- DMC1 (gene)
-
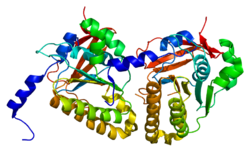
Meiotic recombination protein DMC1/LIM15 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DMC1 gene.[1][2][3][4]
The protein encoded by this gene is essential for meiotic homologous recombination. Genetic recombination in meiosis plays an important role in generating diversity of genetic information. The product of this gene is structurally and evolutionarily related to the products of the yeast RAD51 and E. coli RecA genes. Alternative splice variants of this gene have been described but their full-length nature has not been determined.[4]
Interactions
DMC1 (gene) has been shown to interact with RAD51.[5]
References
- ^ Habu T, Taki T, West A, Nishimune Y, Morita T (May 1996). "The mouse and human homologs of DMC1, the yeast meiosis-specific homologous recombination gene, have a common unique form of exon-skipped transcript in meiosis". Nucleic Acids Res 24 (3): 470–477. doi:10.1093/nar/24.3.470. PMC 145652. PMID 8602360. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=145652.
- ^ Sato S, Seki N, Hotta Y, Tabata S (Mar 1996). "Expression profiles of a human gene identified as a structural homologue of meiosis-specific recA-like genes". DNA Res 2 (4): 183–186. doi:10.1093/dnares/2.4.183. PMID 8590282.
- ^ Thorslund T, Esashi F, West SC (Jun 2007). "Interactions between human BRCA2 protein and the meiosis-specific recombinase DMC1". EMBO J 26 (12): 2915–2922. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601739. PMC 1894777. PMID 17541404. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1894777.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DMC1 DMC1 dosage suppressor of mck1 homolog, meiosis-specific homologous recombination (yeast)". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=11144.
- ^ Masson, J Y; Davies A A, Hajibagheri N, Van Dyck E, Benson F E, Stasiak A Z, Stasiak A, West S C (Nov. 1999). "The meiosis-specific recombinase hDmc1 forms ring structures and interacts with hRad51". EMBO J. (ENGLAND) 18 (22): 6552–6560. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.22.6552. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 1171718. PMID 10562567. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1171718.
Further reading
- Golub EI, Gupta RC, Haaf T et al. (1999). "Interaction of human rad51 recombination protein with single-stranded DNA binding protein, RPA". Nucleic Acids Res. 26 (23): 5388–5393. doi:10.1093/nar/26.23.5388. PMC 148005. PMID 9826763. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=148005.
- Masson JY, Davies AA, Hajibagheri N et al. (2000). "The meiosis-specific recombinase hDmc1 forms ring structures and interacts with hRad51". EMBO J. 18 (22): 6552–6560. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.22.6552. PMC 1171718. PMID 10562567. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1171718.
- Dunham I, Shimizu N, Roe BA et al. (1999). "The DNA sequence of human chromosome 22". Nature 402 (6761): 489–495. doi:10.1038/990031. PMID 10591208.
- Moens PB, Kolas NK, Tarsounas M et al. (2003). "The time course and chromosomal localization of recombination-related proteins at meiosis in the mouse are compatible with models that can resolve the early DNA-DNA interactions without reciprocal recombination". J. Cell. Sci. 115 (Pt 8): 1611–22. PMID 11950880.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–16903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Habu T, Wakabayashi N, Yoshida K et al. (2004). "p53 Protein interacts specifically with the meiosis-specific mammalian RecA-like protein DMC1 in meiosis". Carcinogenesis 25 (6): 889–893. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgh099. PMID 14764457.
- Kinebuchi T, Kagawa W, Enomoto R et al. (2004). "Structural basis for octameric ring formation and DNA interaction of the human homologous-pairing protein Dmc1". Mol. Cell 14 (3): 363–374. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(04)00218-7. PMID 15125839.
- Sehorn MG, Sigurdsson S, Bussen W et al. (2004). "Human meiotic recombinase Dmc1 promotes ATP-dependent homologous DNA strand exchange". Nature 429 (6990): 433–437. doi:10.1038/nature02563. PMID 15164066.
- Collins JE, Wright CL, Edwards CA et al. (2005). "A genome annotation-driven approach to cloning the human ORFeome". Genome Biol. 5 (10): R84. doi:10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r84. PMC 545604. PMID 15461802. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=545604.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–2127. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Kinebuchi T, Kagawa W, Kurumizaka H, Yokoyama S (2005). "Role of the N-terminal domain of the human DMC1 protein in octamer formation and DNA binding". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (31): 28382–28387. doi:10.1074/jbc.M503372200. PMID 15917243.
- Bugreev DV, Golub EI, Stasiak AZ et al. (2005). "Activation of human meiosis-specific recombinase Dmc1 by Ca2+". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (29): 26886–26895. doi:10.1074/jbc.M502248200. PMID 15917244.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature 437 (7062): 1173–1178. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Pezza RJ, Voloshin ON, Vanevski F, Camerini-Otero RD (2007). "Hop2/Mnd1 acts on two critical steps in Dmc1-promoted homologous pairing". Genes Dev. 21 (14): 1758–1766. doi:10.1101/gad.1562907. PMC 1920170. PMID 17639081. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1920170.
PDB gallery Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 22 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.