- Moesian dialects
-
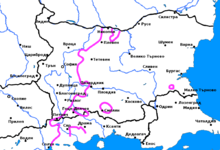
The Moesian dialects are a group of closely related dialects of the Bulgarian language, part of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. The Moesian dialects are spoken in northeastern Bulgaria and in the regions of Karnobat, Aytos, Burgas and Yambol in southern Bulgaria. However, due to the mass population movements that affected eastern Bulgaria during the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century, nowadays, there are very few areas where only Moesian is spoken. In most areas, and especially in southern Bulgaria and Dobruja, Moesian speakers are mixed with speakers speaking Balkan dialects. As a result of this and also due to the influence of the literary language, most features of the Moesian dialects have given way to features typical for the Balkan dialects.
Phonological and morphological characteristics
- Vowel change я/broad е (ʲa/æ) instead of formal Bulgarian я/е (ʲa/ɛ) for Old Church Slavonic ѣ – (бял/бæли instead of бял/бели). As a result of the influence of the Balkan dialects, the broad e (æ) has now been almost universally replaced by (ɛ)
- щ/жд (ʃt/ʒd) for Proto-Slavic *tʲ/*dʲ (as in Standard Bulgarian) - нощ, между (night, between)
- Universal loss of x /x/ and ф /f/. The two consonants are either completely lost or replaced by v or u
- The masculine definite article is о (stressed) and у (unstressed) instead of formal Bulgarian –ът/ъ (гърˈбо, ˈстолу instead of гърˈбът, ˈстолът). As a result of the influence of the Balkan dialects, the о/у definite article has largely been replaced by –ът/ъ
- ending e instead of formal Bulgarian i for multi-syllable masculine nouns (българе instead of българи)
- ending e instead of formal Bulgarian i for plural past active aorist participles (биле instead of били)
- Preposition у instead of formal Bulgarian в (у Русе instead of в Русе)
Sources
Стойков, Стойко: Българска диалектология, Акад. изд. "Проф. Марин Дринов", 2006 [1]
 Dialects of the Bulgarian language
Dialects of the Bulgarian languageEastern MoesianWestern Botevgrad · Vratsa · Ihtiman · Elin Pelin · Sofia · Samokov · Dupnitsa · Kyustendil · Maleshevo-Pirin1 · Solun-Kukush1Diaspora Banat Bulgarian · Wallachian · Transylvanian · Former USSR · Anatolian1 Also considered a dialect of Macedonian. Categories:- Dialects of the Bulgarian language
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.