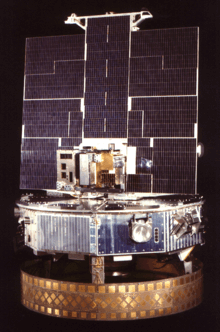
- P78-1
-
P78-1 or Solwind was a United States satellite launched aboard an Atlas F rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on February 24, 1979. The satellite operated until September 13, 1985, when it was shot down in orbit by an F-15 Eagle fighter aircraft during an US Air Force ASM-135 ASAT test. The test outraged some scientists because although five of P78-1's instruments had failed at the time of the test, two instruments remained in operation, and the satellite was what one solar physicist called "the backbone of coronal research through the last seven years."[1]
However, for several months before the ASAT test, the satellite batteries were degrading. This caused more and more frequent 'under-voltage cutoffs', a condition where the satellite detected low main bus voltage and automatically shut down all non-vital systems. As a result, an ever-increasing amount of time and network resources were spent reconfiguring the satellite for normal operation. Data collection from the few remaining payloads was severely limited. Because of the additional burden on the Air Force Satellite Control Network (e.g., extra support and antenna time at the tracking stations), serious discussions were already underway to terminate the mission prior to the ASAT test. It was extended for several weeks solely to support the test. During this final phase, it was often allowed to remain in the under-voltage condition for several days at a time.[citation needed]
Contents
Construction and payload
The Orbiting Solar Observatory (OSO) platform included a solar-oriented sail and a rotating wheel section. Ball Aerospace was the primary contractor for design and construction, and provided the attitude control and determination computer programs.[2] The P78-1 carried a gamma-ray spectrometer, a white light spectrograph, an extreme ultraviolet spectrometer, a high latitude particle spectrometer, an aerosol monitor, and an X-ray monitor. The X-ray monitor, designated NRL-608 or XMON, was a collaboration between the Naval Research Laboratory and Los Alamos National Laboratory.
See also
References
- ^ Science News, Sept 28, 1985: ASAT target was working research satellite by Jonathan Eberhart
- ^ Space Test Program P78-1 at Ball Aerospace[dead link]
External links
- NASA page about the satellite
- List of research papers based on P78-1 observations
- Air Force Link, Milestones Thursday, January 01, 1970 - Sunday, December 31, 1989
- Encyclopedia Astronautica Solwind Page
Categories:- NASA probes
- Intentionally destroyed artificial satellites
- United States spacecraft stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.