- DAZ associated protein 1
-
DAZ associated protein 1 
PDB rendering based on 2dgs.Available structures PDB 2DGS, 2DH8 Identifiers Symbols DAZAP1; MGC19907 External IDs OMIM: 607430 MGI: 1917498 HomoloGene: 23129 GeneCards: DAZAP1 Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • nucleotide binding
• RNA bindingCellular component • nucleus
• nucleolus
• cytoplasmBiological process • multicellular organismal development
• spermatogenesis
• cell differentiationSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 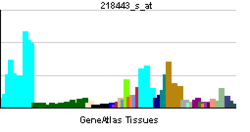
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 26528 70248 Ensembl ENSG00000071626 ENSMUSG00000069565 UniProt Q96EP5 Q0VDX2 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_018959.2 XM_986609 RefSeq (protein) NP_061832.2 XP_991703 Location (UCSC) Chr 19:
1.41 – 1.44 MbChr 10:
79.72 – 79.75 MbPubMed search [1] [2] DAZ-associated protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DAZAP1 gene.[1][2]
Contents
Function
In mammals, the Y chromosome directs the development of the testes and plays an important role in spermatogenesis. A high percentage of infertile men have deletions that map to regions of the Y chromosome. The DAZ (Deleted in Azoospermia) gene cluster maps to the AZFc region of the Y chromosome and is deleted in many azoospermic and severely oligospermic men. It is thought that the DAZ gene cluster arose from the transposition, amplification, and pruning of the ancestral autosomal gene DAZL also involved in germ cell development and gametogenesis. This gene encodes an RNA-binding protein with two RNP motifs that was originally identified by its interaction with the infertility factors DAZ and DAZL. Two isoforms are encoded by transcript variants of this gene.[2]
Interactions
DAZ associated protein 1 has been shown to interact with DAZ1.[1]
References
- ^ a b Tsui S, Dai T, Roettger S, Schempp W, Salido EC, Yen PH (Aug 2000). "Identification of two novel proteins that interact with germ-cell-specific RNA-binding proteins DAZ and DAZL1". Genomics 65 (3): 266–73. doi:10.1006/geno.2000.6169. PMID 10857750.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DAZAP1 DAZ associated protein 1". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=26528.
Further reading
- Dai T, Vera Y, Salido EC, Yen PH (2003). "Characterization of the mouse Dazap1 gene encoding an RNA-binding protein that interacts with infertility factors DAZ and DAZL.". BMC Genomics 2: 6. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-2-6. PMC 57980. PMID 11604102. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=57980.
- Vera Y, Dai T, Hikim AP et al. (2003). "Deleted in azoospermia associated protein 1 shuttles between nucleus and cytoplasm during normal germ cell maturation". J. Androl. 23 (5): 622–8. PMID 12185095.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Prima V, Gore L, Caires A et al. (2005). "Cloning and functional characterization of MEF2D/DAZAP1 and DAZAP1/MEF2D fusion proteins created by a variant t(1;19)(q23;p13.3) in acute lymphoblastic leukemia". Leukemia 19 (5): 806–13. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2403684. PMID 15744350.
- Pan HA, Lin YS, Lee KH et al. (2006). "Expression patterns of the DAZ-associated protein DAZAP1 in rat and human ovaries". Fertil. Steril. 84 Suppl 2: 1089–94. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2005.03.075. PMID 16209998.
- Morton S, Yang HT, Moleleki N et al. (2006). "Phosphorylation of the ARE-binding protein DAZAP1 by ERK2 induces its dissociation from DAZ". Biochem. J. 399 (2): 265–73. doi:10.1042/BJ20060681. PMC 1609909. PMID 16848763. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1609909.
PDB gallery Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 19 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


