- OGLE-2006-BLG-109Lc
-
OGLE-2006-BLG-109Lc Extrasolar planet List of extrasolar planets 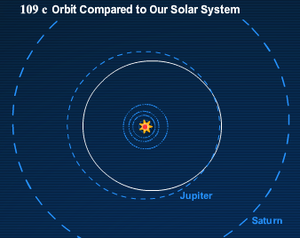
OGLE-2006-BLG-109 c's orbit compared to
Jupiter's orbit (5.2AU) in our Solar System.Parent star Star OGLE-2006-BLG-109L Constellation Sagittarius Right ascension (α) 17h 52m 35s Declination (δ) –30° 05′ 16″ Apparent magnitude (mV) 17.17 Distance 4,920 ± 390 ly
(1,510 ± 120 pc)Observed separation Projected separation (d) 4.5 ± 1 AU Orbital elements Eccentricity (e) 0.15 ± 0.1 Orbital period (P) 4931 ± 1750 d
(13.5 ± 4.79 y)Inclination (i) 64 ± 8° Physical characteristics Mass (m) 0.271 ± 0.022 MJ
(85.8 ± 9.5 M⊕)Temperature (T) 59 ± 7 K Discovery information Discovery date 14 February 2008 Discoverer(s) Gaudi and
Bennett et al.Detection method Gravitational microlensing Discovery status Published Other designations EWS 2006-BUL-109LcDatabase references Extrasolar Planets
Encyclopaediadata SIMBAD data OGLE-2006-BLG-109Lc is an extrasolar planet approximately 4,920 light-years away in the constellation of Sagittarius. The planet was detected orbiting the star OGLE-2006-BLG-109L in 2008 by a research team using Microlensing. The host star is about 50% the mass of the Sun and the planet is about 90% the mass of Saturn.[1][2]
See also
- Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment or OGLE
- 47 Ursae Majoris b
- OGLE-2005-BLG-390Lb
- OGLE-2006-BLG-109Lb
References
- ^ "Discovery of a Jupiter/Saturn Analog in OGLE-2006-BLG-109". MicroFUN (Microlensing Follow-Up Network). http://www.astronomy.ohio-state.edu/~microfun/ob06109/. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
- ^ Gaudi, B. S.; et al. (2008). "Discovery of a Jupiter/Saturn Analog with Gravitational Microlensing". Science 319 (5865): 927–930. arXiv:0802.1920. Bibcode 2008Sci...319..927G. doi:10.1126/science.1151947. PMID 18276883.
External links
- Britt, Robert Roy (2008-02-14). "Solar System Like Ours Found". Space.com. http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/080214-planets-found.html. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
- Dominik, Martin (2006-02-11). "The unlonely planets — Discovery of a Jupiter/Saturn analogue". ARTEMiS. http://www.artemis-uk.org/highlights/unlonely_planets/. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
- Overbye, Dennis (2008-02-14). "Scientists Find Solar System Like Ours". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2008/02/14/science/space/14cnd-planet.html?_r=1&oref=slogin. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
- Rincon, Paul (2008-04-06). "Solar System's 'look-alike' found". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/7333155.stm. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
Coordinates:
 17h 52m 35s, −30° 05′ 16″
17h 52m 35s, −30° 05′ 16″
This extrasolar planet related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
