- Chaplain–Medic massacre
-
Chaplain–Medic massacre
Herman G. Felhoelter, the US Army chaplain who was killed in the massacreLocation Tunam, South Korea Date July 16, 1950
2130 (KST)Target US Army prisoners of war Attack type Mass execution Death(s) 30 injured US soldiers and one chaplain executed Injured One US soldier wounded Perpetrator(s) North Korean Army soldiers The Chaplain–Medic massacre was a war crime that took place in the Korean War on July 16, 1950, on a mountain above the village of Tunam, South Korea. Thirty unarmed, critically wounded US Army soldiers and an unarmed chaplain were killed by members of the North Korean People's Army during the Battle of Taejon.
Operating at the Kum River during the Battle of Taejon, troops of the US Army's 19th Infantry Regiment, 24th Infantry Division, were cut off from resupply by a roadblock established by North Korean troops of the NK 3rd Division. The roadblock proved difficult to break, and forced US troops to move through nearby mountains to evacuate their wounded.
Thirty critically wounded US troops were stranded at the top of a mountain. Attended to by only two noncombatants, a chaplain and a medic, the wounded were discovered by a North Korean patrol. Though the medic was able to escape, the North Koreans executed the unarmed chaplain as he prayed over the wounded, then killed the rest of them.
The massacre was one of several incidents that led US commanders to establish a commission in July to look into war crimes during the war. The same month, the North Korean commanders, concerned about the way their soldiers were treating prisoners of war, laid out stricter guidelines for handling enemy captives.
Contents
Background
North Korea offensive
- Pokpoong (Ongjin
- Kaesong-Munsan
- Gorangpo
- Dongducheon
- Pocheon
- Chuncheon
- Gangneung
- Gimpo
- Okgye
- Korea Strait
- Uijeongbu
- Naechon-Taereung
- Changdong
- Bongilcheon
- Miari
- Hongcheon
- Han River
- Oryudong
- Sinsadong-Gwacheon
- Uljin-Pyeonghae
- Siheung-Anyang-Suwon)
- Jumunjin
UN intervention
- Air campaign
- Suwon Airfield
- Osan
- Pyongtaek
- Chonan
- Chochiwon
- Donglakri
- Danyang
- Jincheon
- Yihwaryeong
- Taejon
- Sangju
- Yeongdeok
- Yongdong
- Hwanggan
- Hwaryeongjang
- Younggang
- Andong
- Hadong
- The Notch
- Pusan Perimeter
- Haeju
- Inchon
- 2nd Seoul
- Hill 282
- Kaesong
- Operation Wonsan
- Wonsan
- Hungham
- Yongju
- Yeonghung
- Kumchon
- Pyongyang
- Huichon
- Chongju
- Chosan
Chinese intervention
- Onjong
- Unsan
- Pakchon
- Ch'ongch'on River
- Wawon
- Chosin Reservoir
- Task Force Faith
- 3rd Seoul
- 1st and 2nd Wonju
- Thunderbolt
- Twin Tunnels
- Roundup
- Hoengsong
- Chipyong-ni
- 3rd Wonju
- Killer
- 4th Seoul
- Courageous
- Tomahawk
- Rugged and Dauntless
- 5th Seoul (Imjin River
- Yultong
- Kapyong)
- Soyang River
Stalemate
- Bloody Ridge
- Han River
- Heartbreak Ridge
- Maryang San
- Sunchon
- Hill Eerie
- Sui-ho Dam
- Old Baldy
- Blaze
- Hudson Harbor
- White Horse
- Triangle Hill
- Jackson Heights
- The Hook
- Pork Chop Hill
- Outpost Harry
- Kumsong
- Samichon River
Post Armistice
- Korean DMZ Conflict (1966–1969)
- Blue House Raid
- Pueblo incident
- EC-121 shootdown
- Major Henderson incident
- Axe murder incident
- Rangoon bombing
- KAL Flight 858
- Gangneung
- Yosu
- 1st Yeonpyeong
- 2nd Yeonpyeong
- Daecheong
- Cheonan incident
- 3rd Yeonpyeong
Outbreak of war
Following the invasion of the Republic of Korea (South Korea) by its northern neighbor, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea), the United Nations committed troops to the conflict to prevent the collapse of the South Korean state. Problematically, the number of US forces in the Far East available to support this effort had been steadily decreasing since the end of World War II, five years earlier. The closest US division, the 24th Infantry Division of the Eighth United States Army, headquartered in Japan,[1] was understrength, and most of its equipment was antiquated due to defense cutbacks enacted in the first Truman administration.[2][3] Nevertheless, the 24th Infantry Division was the first US unit sent into Korea to absorb the initial "shock" of North Korean advances and to buy time for the deployment of additional forces, such as the 7th Infantry Division, 25th Infantry Division, 1st Cavalry Division, and other Eighth Army supporting units.[4]
Delaying action
