- PDZD2
-
PDZ domain containing 2 Identifiers Symbols PDZD2; AIPC; KIAA0300; PAPIN; PDZK3; PIN1 External IDs OMIM: 610697 MGI: 1922394 HomoloGene: 23393 GeneCards: PDZD2 Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • structural molecule activity
• protein bindingCellular component • extracellular region
• nucleus
• cytoplasm
• endoplasmic reticulum
• cell-cell junctionBiological process • cell adhesion Sources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 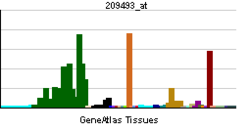
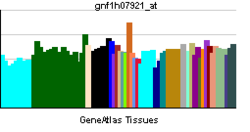
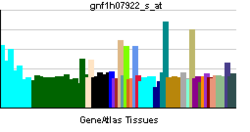
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 23037 68070 Ensembl ENSG00000133401 ENSMUSG00000022197 UniProt O15018 n/a RefSeq (mRNA) NM_178140 NM_001081064.1 RefSeq (protein) NP_835260 NP_001074533.1 Location (UCSC) Chr 5:
31.64 – 32.11 MbChr 15:
12.29 – 12.67 MbPubMed search [1] [2] PDZ domain-containing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDZD2 gene.[1][2]
Proteins containing PDZ domains have been shown frequently to bind the C-termini of transmembrane receptors or ion channels. They have also been shown to bind to other PDZ domain proteins and could possibly be involved in intracellular signalling. The protein encoded by this gene contains six PDZ domains and shares sequence similarity with pro-interleukin-16 (pro-IL-16). Like pro-IL-16, the encoded protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and is thought to be cleaved by a caspase to produce a secreted peptide containing two PDZ domains. In addition, this gene is upregulated in primary prostate tumors and may be involved in the early stages of prostate tumorigenesis.[2]
Interactions
PDZD2 has been shown to interact with PKP4.[3][4]
References
- ^ Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Nakajima D, Ohira M, Seki N, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Nomura N, Ohara O (Sep 1997). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. VII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which can code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res 4 (2): 141–50. doi:10.1093/dnares/4.2.141. PMID 9205841.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: PDZD2 PDZ domain containing 2". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=23037.
- ^ Deguchi, M; Iizuka T, Hata Y, Nishimura W, Hirao K, Yao I, Kawabe H, Takai Y (Sep. 2000). "PAPIN. A novel multiple PSD-95/Dlg-A/ZO-1 protein interacting with neural plakophilin-related armadillo repeat protein/delta-catenin and p0071". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 275 (38): 29875–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005384200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10896674.
- ^ Ohno, Hideki; Hirabayashi Susumu, Iizuka Toshihiko, Ohnishi Hirohide, Fujita Toshiro, Hata Yutaka (Oct. 2002). "Localization of p0071-interacting proteins, plakophilin-related armadillo-repeat protein-interacting protein (PAPIN) and ERBIN, in epithelial cells". Oncogene (England) 21 (46): 7042–9. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205852. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 12370826.
Further reading
- Lindahl P, Abrahamson M, Björk I (1992). "Interaction of recombinant human cystatin C with the cysteine proteinases papain and actinidin". Biochem. J. 281 ( Pt 1) (Pt 1): 49–55. PMC 1130639. PMID 1731767. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1130639.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- Deguchi M, Iizuka T, Hata Y et al. (2000). "PAPIN. A novel multiple PSD-95/Dlg-A/ZO-1 protein interacting with neural plakophilin-related armadillo repeat protein/delta-catenin and p0071". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (38): 29875–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005384200. PMID 10896674.
- Chaib H, Rubin MA, Mucci NR et al. (2001). "Activated in prostate cancer: a PDZ domain-containing protein highly expressed in human primary prostate tumors". Cancer Res. 61 (6): 2390–4. PMID 11289102.
- Ohno H, Hirabayashi S, Iizuka T et al. (2002). "Localization of p0071-interacting proteins, plakophilin-related armadillo-repeat protein-interacting protein (PAPIN) and ERBIN, in epithelial cells". Oncogene 21 (46): 7042–9. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205852. PMID 12370826.
- Nakayama M, Kikuno R, Ohara O (2003). "Protein–Protein Interactions Between Large Proteins: Two-Hybrid Screening Using a Functionally Classified Library Composed of Long cDNAs". Genome Res. 12 (11): 1773–84. doi:10.1101/gr.406902. PMC 187542. PMID 12421765. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=187542.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Yeung ML, Tam TS, Tsang AC, Yao KM (2003). "Proteolytic cleavage of PDZD2 generates a secreted peptide containing two PDZ domains". EMBO Rep. 4 (4): 412–8. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.embor804. PMC 1319160. PMID 12671685. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1319160.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Ma RY, Tam TS, Suen AP et al. (2006). "Secreted PDZD2 exerts concentration-dependent effects on the proliferation of INS-1E cells". Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 38 (5–6): 1015–22. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2005.11.012. PMID 16413998.
Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 5 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
