American Indians, Vol. 5: Linguistics. R. Wauchope (General Editor). Austin: University of Texas Press. pp. 63–78. ISBN 0-292-73665-7. OCLC 277126.
- Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (Ed.) (2005). "Chicomuceltec" (online version). Ethnologue: Languages of the World (Fifteenth ed.). Dallas, TX: SIL International. ISBN 1-55671-159-X. OCLC 60338097. http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=cob. Retrieved 2006-12-15.
- Kaufman, Terrence (2001) (PDF). The history of the Nawa language group from the earliest times to the sixteenth century: some initial results. Revised March 2001. Project for the Documentation of the Languages of Mesoamerica. http://www.albany.edu/anthro/maldp/Nawa.pdf. Retrieved 2008-04-03.
- Kroeber, Alfred L. (1939). "The historical position of Chicomuceltec in Mayan". International Journal of American Linguistics (Baltimore, MD: Published at Waverly Press by Indiana University) 10 (4): 159–160. doi:10.1086/463837. ISSN 0020-7071. OCLC 1753556.
- Miles, S. W. (1971). "Summary of Preconquest Ethnology of the Guatemala-Chiapas Highlands and Pacific Slopes". In Gordon R. Willey (Volume ed.). Handbook of Middle American Indians, Vol. 2: Archaeology of Southern Mesoamerica, Part I. R. Wauchope (General Editor). Austin: University of Texas Press. pp. 275–287. ISBN 0-292-73260-0. OCLC 277126.
- Sapper, Karl (1897). Das nördliche Mittel-Amerika nebst einem Ausflug nach dem Hochland von Anahuac. Braunschweig, Germany: Friedrich Vieweg und Sohn. OCLC 70337620. (German)
- Sapper, Karl (1912). "Über einige Sprachen von Südchiapas". Proceedings of the Seventeenth International Congress of Americanists (1910). pp. 295–320. (German)
- Termer, Franz (1930). "Über die Mayasprache von Chicomucelo". Proceedings of the Twenty-third International Congress of Americanists (New York, 1928). pp. 926–936. (German)
- Wichmann, Søren; and Cecil H. Brown (2002). "Contácto Lingüístico dentro del área maya: los casos del ixhil, el q'eqchii' y del chikomuselteko" (PDF online reprint). Pueblos y fronteras (San Cristóbal de las Casas, Chiapas, Mex.: Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Instituto de Investigaciones Antropológicas, Programa de Investigaciones Multidisciplinarias sobre Mesoamérica y el Sureste) 4: 133–167. ISSN 1870-4115. OCLC 164600251. http://www.pueblosyfronteras.unam.mx/a02n4/pdfs/7_contacto.pdf. (Spanish)
- Zimmermann, Günther (1955). "Cotoque. Die Maya-Sprache von Chicomucelo". Zeitschrift für Ethnologie (Braunschweig, Germany: Deutschen Gesellschaft für Völkerkunde; Berliner Gesellschaft für Anthropologie, Ethnologie und Urgeschichte) 80: 59–87. ISSN 0044-2666. OCLC 1770462. (German)
Categories:- Agglutinative languages
- Indigenous languages of Mexico
- Mayan languages
- Mesoamerican languages
- Extinct languages of North America
- Huastecan
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
