- Emirate of Granada
-
"Kingdom of Granada" redirects here. For the post-1492 kingdom under the Crown of Castile, see Kingdom of Granada (Crown of Castile).
Emirate of Granada
إمارة غرﻧﺎﻃﺔ
Imarat Gharnāṭah (Arabic)Vassal of the Crown of Castile ← 
1238–1492  →
→

Flag Coat of arms Motto
Wa lā gāliba illā-llāh
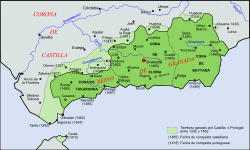
(There is no conqueror but Allah)Size of the Nasrid Kingdom Capital Granada Language(s) Official language:
Arabic
Minority languages:
Castilian, LadinoReligion Majority religion:
Islam
Minority religions:
Roman Catholicism, JudaismGovernment Monarchy Sultan - 1238–1273 Mohammed I ibn Nasr - 1273–1302 Muhammed II al-Faqih Historical era Early modern period - Established 1238 - Disestablished 1492 Today part of  Spain
SpainHistory of Al-Andalus
711–1492711–732 Muslim conquest
- Battles : Battle of Guadalete
Battle of Toulouse | Battle of Tours
756–1031 Omayyads of Córdoba
1009–1106 First Taifa period
1085–1145 Almoravid rule
- Almoravid conquest
- Battle of Sagrajas
1140-1203 Second Taifa period
1147–1238 Almohad rule
1232–1287 Third Taifa period
1238–1492 Emirate of Granada
connected articles - Map of Al-Andalus
- Reconquista
The Emirate of Granada (Arabic: إمارة غرﻧﺎﻃﺔ, trans. Imarat Gharnāṭah), also known as the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada (Spanish: Reino nazarí de Granada), was an emirate established in 1238 following the defeat of Muhammad an-Nasir of the Almohad dynasty by an alliance of Christian kingdoms at the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212. After prince Idris left Iberia to take the Almohad leadership, the ambitious Mohammed I ibn Nasr established the last Muslim dynasty on the Iberian peninsula - the Nasrids. The Nasrid emirs were responsible for building the Alhambra palace complex. Arabic was the official language and mother tongue of the majority of the population.
Contents
Tributary State
With the Reconquista in full swing after the conquest of Córdoba in June 1236, Mohammed I ibn Nasr aligned Granada with Ferdinand III of Castile in 1238, thereby creating a tributary state, or taifa, under the Crown of Castile. Granada remained a tributary state for the next 250 years, with Nasrid emirs paying tribute to Castilian kings mostly in the form of gold from present-day Mali and Burkina Faso that was carried to Iberia through the merchant routes in the Sahara. The Nasrids also provided military assistance to Castile for its conquest of areas under Muslim control, most notably Seville in November 1248 and the Taifa of Niebla in 1262.
In 1305, Granada conquered Ceuta, but lost control of the city in 1309 to the Kingdom of Fez with the assistance of the Crown of Aragon. Granada re-captured Ceuta a year later, but again lost it in 1314. Granada again held the city from 1315 to 1327. In 1384, Granada again re-took Ceuta but lost it definitively in 1387.
Granada's peace with Castile broke down on various occasions. Granada lost territory to Castile at the Battle of Teba in 1330. In 1340, Granada under Yusuf I supported the failed Marinid invasion of the Iberian Peninsula, which ended at the Battle of Río Salado.
Regional Entrepôt
Granada's status as a tributary state and its favorable geographic location, with the Sierra Nevada mountains as a natural barrier, helped to prolong Nasrid rule and allowed the Emirate to prosper as a regional entrepôt with the Maghreb and the rest of the Africa. In fact, Granada was a prosperous city during the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages when much of Europe stagnated. Granada also served as a refuge for Muslims fleeing during the Reconquista. Regardless of its comparative prosperity, intra-political strife was constant, skirmishes along the border occurred frequently and territory was gradually lost to Castile.
Granada was tightly integrated in Mediterranean trade networks and heavily financed by Genoese bankers aiming to gain control of the gold trade carried in through Saharan caravan routes.[1] However, after Portugal opened direct trade routes to Africa by sea in the 15th century, Granada became less important as a regional commercial center. With the union of Castile and Aragon in 1469, these kingdoms set their sights on annexing Granada.
