- PMDTA
-
PMDTA 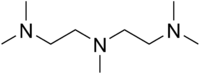 N,N,N',N',N-PentamethyldiethylenetriamineOther namesPentamethyldiethylenetriamine,
N,N,N',N',N-PentamethyldiethylenetriamineOther namesPentamethyldiethylenetriamine,
PMDTA,
PMDETA,
PMDT,
pmdien,
Me5dien,
1,2-Ethanediamine,
N-(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl)-N,N',N'-trimethyl- (9CI),
1,1,4,7,7-Pentamethyldiethylenetriamine,
2,5,8-Trimethyl-2,5,8-triazanonaneIdentifiers CAS number 3030-47-5 
PubChem 18196 Properties Molecular formula C9H23N3 Molar mass 173.3 g mol−1 Appearance liquid Density 0.83 g/cm3 Melting point -20 °C
Boiling point 198 °C
Solubility in water sl sol H2O;
sol ethanol, acetone, ethers, alkanesHazards R-phrases R22 R24 R34 S-phrases S26 S36/37/39 S45  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references PMDTA, formally N,N,N',N',N"-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine, is an organic compound with the formula [Me2NCH2CH2]2NMe (Me is CH3). PMDTA is a basic, bulky, and flexible, tridentate ligand that is a used in organolithium chemistry.
Contents
Synthesis
PMDTA is prepared by methylating diethylenetriamine with formaldehyde and formic acid.[1]
- [H2N(CH2)2]2NH + 5 CH2O + 5 HCO2H → [Me2NCH2CH2]2NMe + 5 CO2 + 5 H2O
Dien versus PMDTA
Unlike diethylenetriamine, all three amines in PDMTA are tertiary. Both PMDTA and dien are tridentate ligands that form two five-membered chelate rings. The σ-donating properties of the amino groups of dien are greater than that of PMDTA in copper(II) complexes.[2] Both ligands can coordinate metal complexes in arrangements where the three nitrogen centers are co-planar or mutually cis.
Organolithium compounds and PMDTA
Alkyllithium compounds such as n-butyllithium (BuLi) are used to deprotonate weak acids, e.g. hydrocarbons. It is well known that organolithium aggregates are broken up by Lewis bases to give reagents that EW a more efficient base than untreated BuLi.[3] Commonly, the ditertiary amine TMEDA is used in these applications; it binds to the lithium center as a bidentate ligand. PMDTA behaves analogously, but since it is tridentate, it binds more strongly to lithium. In contrast to TMEDA, PMDTA forms monomeric complexes with organolithium compounds. Both amines affect the regiochemistry of metalation.[3][4]
In the PMDTA-n-BuLi adducts, the Li-C bonds are highly polarized, thus increasing the basicity of the butyl group.[5]
The effect of PMDTA on lithium anilide is illustrative of PMDTA's complexing power. The complex, [{PhN(H)Li}3·2PMDTA], is trinuclear, featuring approximately colinear Li+ centers that are three-, four-, and five-coordinate. The central three-coordinate lithium atom is not bonded to PMDTA. One of the terminal Li centers is pseudo-tetrahedral in an N4 coordination sphere. The other terminal lithium atom is five-coordinate and binds to two anilino N centers and the PMDTA.[6]
Transition metal and aluminium complexes
PMDTA often forms five-coordinate complexes due to steric bulk of the methyl groups. PMDTA stabilize unusual cations. The first cationic derivative of alane. [H2Al(PMDTA)]+[AlH4]- was prepared by treating H3AlNMe3 with PMDTA.[5]
References
- ^ A. Marxer, K. Miescher (1951). "Über die stufenweise Quaternisierung von aliphatischen Polyaminen. Neue Verbindungen mit ganglienblockierender Wirkung". Helvetica Chimica Acta 34 (3): 924–931. doi:10.1002/hlca.19510340327.
- ^ Angelici, R. J.; Allison, J. W. (171). "Stability Constants for Amino Acid Coordination bySubstituted Diethylenetriamine Complexes of Copper(I1) and the Kinetics of Amino Acid Ester Hydrolysis". Inorganic Chemistry 10: 2238–2243. doi:10.1021/ic50104a30.
- ^ a b Strohmann, C. and Gessner, V. H. (2007). "From the Alkyllitium Aggregate [{(nBuLi)2·PMDTA}2] to Lithiated PMDTA". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46: 4566–4569. doi:10.1002/anie.200605105.
- ^ Fraenkel, G. (2002). "PMDTA". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Weinheim: Wiley-VCH): 806–813. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rp028.
- ^ a b Elschenbroich, C. (2006). Organometallics. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. pp. 45–46. ISBN 978-3-29390-6.
- ^ Barr, D.; Clegg, W.; Cowton, L.; Horsburgh, L.; Mackenzie, F. M.; Mulvey, R. (1995). "Lithium Anilide Complexed by pmdeta: Expectations of a simple monomer, but in Reality an Odd Trinuclear Composition Combining Three-, Four-, and Five-coordinate Lithium". J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 8 (8): 891–892. doi:10.1039/C39950000891.
Categories:- Polyamines
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
