- N-Acetylaspartic acid
-
N-Acetylaspartic acid 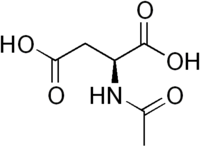 (2S)-2-Acetamidobutanedioic acidOther namesAcetylaspartic acid
(2S)-2-Acetamidobutanedioic acidOther namesAcetylaspartic acid
N-Acetylaspartic acid
N-Acetyl-L-aspartate
Acetyl-L-aspartic acid
N-Acetyl-L-aspartic acidIdentifiers Abbreviations NAA CAS number 997-55-7 
PubChem 65065 ChemSpider 58576 
EC number 213-643-9 MeSH N-acetylaspartate RTECS number CI9098600 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CC(=O)N[C@@H](CC(=O)O)C(=O)O
Properties Molecular formula C6H9NO5 Molar mass 175.139 g/mol Melting point 137-140 °C
Hazards S-phrases S22 S24/25  acid (verify) (what is:
acid (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references N-Acetylaspartic acid, or N-acetylaspartate (NAA), is a derivative of aspartic acid with a formula of C6H9NO5 and a molecular weight of 175.139.
NAA is the second-most-concentrated molecule in the brain after the amino acid glutamate. It is synthesized in neurons from the amino acid aspartic acid and acetyl-coenzyme A. The various functions served by NAA are still under investigation, but the primary proposed functions include its being:
- A neuronal osmolyte that is involved in fluid balance in the brain
- A source of acetate for lipid and myelin synthesis in oligodendrocytes, the glial cells that myelinate neuronal axons
- A precursor for the synthesis of the important neuronal dipeptide N-Acetylaspartylglutamate
- A contributor to energy production from the amino acid glutamate in neuronal mitochondria.
In the brain, NAA is thought to be present predominantly in neuronal cell bodies, where it acts as a neuronal marker [1]. NAA gives off the largest signal in magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the human brain, and the levels measured there are decreased in numerous neuropathological conditions ranging from brain injury to stroke to Alzheimer's disease. This fact makes NAA a reliable diagnostic molecule for doctors treating patients with brain damage or disease.
NAA may also be a marker of creativity.[2]
See also
References
- N-Acetylaspartate: A Unique Neuronal Molecule in the Central Nervous System, eds., J.R.Moffett, S.B.Tieman, D.R.Weinberger, J.T.Coyle, and M.A.Namboodiri, pp. 7–26. New York, NY: Springer Science + Business Media, 2006.
http://www.n-acetylaspartate.com
Finds correlations between measure of creativity and fMRIs of NAA levels in areas of brain: Biochemical Support for the "Threshold" Theory of Creativity: A Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study, Rex E. Jung et al., April 22, 2009, 29(16):5319-5325; doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0588-09.2009
- ^ Chatham JC, Blackband SJ. (2001). "Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging in animal research.". ILAR J 42 (3): 189–208. PMID 11406719.
- ^ http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg20227084.300-creativity-chemical-favours-the-smart.html
External links
Categories:- Amino acid derivatives
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
