- Negative frequency
-
The concept of negative and positive frequency can be as simple as a wheel rotating one way or the other way.[citation needed] A signed value of frequency indicates both the rate and direction of rotation.[citation needed] The rate is expressed in units such as revolutions (aka cycles) per second (hertz) or radian/second (where 1 cycle corresponds to 2π radians).
Contents
Sinusoids
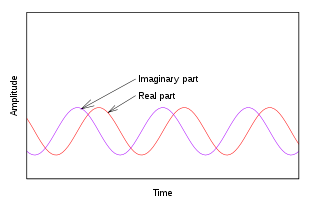
A sinusoid is a function of an angular argument, and its amplitude varies cyclically as the angle (aka phase) steadily increases or decreases. When the angle is a function of time, the concept of negative frequency is sometimes used to distinguish a decreasing angle from an increasing one. But sinusoids are not monotonic functions. Consequently,
 does not preserve the sign of
does not preserve the sign of  , just as
, just as  does not preserve the sign of
does not preserve the sign of  . Note that
. Note that  represents a usually unknown, random phase offset. In most cases of dealing with a single, real-valued sinusoid, it is sufficient to assume that
represents a usually unknown, random phase offset. In most cases of dealing with a single, real-valued sinusoid, it is sufficient to assume that  is positive. It represents the frequency, in units of radian/s.
is positive. It represents the frequency, in units of radian/s.Sometimes there are two sinusoids with the same frequency, and a known phase difference, for instance:
and
When
 ,
,  appears to lead
appears to lead  by
by  cycle (
cycle ( radians). But when
radians). But when  , the roles are reversed. So in that case it is possible to distinguish negative and positive frequencies. The diagram depicts a negative frequency.
, the roles are reversed. So in that case it is possible to distinguish negative and positive frequencies. The diagram depicts a negative frequency.  and
and  are referred to as real and imaginary, respectively. And
are referred to as real and imaginary, respectively. And  .
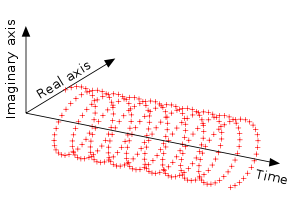
.A parametric plot of imaginary vs real would trace a circular path (like the rotating wheel). The addition of a time dimension creates a corkscrew pattern. A negative frequency (decreasing phase) causes a clockwise rotation in a right hand coordinate system as time increases:
Complex sinusoids
The complex function:
 facilitates many kinds of mathematical operations involving
facilitates many kinds of mathematical operations involving  , due in large part to Euler's simplification:
, due in large part to Euler's simplification:This very useful form is often referred to as a complex sinusoid, and it preserves the distinction between positive and negative
 .
.- For positive values, it is also called the analytic representation of
 .
.
The Fourier transform of
 produces a non-zero response only at frequency
produces a non-zero response only at frequency  .
.- The transform of
 has responses at both
has responses at both  and
and  , which reflects the fact that
, which reflects the fact that  is insufficient to determine the sign of
is insufficient to determine the sign of  .
.
- An alternative, and surprisingly useful, viewpoint is that both frequencies are present, as implied by the inverse of Euler's formula:
 .
.
- An alternative, and surprisingly useful, viewpoint is that both frequencies are present, as implied by the inverse of Euler's formula:
Sampling of positive and negative frequencies and aliasing

When a complex sinusoid is sampled at regular intervals, its frequency becomes indistinguishable from certain other frequencies, including negative ones (referred to as aliasing). The adjacent figure illustrates this effect for several cases. The red indicates 0 Hz (aka DC). Successively higher frequencies are indicated by orange, blue, purple, violet, black, and blue. Note that some frames depict "R" and "I" for the same frequency, and others depict the "I" samples of different frequencies that are aliases of each other.
For instance, the fourth frame (purple and green) compares samples of the imaginary component of the fractional frequency +
 with those of negative frequency
with those of negative frequency  , to illustrate that they are indistinguishable. Or in other words:
, to illustrate that they are indistinguishable. Or in other words:  for integer values of n, representing the sample number. The underlying waveforms are just the imaginary components of:
for integer values of n, representing the sample number. The underlying waveforms are just the imaginary components of:  and
and  , where
, where  is the sample rate (samples/sec).
is the sample rate (samples/sec).Likewise +
 is indistinguishable from
is indistinguishable from  . And
. And  (last plot) is indistinguishable from
(last plot) is indistinguishable from  (first plot).
(first plot).Negative frequency as a matched filter for positive frequencies
The rows of the DFT matrix begin at zero frequency, and get more negative as we move downward, row by row. This is because each of these rows functions as a matched filter to measure increasingly positive frequencies in the signal under test. For example, the top row of the 8 point DFT matrix measures DC in the signal, while the next row, which is a signal of fractional frequency −1/8, measures the strength at +1/8 fractional frequency in the signal under test.
Negative frequency in Doppler radar
In Doppler radar, the usual convention is that objects moving toward the radar are considered to induce a positive (differential) frequency, and objects going away are considered to induce a negative frequency.[citation needed]
See also
External links
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.