- Distance measures (cosmology)
-
Physical cosmology 
Universe · Big Bang
Age of the universe
Timeline of the Big Bang
Ultimate fate of the universeEarly universeExpanding universeComponentsDistance measures are used in physical cosmology to give a natural notion of the distance between two objects or events in the universe. They are often used to tie some observable quantity (such as the luminosity of a distant quasar, the redshift of a distant galaxy, or the angular size of the acoustic peaks in the CMB power spectrum) to another quantity that is not directly observable, but is more convenient for calculations (such as the comoving coordinates of the quasar, galaxy, etc). The distance measures discussed here all reduce to the naïve notion of Euclidean distance at low redshift.
In accord with our present understanding of cosmology, these measures are calculated within the context of general relativity, where the Friedmann–Lemaitre–Robertson–Walker solution is used to describe the universe.
Contents
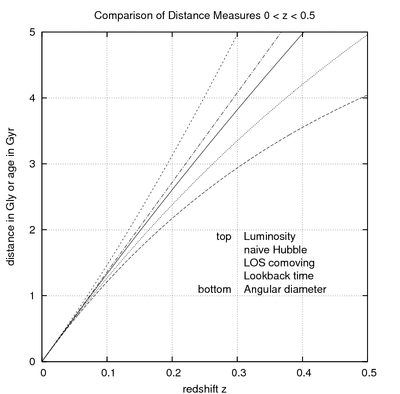
Types of distance measures
- Angular diameter distance is a good indication (especially in a flat universe) of how near an astronomical object was to us when it emitted the light that we now see.
- Luminosity distance.
- Comoving distance. The distance between two points measured along a path defined at the present cosmological time.
- Cosmological proper distance. The distance between two points measured along a path defined at a constant cosmological time. The cosmological proper distance should not be confused with the more general proper length or proper distance.
- Light travel time or lookback time. This is how long ago light left an object of given redshift.
- Light travel distance (LTD). The light travel time times the speed of light. For values above 2 billion light years, this value does not equal the comoving distance or the angular diameter distance anymore, because of the expansion of the universe. Also see misconceptions about the size of the visible universe.
- Naive Hubble's law, taking z = H0d/c, with H0 today's Hubble constant, z the redshift of the object, c the speed of light, and d the "distance."
Comparison of distance measures
- light-travel distance – simply the speed of light times the cosmological time interval, i.e. integral of c dt, while the comoving distance is the integral of c dt/a(t).
- dL luminosity distance
- dpm proper motion distance
- called the angular size distance by Peebles 1993, but should not be confused with angular diameter distance [1])
- sometimes called the coordinate distance
- sometimes dpm is called the angular diameter distance
- da angular diameter distance
The latter three are related by:
- da = dpm/(1 + z) = dL/(1 + z)2
where z is the redshift.
If and only if the curvature is zero, then proper motion distance and comoving distance are identical, i.e. dpm = χ.
For negative curvature,
while for positive curvature,
where RC is the (absolute value of the) radius of curvature.
A practical formula for numerically integrating dp to a redshift z for arbitrary values of the matter density parameter Ωm, the cosmological constant density parameter ΩΛ, and the equation of state parameter w is
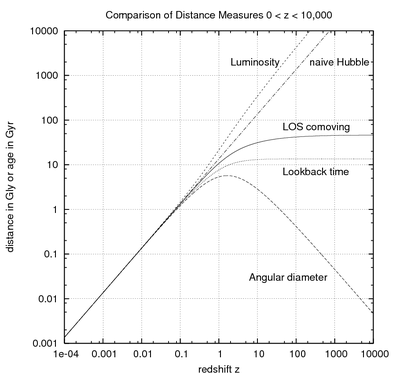 A comparison of cosmological distance measures, from redshift zero to redshift of 10,000, corresponding to the epoch of matter/radiation equality. The background cosmology is Hubble parameter 72 km/s/Mpc, Omega_lambda = 0.732, Omega_matter = 0.266, Omega_radiation = 0.266/3454, and Omega_k chosen so that the sum of Omega parameters is one.
A comparison of cosmological distance measures, from redshift zero to redshift of 10,000, corresponding to the epoch of matter/radiation equality. The background cosmology is Hubble parameter 72 km/s/Mpc, Omega_lambda = 0.732, Omega_matter = 0.266, Omega_radiation = 0.266/3454, and Omega_k chosen so that the sum of Omega parameters is one.
where c is the speed of light and H0 is the Hubble constant.
By using sin and sinh functions, proper motion distance dpm can be obtained from dp.
See also
- Big Bang
- Comoving distance
- Friedmann equations
- Physical cosmology
- Cosmic distance ladder
- Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker metric
References
- P. J. E. Peebles, Principles of Physical Cosmology. Princeton University Press (1993)
- Scott Dodelson, Modern Cosmology. Academic Press (2003).
External links
- 'The Distance Scale of the Universe' compares different cosmological distance measures.
- 'Distance measures in cosmology' explains in detail how to calculate the different distance measures as a function of world model and redshift.
- iCosmos: Cosmology Calculator (With Graph Generation ) calculates the different distance measures as a function of cosmological model and redshift, and generates plots for the model from redshift 0 to 20.
Categories:- Physical cosmology
- Physical quantities
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.