- Charge pump
-
A charge pump is a kind of DC to DC converter that uses capacitors as energy storage elements to create either a higher or lower voltage power source. Charge pump circuits are capable of high efficiencies, sometimes as high as 90–95% while being electrically simple circuits.
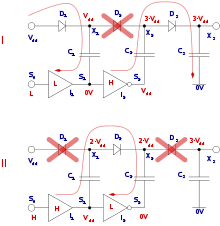
Charge pumps use some form of switching device(s) to control the connection of voltages to the capacitor. For instance, a two-stage cycle can be used to generate a higher pulsed voltage from a lower-voltage supply. In the first stage of the cycle, a capacitor is connected across the supply, charging it to that same voltage. In the second stage of the cycle, the circuit is reconfigured so that the capacitor is in series with the supply to the load. Ignoring leakage effects, this effectively provides double the supply voltage to the load (the sum of the original supply and the capacitor). The pulsing nature of the higher voltage output is typically smoothed by the use of an output capacitor.
An external or secondary circuit drives the switching, typically at tens of kilohertz up to several megahertz. The high frequency minimizes the amount of capacitance required as less charge needs to be stored and dumped in a shorter cycle. The capacitor used as the charge pump is typically known as the "flying capacitor".
Another way to explain the operation of a charge pump is to consider it as the combination of a DC to AC converter (the switches) followed by a voltage multiplier.
The voltage is load-dependent; higher loads result in lower average voltages.
Charge pumps can double voltages, triple voltages, halve voltages, invert voltages, fractionally multiply or scale voltages such as x3/2, x4/3, x2/3, etc. and generate arbitrary voltages, depending on the controller and circuit topology.
The term 'charge pump' is also used in phase-locked loop (PLL) circuits. This is a completely different application. In a PLL the phase difference between the reference signal (often from a crystal oscillator) and the output signal is translated into two signals – UP and DN. The two signals control switches to steer current into or out of a capacitor, causing the voltage across the capacitor to increase or decrease. In each cycle, the time during which the switch is turned on is proportional to the phase difference, hence the charge delivered is dependent on the phase difference also. The voltage on the capacitor is used to tune a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO), generating the desired output signal frequency. The use of a charge pump naturally adds a pole at the origin in the loop transfer function of the PLL, since the charge-pump current is driven into a capacitor to generate a voltage (V=I/(sC)). The additional pole at the origin is desirable because when considering the closed-loop transfer function of the PLL, this pole at the origin integrates the error signal and causes the system to track the input with one more order. The charge pump in a PLL design is constructed in integrated-circuit (IC) technology, consisting of pull-up, pull-down transistors and on-chip capacitors. A resistor is also added to stabilize the closed-loop PLL.
Contents
Applications
- A common application for charge pump circuits is in RS-232 level shifters where they are used to derive positive and negative voltages (often +10 V and −10 V) from a single 5 V or 3 V power supply rail.
- Charge pumps can also be used as LCD or white LED drivers, generating high bias voltages from a single low-voltage supply, such as a battery.
- A charge pump providing a negative voltage spike has been used in NES-compatible games not licensed by Nintendo in order to stun the Nintendo Entertainment System lockout chip.[1]
- As of 2007, charge pumps are integrated into nearly all EEPROM and flash memory integrated circuits. These devices require a high voltage pulse to "clean out" any existing data in a particular memory cell before it can be written with a new value. Early EEPROM and flash memory devices required two power supplies: +5V (for reading) and +12 V (for erasing). As of 2007[update], commercially available flash memory and EEPROM memory requires only one external power supply – generally 1.8 or 3.3V. A higher voltage, used to erase cells, is generated internally by an on-chip charge pump. However, some researchers say that a solid-state drive using a single large boost converter will cost less and use 33 percent less power than current SSDs which use a charge pump on every flash chip.[2]
References
- ^ Kevin Horton. Colordreams Revision C. Last modified 2007-09-30. Accessed 2011-09-15.
- ^ "New SSD Power Supply System To Save Energy, Cost" by Shawn Oliver 2009
Applying the equivalent resistor concept to calculating the power losses in the charge pumps
- J. C. Maxwell, A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism, Oxford, The Clarendon Press, 1873, pp. 420-425, “Intermittent current,” Art. 775, 776.
- Z. Singer, A. Emanuel, and M. S. Erlicki, “Power regulation by means of a switched capacitor,” in Proc. of the Institution of Electrical Engineers, Vol. 119, №2, 1972, pp. 149-152.
- G. van Steenwijk, K. Hoen, and H. Wallinga, “Analysis and design of a charge pump circuit for high output current applications”, in Proc. 19th European Solid-State Circuits Conference (ESSCIRC) 1993, pp. 118-121.
- J. W. Kimball, P. T. Krein, and K. R. Cahill, “Modeling of capacitor impedance in switching converters,” IEEE Power Electronics Letters, Vol. 3, №4, 2005, pp. 136-140.
- K. Itoh, M. Horiguchi, and H. Tanaka, Ultra-Low Voltage Nano-Scale Memories, Series on Integrated Circuits and Systems, Springer, 2007, 400p.
- M. D. Seeman and S. R. Sanders, “Analysis and optimization of switched capacitor DC-DC Converters,” IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, Vol. 23, №2, 2008, pp. 841-851.
- S. Ben-Yaakov and M. Evzelman, “Generic and unified model of switched capacitor converters,” IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Expo. (ECCE) 2009, pp.3501-3508.
- S. Ben-Yaakov, "On the influence of switch resistances on switched capacitor converters losses," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2011.
The charge pumps, where the voltages across the capacitors follow the binary number system
- F. Ueno, T. Inoue, and I. Oota, “Realization of a new switched-capacitor transformer with a step-up transformer ratio 2n–1 using n capacitors,” IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) 1986, pp. 805-808.
- J. A. Starzyk, Y.-W. Jan, and F. Qiu, “A DC-DC charge pump design based on voltage doublers,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, Part I, Vol. 48, №3, 2001, pp. 350-359.
- F. L. Luo, and H. Ye, “Positive output multiple-lift push–pull switched-capacitor Luo-converters,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, Vol. 51, №3, 2004, pp. 594-602.
- S. Ben-Yaakov and A. Kushnerov, “Algebraic foundation of self-adjusting switched capacitors converters,” IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Expo. (ECCE) 2009, pp. 1582-1589.
External links
- Charge Pump DC/DC Converters. Applications, circuits and solutions using inductorless (charge pump) dc/dc converters.
- DC/DC Conversion without Inductors. General description of charge pump operation; example applications using Maxim controllers.
- Charge-Pump and Step-Up DC-DC Converter Solutions for Powering White LEDs in Series or Parallel Connections
- Circuit Board Layout Guidelines for White LED Charge Pumps
- Linearized three state phase detector by Steven F. Gillig (patent filed 1990, awarded 1990, assigned to Motorola)
- Linearized digital phase and frequency detector by John D. Hatchett and Andrew S. Olesin (patent filed 1980, awarded 1983, assigned to Motorola)
See also
Categories:- Electrical power conversion
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.