Advance elements of the 24th Infantry Division were badly defeated in the Battle of Osan on July 5, during the first battle between American and North Korean forces.[5] The force at the battle, Task Force Smith, retreated from Osan, and US forces were again defeated in the Battle of Pyongtaek.[6] For over a week after the defeat of Task Force Smith, 24th Infantry Division soldiers were repeatedly defeated and forced south by the North Korean force's superior numbers and equipment.[6][7] The regiments of the 24th Infantry Division were systematically pushed south at and around Chochiwon, Chonan, Pyongtaek, Hadong, and Yechon.[7] These American soldiers, most of whom had experienced only occupation duty in Japan and no actual combat, were unprepared compared to the more disciplined North Korean units.[8][9]
On July 12, the division's commander, Major General William F. Dean, ordered the division's 19th, 21st, and 34th Infantry Regiments to cross the Kum River, destroying all bridges behind them, and to establish defensive positions around Taejon. Taejon was a major South Korean city 100 miles (160 km) south of Seoul and 130 miles (210 km) northwest of Pusan, and was the site of the 24th Infantry Division's headquarters.[10] Dean formed a line with the 34th Infantry and 19th Infantry facing east, and held the heavily battered 21st Infantry in reserve to the southeast.[11] The Kum River wrapped north and west around the city, providing a defensive line 10 to 15 miles from the outskirts of Taejon, which is protected on the south by the Sobaek Mountains. With major railroad lines and roads emanating in all directions, Taejon stood as a major transportation hub between Seoul and Taegu, giving it great strategic value for both the American and North Korean forces.[12] Taejon had to be held to stop the North Korean forces from converging on the unfinished defensive lines around Pusan.[13]
Massacre
North Korean attack
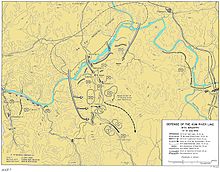
Main article: Battle of TaejonFollowing an initial penetration to the north, the retreating 34th Infantry moved south to Nonsan.[14] On July 15, the 19th Infantry moved its 2nd Battalion to fill some of the gaps left by the 34th.[15] There, it was reinforced by troops from the Republic of Korea Army.[14][15] The combined forces observed a large build-up of North Korean troops on the west side of the river. At 03:00 on July 16, the North Koreans launched a massive barrage of tank, artillery and mortar fire on the 19th Infantry positions and North Korean troops began to cross the river in boats.[14] The North Korean forces gathered on the west bank and assaulted the positions of the 1st Battalion's C and E Companies, followed by a second landing against B Company.[16] North Korean forces pushed against the entire battalion, threatening to overwhelm it. The regimental commander ordered all support troops and officers to the line and they were able to repulse the assault. However, in the melee, North Korean forces infiltrated their rear elements, attacking the reserve forces and blocking supply lines.[17] Stretched thin, the 19th Infantry was unable to hold the line at the Kum River and simultaneously repel the North Korean forces.[18]
Roadblock
North Korean troops promptly set up a roadblock directly behind the 19th Infantry's line in its main route of supply along the road near the village of Tunam, just south of Yusong on Taejon's eastern outskirts.[19] The roadblock quickly became a serious problem for US forces trying to move ammunition and wounded to and from the Kum River line.[20] Around 13:00 on July 16 the 19th Infantry Regimental commander contacted Dean, who ordered him to break the roadblock.[21] However, North Korean troops had set up at least six machine-gun nests above the road at Tunam, and repeated attacks against it were unable to drive the North Korean troops away.[21][22]
The roadblock was preventing evacuation of the wounded.[23] Troops attempted to drive wounded in jeeps through the roadblock, but this exposed them to machine-gun fire. By 16:00 supply columns were also piling up at the block, unable to proceed as armor and airstrikes attempted to dislodge the North Koreans.[23][24] Five hundred men from the regiment were gathered waiting to break the roadblock while heavy armor units from Taejon moved against it from the other side.[25] During this time, US troops from the 19th Infantry, desperate to move around the roadblock to obtain supplies and care for wounded, began moving through the surrounding hills. One tank was able to make it through the roadblock to evacuate the 19th Infantry's wounded commander, but by 19:00 commanders ordered the regiment to move its wounded along the ridges to the east of the roadblock.[26][27]
Execution
