- Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer
-
Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer 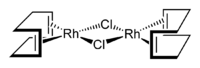
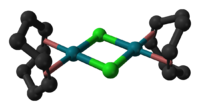 di-μ-chlorido-
di-μ-chlorido-
bis[η2,η2-(cycloocta-1,5-diene)rhodium]Other namesCyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimerIdentifiers CAS number 12092-47-6 
ChemSpider 21171524 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - Cl[Rh].Cl[Rh].C=1CC\C=C/CCC=1.C/1C\C=C/CC\C=C\1
- InChI=1S/2C8H12.2ClH.2Rh/c2*1-2-4-6-8-7-5-3-1;;;;/h2*1-2,7-8H,3-6H2;2*1H;;/q;;;;2*+1/p-2/b2*2-1-,8-7-;;;;

Key: QSUDXYGZLAJAQU-MIXQCLKLSA-L
InChI=1/2C8H12.2ClH.2Rh/c2*1-2-4-6-8-7-5-3-1;;;;/h2*1-2,7-8H,3-6H2;2*1H;;/q;;;;2*+1/p-2/b2*2-1-,8-7-;;;;/r2C8H12.2ClRh/c2*1-2-4-6-8-7-5-3-1;2*1-2/h2*1-2,7-8H,3-6H2;;/b2*2-1-,8-7-;;
Key: QSUDXYGZLAJAQU-PXXGERDABU
Properties Molecular formula C16H24Cl2Rh2 Molar mass 493.0806 g/mol Melting point 243 °C<
Solubility in other solvents insol.  rhodium chloride dimer (verify) (what is:
rhodium chloride dimer (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer is the chemical compound with the formula Rh2Cl2(C8H12)2, commonly abbreviated [RhCl(COD)]2 or Rh2Cl2(COD)2. This yellow-orange, air-stable compound is a widely used precursor to homogeneous catalysts.[1].
Preparation and reactions
The synthesis of [RhCl(COD)]2 involves treatment of hydrated rhodium trichloride with 1,5-cyclooctadiene in hot, deoxygenated aqueous ethanol in the presence of sodium carbonate:[1]
- 2 RhCl3.3(H2O) + 2 COD + 2 CH3CH2OH + 2 Na2CO3 → [RhCl(COD)]2 + 2 CH3CHO + 8 H2O + 2 CO2 + 4 NaCl
[RhCl(COD)]2 is the principal source of the versatile electrophile "[Rh(COD)]+."
- [RhCl(COD)]2 + n L → [LnRh(COD)]+Cl- (where L = PR3, alkene, etc. and n = 2 or 3)
In this way, chiral phosphines such as chiraphos, DIPAMP, and DIOP have been attached to Rh. The resulting chiral catalysts are capable of asymmetrically hydrogenating certain prochiral alkenes.[2]
References
- ^ a b Giordano, G.; Crabtree, R. H. “Di-μ-chloro-bis(η4-1,5-cyclooctadiene)dirhodium(I)” Inorganic Syntheses, 1990, volume 28, pages 88-90. ISBN 0-471-52619-3.
- ^ W. S. Knowles (2003). "Asymmetric Hydrogenations (Nobel Lecture 2001)". Advances in Synthesis and Catalysis 345 (1–2): 3. doi:10.1002/adsc.200390028.
Rhodium compounds 
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
