Miquel's theorem — A diagram showing circles passing through the vertices of a triangle ABC and points A´, B´ and C´ on the adjacent sides of the triangle intersecting at a common point, M. Miquel s theorem is a theorem in geometry, named after Auguste Miquel,… … Wikipedia
Malfatti circles — In geometry, the Malfatti circles are three circles inside a given triangle such that each circle is tangent to the other two and to two sides of the triangle. They are named after Gian Francesco Malfatti, who made early studies of the problem of … Wikipedia
Circle packing theorem — Example of the circle packing theorem on K5, the complete graph on five vertices, minus one edge. The circle packing theorem (also known as the Koebe–Andreev–Thurston theorem) describes the possible tangency relations between circles in the plane … Wikipedia
Descartes' theorem — For other uses, see Descartes theorem (disambiguation). In geometry, Descartes theorem, named after René Descartes, establishes a relationship between four kissing, or mutually tangent, circles. The theorem can be used to construct a fourth… … Wikipedia
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem — This article collects together a variety of proofs of Fermat s little theorem, which states that:a^p equiv a pmod p ,!for every prime number p and every integer a (see modular arithmetic). Simplifications Some of the proofs of Fermat s little… … Wikipedia
Pythagorean theorem — See also: Pythagorean trigonometric identity The Pythagorean theorem: The sum of the areas of the two squares on the legs (a and b) equals the area of the square on the hypotenuse (c) … Wikipedia
Fáry's theorem — states that any simple planar graph can be drawn without crossings so that its edges are straight line segments. That is, the ability to draw graph edges as curves instead of as straight line segments does not allow a larger class of graphs to be … Wikipedia
List of circle topics — This list of circle topics includes things related to the geometric shape, either abstractly, as in idealizations studied by geometers, or concretely in physical space. It does not include metaphors like inner circle or circular reasoning in… … Wikipedia
List of mathematics articles (F) — NOTOC F F₄ F algebra F coalgebra F distribution F divergence Fσ set F space F test F theory F. and M. Riesz theorem F1 Score Faà di Bruno s formula Face (geometry) Face configuration Face diagonal Facet (mathematics) Facetting… … Wikipedia
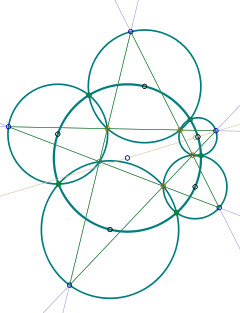
Clifford's circle theorems — In geometry, Clifford s theorems, named after the English geometer William Kingdon Clifford, are a sequence of theorems relating to intersections of circles. The first theorem considers any four circles passing through a common point M. Four new… … Wikipedia