At 21:00, about 100 men of the 19th Infantry moved into the hills to the east of the town.[6][28] They carried with them about 30 wounded, including several litter-bound patients too seriously hurt to walk. Some of the group of 100 were ordered to carry these men, but many of them separated from the group in the mountains.[29] By the time they reached the top of the mountain, officers decided some of the seriously wounded could not be carried any further, as their carriers were exhausted. The regimental medical officer, Captain Linton J. Buttrey, and Chaplain Herman G. Felhoelter[30] remained behind with the wounded, intending to move them when another group of troops came through who could carry them.[28][29] Buttrey wore a Red Cross brassard identifying him as a medic, while Felhoelter wore a large white Latin cross brassard, identifying him as a military chaplain in the US Army Chaplain Corps. The two who remained and the wounded were noncombatants under international law, as they carried no weapons.[31]
Soon after, Buttrey and Felhoelter heard a North Korean patrol approaching, a group of men from the North Korean 3rd Division which had infiltrated the US lines.[28] Felhoelter told Buttrey to escape, and although Buttrey was shot and severely wounded in the ankle by North Korean fire while running, he was able to get away.[29][31] Felhoelter then began administering last rites and extreme unction to the wounded as they lay on their litters. From this point, observers from the 19th Infantry's regimental Headquarters and Headquarters Company watched through binoculars from a distance as a patrol of young-looking and possibly untrained North Korean troops approached the site of the wounded.[28][29] The troops were armed with Soviet-made rifles and PPSh-41 "burp guns". As Felhoelter knelt to pray over the wounded US soldiers, the North Korean troops shot him in the head and back.[29][31] They then proceeded to shoot and kill all of the 30 critically wounded soldiers with their automatic weapons before withdrawing into the wilderness.[28][29][31][32]
Aftermath
American troops were able to recover only three of the victims of the massacre due to the chaos of the battle and subsequent American withdrawal, and were unable to capture any North Korean troops who participated in the massacre. For his actions in volunteering to stay behind with the wounded, Herman G. Felhoelter was awarded the Distinguished Service Cross, the second highest decoration for valor awarded by the US military, posthumously. He was the first chaplain of the war to receive an award for valor.[32] He received a brief obituary in Time Magazine in December 1952. Felhoelter was the first of twelve chaplains killed or missing at that point in the war, including Emil J. Kapaun, the second chaplain of the war to be awarded a Distinguished Service Cross.[33]
US response
The incident would be one of the first of a series of atrocities the US forces accused North Korean soldiers of committing. After the Chaplain–Medic, Hill 303 and Bloody Gulch massacres, US commanders established a commission on July 27 to investigate allegations of war crimes and collect evidence.[34][35]
In late 1953, the United States Senate Committee on Government Operations, led by Joseph McCarthy, conducted an investigation of up to 1,800 reported incidents of war crimes allegedly committed throughout the Korean War. The Chaplain–Medic massacre was one of the first to be investigated, and it was here that the incident got its name.[36] Buttrey, the lone survivor of the executions, was called to testify before the committee, and the US Government concluded that the North Korean army violated the terms of the Geneva Convention, and condemned its actions.[37]
In 1981, the United States erected a series of monuments in Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington, Virginia, listing the names of chaplains killed in various wars including World War II, the Korean War and the Vietnam War. Felhoelter's name was among those engraved in the memorial.[38]
North Korean response
Generally subsequent research has found the North Korean command did not directly order its troops to mistreat prisoners[39] or unarmed wounded during the early phase of the war.[34] The Chaplain–Medic massacre and similar atrocities are believed to have been conducted by "uncontrolled small units, by vindictive individuals, or because of unfavorable and increasingly desperate situations confronting the captors."[39] The more North Korean troops suffered from worsening conditions on the front lines, the more they mistreated American wounded and prisoners.[40] T. R. Fehrenbach, a military historian, wrote in his analysis of the event that North Korean troops committing these acts were probably accustomed to torture and execution of prisoners due to decades of rule by oppressive armies of the Empire of Japan up until World War II.[41]
