- Estlink
-
Estlink 1 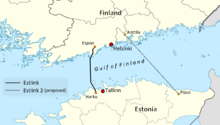
Location of EstlinkLocation Country Estonia, Finland General direction south–north–south From Harku converter station, Estonia 59°23′5″N 24°33′37″E / 59.38472°N 24.56028°E Passes through Gulf of Finland To Espoo converter station, Finland 60°12′14″N 24°33′06″E / 60.20389°N 24.55167°E Ownership information Owner AS Nordic Energy Link Partners Eesti Energia, Latvenergo, Lietuvos Energija, Pohjolan Voima, Helsingin Energia Construction information Manufacturer of conductor/cable ABB Installer of conductor/cable Global Marine Systems Cable layer CS Sovereign Manufacturer of substations ABB Installer of substations ABB Construction started 2006 Commissioned 2006 Technical information Type subsea cable Type of current HVDC Total length 105 km (65 mi) Power rating 350 MW AC Voltage 330 kV (Estonia), 400 kV (Finland) DC Voltage ±150 kV Number of poles 2 Estlink 2 
Location of Estlink 2Location Country Estonia, Finland General direction south–north–south From Püssi converter station, Estonia 59°22′02″N 27°03′50″E / 59.36722°N 27.06389°E Passes through Gulf of Finland To Anttila converter station, Finland 60°22′40″N 25°22′11″E / 60.37778°N 25.36972°E Ownership information Partners Elering, Fingrid Construction information Manufacturer of conductor/cable Nexans Installer of conductor/cable Nexans Cable layer C/S Nexans Skagerrak Manufacturer of substations Siemens Installer of substations Siemens Contractors Empower Oy Expected 2014 Technical information Type subsea cable, overhead line Type of current HVDC Total length 171 km (106 mi) Power rating 650 MW AC Voltage 330 kV (Estonia), 400 kV (Finland) DC Voltage 450 kV Number of poles 1 Estlink is a set of HVDC submarine cables between Estonia and Finland. Estlink 1 is the first interconnection between the Baltic and Nordic electricity markets following by Estlink 2 in 2014. The main purpose of the Estlink connection is to secure power supply in both regions to integrate Baltic and Nordic energy markets.[1][2][3]
Contents
Estlink 1
History
First plans for a submarine power cable between the Baltic and the Nordic regions were proposed in 1990s. Negotiations between Eesti Energia, Pohjolan Voima, Helsingin Energia, Granige (now E.ON Sverige), Latvenergo, Statkraft and TXE Nordic Energy, a subsidiary of TXU (now Energy Future Holdings Corporation) started In 1999, and on 9 October 2001 a contract was signed in Tallinn.[4] However, only after the harsh winter of 2002–2003 which resulted in an increased demand for power, the project of the submarine cable between Estonia and Finland got a boost.[5][6] The letter of intention for underwater sea cable was signed between Eesti Energia, Pohjolan Voima, Helsingin Energia and Latvenergo on 31 March 2003.[7] In May 2004, the Lithuanian power company Lietuvos Energija agreed to participate in the project, shortly after which the project company AS Nordic Energy Link was established.[8][9] On 29 April 2005, the Estlink project was launched.[6][10] Construction of Harku converter station and land cable installation begins on 5 April 2006.[11] The submarine cable was laid in September 2006.[12][13][14] The Estlink cable was inaugurated on 4 December 2006 and it became fully operational on 5 January 2007.[15][16]
Description
The 105 kilometres (65 mi) long (including 74 kilometres (46 mi) under water) +/-150 kV, 350 MW HVDC link cable is connected to the Estonian electrical system at the Harku 330 kV converter station and to the Finnish transmission network at Espoo 400 kV converter station in Järvikylä using HVDC Light transmission technology.[5][17][10][18] The installation of land cable began on 4 May 2006 in Harku. The submarine cable was laid on the seabed of the Gulf of Finland in the autumn of 2006. The cable's maximum depth on the seabed is 100 metres (330 ft).
