- Optical circulator
-
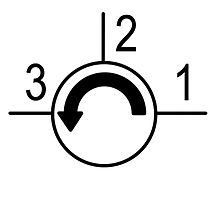
An optical circulator is a special fiber-optic component that can be used to separate optical signals that travel in opposite directions in an optical fiber, analogous to the operation of an electronic circulator. An optical circulator is a three-port device designed such that light entering any port exits from the next. This means that if light enters port 1 it is emitted from port 2, but if some of the emitted light is reflected back to the circulator, it does not come out of port 1, but instead exits from port 3. Circulators can be used to achieve bi-directional transmission over a single fiber. Because of its high isolation of the input and reflected optical powers and its low insertion loss, optical circulators are widely used in advanced communication systems and fiber-optic sensor applications.
Optical circulators are non-reciprocal optics, which means that changes in the properties of light passing through the device are not reversed when the light passes through in the opposite direction. This can only happen when the symmetry of the system is broken, for example by an external magnetic field. A Faraday rotator is another example of a non-reciprocal optical device.
See also
Categories:- Optical devices
- Optics stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.