A July 28, 1950, order by General Lee Yong Ho, commander of the North Korean 3rd Division, was intercepted by UN intelligence. The document was signed by Kim Chaek, Commander-in-Chief,[39] and Choi Yong-kun, commander of the Advanced General Headquarters of the North Korean Army, and stated that killing prisoners of war was "strictly prohibited." Lee directed individual units' Cultural Sections to inform the division's troops of the rule. The more high-profile Hill 303 massacre the next month prompted North Korean division commanders to issue sterner orders on the treatment of prisoners of war.[39]
See also
References
Citations
- ^ Appleman 1998, p. 59
- ^ Varhola 2000, p. 3
- ^ Appleman 1998, p. 60
- ^ Alexander 2003, p. 52
- ^ Catchpole 2001, p. 15
- ^ a b c Alexander 2003, p. 90
- ^ a b Varhola 2000, p. 4
- ^ Fehrenbach 2001, p. 60
- ^ Alexander 2003, p. 63
- ^ Summers 2001, p. 266
- ^ Fehrenbach 2001, p. 88
- ^ Alexander 2003, p. 121
- ^ Fehrenbach 2001, p. 92
- ^ a b c Appleman 1998, p. 135
- ^ a b Millett 2010, p. 187
- ^ Fehrenbach 2001, p. 93
- ^ Alexander 2003, p. 84
- ^ Fehrenbach 2001, p. 94
- ^ Alexander 2003, p. 85
- ^ Appleman 1998, p. 139
- ^ a b Alexander 2003, p. 86
- ^ Appleman 1998, p. 140
- ^ a b Alexander 2003, p. 87
- ^ Appleman 1998, p. 141
- ^ Alexander 2003, p. 88
- ^ Appleman 1998, p. 142
- ^ Alexander 2003, p. 89
- ^ a b c d e Appleman 1998, p. 143
- ^ a b c d e f Alexander 2003, p. 91
- ^ At the following webpage, scroll down to "Captain Herman G. Felhoelter • Korean War • 1914-1950". Centner, Pat. "No Greater Love: A Memorial Day Salute to Military Chaplains". American Family Association. http://afajournal.org/2003/may/503_chaplains_dw.html. Retrieved 2011-11-06. "A Catholic priest from Washington state, Chaplain Herman Felhoelter had been assigned to the U.S. Army’s 19th Infantry Regiment. .... Four days before his death, he had written his mother: 'Don’t worry, Mother. God’s will be done. I feel so good to know the power of your prayers accompanying me. ... I am happy in the thought that I can help some souls who need help. ...'"
- ^ a b c d McCarthy 1954, p. 7
- ^ a b Millett 2010, p. 161
- ^ Religion: Chaplains Courageous, Time Magazine, 1952-12-01, http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,817474,00.html, retrieved 2011-08-28
- ^ a b Fehrenbach 2001, p. 136
- ^ Millett 2010, p. 160
- ^ McCarthy 1954, p. 1
- ^ McCarthy 1954, p. 16
- ^ Chaplain's Hill and Three Monuments, Arlington National Cemetery, 2010, http://www.arlingtoncemetery.mil/VisitorInformation/MonumentMemorials/ChaplainsHill.aspx, retrieved 2011-08-28
- ^ a b c d Appleman 1998, p. 350
- ^ Alexander 2003, p. 144
- ^ Fehrenbach 2001, p. 137
Sources
- Alexander, Bevin (2003), Korea: The First War We Lost, New York City, New York: Hippocrene Books, ISBN 978-0781810197
- Appleman, Roy E. (1998), South to the Naktong, North to the Yalu: United States Army in the Korean War, Washington, D.C.: Department of the Army, ISBN 978-0160019180, http://www.history.army.mil/books/korea/20-2-1/toc.htm
- Catchpole, Brian (2001), The Korean War, London: Robinson Publishing, ISBN 978-1841194134
- Fehrenbach, T.R. (2001), This Kind of War: The Classic Korean War History – Fiftieth Anniversary Edition, Herndon, VA: Potomac Books Inc., ISBN 978-1574883343
- McCarthy, Joseph; Karl E. Mundt, John L. McLellan, Margaret C. Smith, et. al. (1954), Korean War Atrocities Report of the Committee on Government Operations, US Government Printing Office, http://www.loc.gov/rr/frd/Military_Law/pdf/KW-atrocities-Report.pdf, retrieved 2010-07-11
- Millett, Allan R. (2010), The War for Korea, 1950–1951: They Came from the North, Lawrence, KS: University Press of Kansas, ISBN 978-0700617098
- Summers, Harry G. (2001), Korean War Almanac, Bridgewater, NJ: Replica Books, ISBN 978-0735102095
- Varhola, Michael J. (2000), Fire and Ice: The Korean War, 1950–1953, Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press, ISBN 978-1882810444
Categories:- 1950 in South Korea
- Daejeon
- Korean War crimes
- Korean War prisoners of war
- Massacres committed by North Korea
- Massacres in South Korea
- Military scandals
- North Korea–United States relations
- North Korean war crimes
- Recipients of the Distinguished Service Cross (United States)
- War crimes in South Korea
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.