The cable is constructed by ABB.[10] The submarine cable was laid by Global Marine Systems using Sovereign service vessel.[6] The project cost €110 million.[12]
Project company
The Estlink cable is operated by AS Nordic Energy Link company, founded by Baltic and Finnish power companies. The main shareholder is Eesti Energia with 39.9% of the shares, Latvenergo and Lietuvos Energija have 25% each, and the remaining 10.1% are divided between Pohjolan Voima and Helsingin Energia (Finestlink).[5] Nordic Energy Link shareholders have agreed to sell the interconnector to the transmission system operators Elering and Fingrid before 2013.[5]
Sites
Name Coordinates Harku 59°23′5″N 24°33′37″E / 59.38472°N 24.56028°E Finland - Espoo 60°12′14″N 24°33′06″E / 60.20389°N 24.55167°E Estlink 2
Elering and Fingrid are building a new 650 MW link from Püssi substation in Estonia to Anttila substation in Finland. The links is expected to be operational by 2014.[1]
History
A preliminary agreement on EstLink 2 was signed between Elering and Fingrid on 15 February 2010 in Tallinn.[19][20] Capital investment decision by Fingrid was made on 20 May 2010.[21] A construction agreement was signed on 1 November 2010.[22]
On 23 December 2010, the contract to manufacture and install the subsea and undeground cables was awarded to Nexans, the contract to build converter stations was awarded to Siemens, the contract to build the Nikuviken cable terminal station and to expand the Anttila substation in Finland was awarded to Empower Oy, and the contract to build the transmission line between Anttila and Nikuviken was awarded to ETDE, a part of Bouygues.[1][2][23][24]
Description
The total length of Estlink 2 would be 171 kilometres (106 mi), including a 145-kilometre (90 mi) long offshore cable, a 12-kilometre (7.5 mi) long onshore cable in Estonia, and 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) of overhead lines in Finland.[1] The 12-kilometre (7.5 mi) long underground cable starts at the Püssi substation and runs the coast of the Gulf of Finland. From there the 145-kilometre (90 mi) long offshore cable runs to the Nikuviken cable terminal station in Finland. The Nikuviken cable terminal station will be connected with the Attila converter station by the 14-kilometre (8.7 mi) long overhead line.[23] The subsea cable will be laid by the cable ship Nexans Skagerrak.[2]
Estlink 2 will be a classic monopolar high-voltage direct current connection with line-commutated converter thyristors. Its maximum transmission rate will be 650 MW and it will operate with a voltage of 450 kV.[2] Its estimated cost is about €320 million, of which converter stations cost €100 million and cable €180 million.[1][23] The European Commission has decided to allocate €100 million to the project.[25][26]
See also
- Baltic Cable (between Germany and Sweden)
- Balticconnector (proposed gas pipeline between Estonia and Finland)
- Fenno-Skan (between Finland and Sweden)
- NordBalt (planned between Lithuania and Sweden)
- SwePol (between Poland and Sweden)
References
- ^ a b c d e "Siemens secures EUR100m order to supply converter stations for Estlink 2". Power-Gen Worldwide (PennWell Corporation). 2010-12-23. http://www.powergenworldwide.com/index/display/articledisplay/7636796494/articles/powergenworldwide/t-and-d/t-and-d-infrastructure/2010/12/siemens-secures_eur100m.html. Retrieved 2010-12-31.
- ^ a b c d "Nexans Wins Contract for EstLink 2 Power Submarine Link Between Finland and Estonia". OilVoice. 2010-12-26. http://www.oilvoice.com/n/Nexans_Wins_Contract_for_EstLink_2_Power_Submarine_Link_Between_Finland_and_Estonia/780a97dd0.aspx. Retrieved 2010-12-31.
- ^ "Estlink-2 to tie Baltic power producers closer to the Nordic markets". Nordic Investment Bank. December 2010. http://www.nib.int/news_publications/cases_and_feature_stories/2010-12_estlink-2. Retrieved 2010-12-31.
