- List of Indo-Aryan languages
-
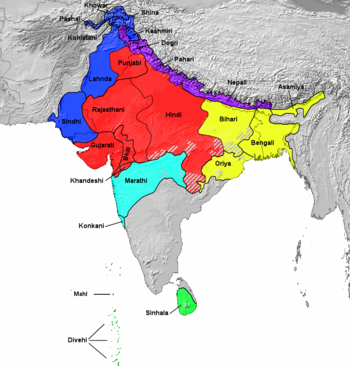
The Indo-Aryan languages include some 210 (SIL estimate) languages and dialects spoken by many people in Asia; this language family is a part of the Indo-Iranian language family.
Contents
Historical
Further information: Linguistic history of India- Old Indic (ca. 1500-300 BC)
- early Old Indic: Vedic Sanskrit (1500 to 500 BCE)
- late Old Indic: Epic Sanskrit, Classical Sanskrit (500 to 300 BCE)
- Middle Indic (ca. 300 BCE to 1500 CE)
- early phase: 3rd century BC
- Ashoka-Prakrits (3rd century BC regional dialects)
- Pali (language of the Buddhist canon)
- early Ardhamagadhi (language of the oldest Jain sutras)
- middle phase (200 BCE to 700 CE)
- Niya Prakrit
- Ardhamagadhi (later Jain canon)
- Dramatic Prakrits (Maurya period)
- Maharashtri Prakrit
- Magadhi Prakrit
- Sauraseni Prakrit
- Sinhala Prakrit
- hybrid Sanskrit (Mahayana canon)
- late phase: Apabhramsa (700 CE to 1500 CE)
- early phase: 3rd century BC
- Early Modern Indic (Mughal period, 1500 to 1800)
Contemporary languages
This classification follows Kausen (2005). The main differences from SIL are noted.
(SIL includes the Nuristani languages within Indo-Aryan.)
Dardic
Main article: Dardic languages(The relation of this family to other Indo-Aryan languages is unclear; SIL includes it in the Northwestern zone, despite these languages having a very different grammatical structure from that of the Classical Indo-Aryan languages.)
- Kunar languages
- Pashayi
- Gawar-Bati
- Dameli
- Shumashti
- Nangalami (includes Grangali)
- Chitral languages
- Kohistani languages
- Shina languages
- Shina language
- Brokskad (the Shina of Baltistan and Ladakh)
- Ushojo
- Domaaki
- Palula
- Savi
- Kashmiri
- Kashmiri
- Poguli
Northern Zone
North-Western Zone


Map of areas where Dogri-Kangri languages are spoken- Dogri-Kangri languages (Western Pahari)
(included in Pahari by SIL)
- Dogri-Kangri
- Gaddi
- Churahi
- Bhattiyali
- Bilaspuri
- Harijan Kinnauri
- Chambeali
- Mandeali
- Mahasu Pahari
- Jaunsari
- Pangwali
- Potwari (also known as Mirpuri or Pothohari and usually classified as Pahari)
- Hindko
- Saraiki (South Punjabi or Multani)
- Sindhi languages
- Sindhi
- Jadgali
- Kachchi
Western Zone
(SIL includes these languages in the Central zone)
- Mewati (of uncertain affiliation)
- Southern Gujarati
- Vasavi
- Sourashtra
- Khandeshi
- Ahirani (Kandeshi)
- Domari-Romani
(treated as a separate group by Klausen)
Central Zone
Main article: Hindi languages- North Central Zone (Punjabi)
- Eastern or Central Punjabi
- Majhi or Majhail
- Malwi or Malwai
- Doabi
- Powadhi
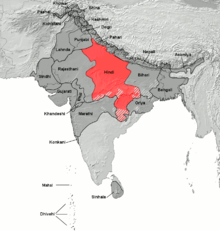
- West Central Zone (Western Hindi)
- Hindi-Urdu
- Braj Bhasa-Kanauji
- Haryanvi
- Bundeli
- Bhaya
- Sansi
- Chamari
- Ghera
- Gowli
- East Central Zone (Eastern Hindi)
- Awadhi (includes Fijian Hindi)
- Bagheli
- Chhattisgarhi
Eastern Zone (Magadhan)
These languages derive from Magadhi Prakrit through Ardhamagadhi ("Half-Magadhi").
- Assamese–Bengali languages
- Assamese (Ôxômiya)
- Bengali (Bangla) (includes Mal Paharia)
- Bishnupriya Manipuri (Imar Thar)
- Chakma
- Chittagonian
- Hajong
- Kharia Thar
- Rajbangsi
- Rohingya
- Sylheti
- Tanchangya
- Oriya languages
- Oriya (Oŗia)
- Adivasi Oriya
- Halbi
- Tharu
- Tharu (several languages)
Southern Zone languages
- Insular Indic
The insular languages are spoken in the islands of Sri Lanka and Maldives along with the island of Minicoy. The insular languages share several characteristics which set them apart significantly from their continental sister languages. (SIL makes them a separate branch of Indo-Aryan.) However, Sinhala and Dhivehi are no longer mutually intelligible.[1]
- Dhivehi
- Sinhala
- Vedda
Unclassified
The following languages have not been classified within the Indo-Aryan family.
- Dhanwar Rai
- Tippera
- Kanjari
- Od
- Usui
- Vaagri Booli
- Darai
- Kumhali
- Chinali
See also
- Nuristani languages
- Varieties of Hindi
- Proto-Indo-Iranian
- List of languages of India
References
- Ernst Kausen, 2006. Die Klassifikation der indogermanischen Sprachen (Microsoft Word, 133 KB)
- SIL Ethnologue, 2000. (online edition)
Categories:- Indo-Aryan languages
- Lists of Indo-European languages
- Old Indic (ca. 1500-300 BC)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.