Fall of Granada
The invasion of Granada would offer an opportunity for Ferdinand and Isabella to harness the restless Castilian nobility against a common enemy and instill subjects with a sense of loyalty to the crown.[2] The Emirate's attack on the Castilian frontier town of Zahara in December 1481 provided the pretext for a Christian invasion.[2] The Granada War began in 1482, with Christian forces capturing Alhama de Granada in February 1482. This marked the beginning of a grinding 10-year war. The Christian force was made up of troops provided by Castilian nobles, towns, and the Santa Hermandad, as well as Swiss mercenaries.[3] The Catholic Church also encouraged other Christian countries to offer their troops and their finances to the war effort. Meanwhile civil war erupted in Granada as a result of succession struggles in the Nasrid ruling house. Castile used this internal strife as an opportunity to push further into Granada. By 1491, the city of Granada itself lay under siege. On November 25, 1491, the Treaty of Granada (1491) was signed, which was a truce that only delayed the inevitable. On January 2, 1492, the last Muslim leader, Muhammad XII, known as Boabdil to the Spanish, surrendered complete control of Granada, to Ferdinand and Isabella, Los Reyes Católicos ("The Catholic Monarchs").
Aftermath
The Christian ousting of Muslim rule on the Iberian Peninsula with the conquest of Granada did not extinguish the spirit of the Reconquista. Isabella urged Christians to pursue a conquest of Africa.[4] About 200,000 Muslims are thought to have emigrated to North Africa after the fall of Granada. Those who remained were guaranteed their property, laws, customs, and religion. These rights were not always respected and Muslims in the area saw a slow decline in these liberties. However, Islamic culture persisted and was incorporated in local cultures, even under Christian rule.
See also
- Nasrid dynasty
- Romance of Abenamar
- Taifa of Granada
- List of Sunni Muslim dynasties
References
- ^ Arrighi, Giovanni (2010). The Long Twentieth Century. Verso. p. 120. ISBN 978-1-84467-304-9.
- ^ a b Barton, Simon (2004). A History of Spain. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 103. ISBN 978-0-230-20012-8.
- ^ Barton, Simon (2004). History of Spain. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-230-20012-8.
- ^ Barton, Simon (2004). A History of Spain. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 105. ISBN 978-0-230-20012-8.
Bibliography
- Fernández Puertas, Antonio (1997). The Alhambra. Vol 1. From the Ninth Century to Yusuf I (1354). Saqi Books. ISBN 0-86356-466-6.
- Fernández Puertas, Antonio. The Alhambra. Vol. 2. (1354 - 1391). Saqi Books. ISBN 0-86356-467-4.
- Harvey, Leonard Patrick (1992). Islamic Spain 1250 to 1500. University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-31962-8.
- Watt, W. Montgomery (1965). A History of Islamic Spain. Edinburgh University Press. ISBN 0-7486-0847-8.
- Arié, Rachel (1990) (in french). L’Espagne musulmane au Temps des Nasrides (1232–1492) (2nd ed.). De Boccard. ISBN 2-7018-0052-8.
- Bueno, Francisco (2004) (in Spanish). Los Reyes de la Alhambra. Entre la historia y la leyenda. Miguel Sánchez. ISBN 84-7169-082-9.
- Cortés Peña, Antonio Luis; Vincent, Bernard (1983-1987) (in Spanish). Historia de Granada. 4 vols.. Editorial Don Quijote.
External links
- (Spanish) Al-Ándalus III: el Sultanato De Granada (1232-1492) y Una Breve Reseña Sobre la Alhambra
- (Spanish) R.H. Shamsuddín Elía, Historia de Al-Andalus, Boletín N° 53 -08/2006 Al-Ándalus III: El Sultanato De Granada (1232-1492)
- (Spanish) Nicolás Homar Vives, Genealogy of the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada
- (French) Genealogy of the muslim dynasties in Spain
- (Arabic) بنو نصر/النصريون/بنو الأحمر في غرناطة Les Nasrides, Les Banû al-Ahmar à Grenade
Categories:- Former countries in Europe
- Former vassal states
- States and territories established in 1238
- States and territories disestablished in 1492
- Al-Andalus
- Nasrid dynasty
- Former Muslim countries in Europe
- Former emirates
- Granada
- Battles : Battle of Guadalete
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.