- ^ Kurm, Kairi; Gunter, Aleksei (2001-10-11). "New power cable to unite Baltic and Scandinavian power supplies". The Baltic Times. http://brilliantfixer.wordpress.com/2001/10/11/new-power-cable-to-unite-baltic-and-scandinavian-power-supp/. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ a b c d Pajo, Raine; Aarna, Indrek; Lahtinen, Matti (2007-04-01). "Estlink Tie Improves Baltic States System". Transmission & Distribution World (Penton Media, Inc.). (subscription required). http://tdworld.com/underground_transmission_distribution/power_estlink_tie_improves/. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ a b c "Case Studies - Estlink". Global Marine Systems. http://www.globalmarinesystems.com/energy/Case_Studies/estlink. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ Hõbemägi, Toomas (2003-03-31). "Estonia- Latvia- Finland power groups sign undersea cable protocol". Baltic Business News. http://bbn.ee/Default2.aspx?ArticleID=7326502b-5697-4464-82a3-1ceb3ea9bbc2. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ Hõbemägi, Toomas (2004-05-13). "Lietuvos Energija agrees to invest in Estlink". Baltic Business News. http://bbn.ee/Default2.aspx?ArticleID=df65b2b1-5f85-4bf0-8172-862bc3b807ce. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ "Sea cable Estlink partners formed joint venture". Baltic Business News. 2004-06-07. http://bbn.ee/Default2.aspx?ArticleID=d14ce18a-e9b2-4aa9-9516-586996df4225. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ a b c Hõbemägi, Toomas (2005-05-02). "Estonian-Finnish undersea power cable project launched". Baltic Business News. http://bbn.ee/Default2.aspx?ArticleID=610e929d-ac6f-4fbe-87bc-031416452ffd. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ Hõbemägi, Toomas (2006-04-05). "Construction work for Estlink submarine cable converter station begins". Baltic Business News. http://bbn.ee/Default2.aspx?ArticleID=9934b5a1-3749-4c66-b3da-7766c0fc5e73. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ a b "Work on Estlink cable begins in Gulf of Finland". New Europe. 2006-09-13. http://www.neurope.eu/articles/64691.php. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ Hõbemägi, Toomas (2006-09-11). "Laying of Estlink submarine cable on seabed begins near Tallinn". Baltic Business News. http://bbn.ee/Default2.aspx?ArticleID=9a55181c-386c-4a25-9013-6a0f416ab4ac. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ Hõbemägi, Toomas (2006-09-29). "Laying of Estlink cable on the seabed is completed". Baltic Business News. http://bbn.ee/Default2.aspx?ArticleID=4dc60ad0-cdd5-476f-960f-7b87dd2f6d26. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ Hõbemägi, Toomas (2006-12-24). "EUR 110 mln power link between Baltics and Finland inaugurated today". Baltic Business News. http://bbn.ee/Default2.aspx?ArticleID=177957f7-4dcc-43fc-ac47-36ade7b4a758. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ Hõbemägi, Toomas (2007-01-05). "Estlink subsea cable between Estonia and Finland becomes operational". Baltic Business News. http://bbn.ee/Default2.aspx?ArticleID=1879212c-0b2b-459f-aa6b-8523087ca40e. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ "Finland-Estonia power cable at least a week late". Reuters. 2006-11-30. http://uk.reuters.com/article/oilRpt/idUKL3087437620061130. Retrieved 2009-02-07.
- ^ "Estlink HVDC Light link". ABB. http://www.abb.com/industries/ap/db0003db004333/ce9eeddef52ff677c125774a002e109b.aspx. Retrieved 2010-10-02.
- ^ "Preliminary agreement signed on EstLink 2 cable connection" (Press release). Nord Pool Spot. 2010-02-15. http://www.nordpoolspot.com/Market_Information/Exchange-information/No-092010-NPS---Preliminary-agreement-signed-on-EstLink-2-cable-connection/. Retrieved 2010-12-31.
- ^ "Power firms sign new Finland-Estonia link deal". Reuters. 2010-02-15. http://uk.reuters.com/article/idUKLDE61E1JY20100215. Retrieved 2010-12-31.
- ^ "Fingrid's capital investment decision on submarine cable link to Estonia" (Press release). Nord Pool Spot. 2010-05-20. http://www.nordpoolspot.com/Market_Information/Exchange-information/No-312010-NPS----Fingrids-capital-investment-decision-on-submarine-cable-link-to-Estonia/. Retrieved 2010-12-31.
- ^ "Electricity market expanding further to the Baltic countries" (Press release). Fingrid. 2010-11-01. http://www.fingrid.fi/portal/in_english/news_and_releases/press_releases?bid=1174. Retrieved 2010-12-31.
- ^ a b c "Contractors chosen for new submarine cable connection between Finland and Estonia:total value of contracts almost 300 million euros" (Press release). Fingrid. 2010-12-23. http://www.fingrid.fi/portal/in_english/news_and_releases/press_releases?bid=1207. Retrieved 2010-12-31.
- ^ Kinnunen, Terhi (2010-12-23). "Nexans Norway, Siemens win Estlink 2 contracts". Reuters. http://uk.reuters.com/article/idUKLDE6BM0MK20101223. Retrieved 2010-12-31.
- ^ "European Commission endorses Estlink 2 investment". Baltic News Service. Estonia.eu. 2010-07-12. http://estonia.eu/news/150-european-commission-endorses-estlink-2-investment.html. Retrieved 2010-10-02.
- ^ "Economic Recovery: Second batch of 4-billion-euro package goes to 43 pipeline and electricity projects". European Commission. 2010-03-04. http://europa.eu/rapid/pressReleasesAction.do?reference=IP/10/231&format=HTML&aged=0&language=EN&guiLanguage=en. Retrieved 2010-03-08.
External links
Categories:- 2006 establishments
- HVDC transmission lines
- Submarine power cables
- Connections across the Baltic Sea
- Energy in Estonia
- Energy in Finland
- Electric power in Estonia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
