- Activator (genetics)
-
An activator is a DNA-binding protein that regulates one or more genes by increasing the rate of transcription. The activator may increase transcription by virtue of a connected domain which assists in the formation of the RNA polymerase holoenzyme, or may operate through a coactivator. A coactivator binds the DNA-binding activator and contains the domain assisting holoenzyme formation. A particular activator may bind one or more specific coactivators.
Role in transcriptional regulation
RNA polymerase (RNAP) is usually bound to the promoter region on the gene which creates a complex that sometimes undergoes a transition that allows transcription to take place. An activator essentially recruits the RNAP to its promoter region, by binding to the activator binding site itself which serves as a liaison between the RNA polymerase and the DNA. Sometimes, the activator is required for the RNA polymerase to change DNA conformation through allostery to initiate transcription. RNAP does not spontaneously transform into the open complex and requires the activator.
Examples
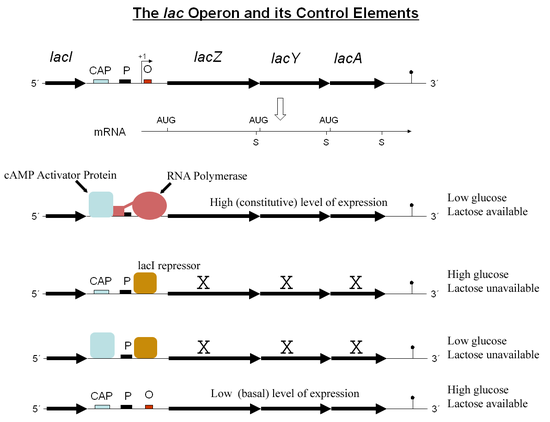
In the lac operon of the bacteria Escherichia coli, the Lac repressor is constitutively expressed and always bound to the operator region of the promoter, interfering with the ability of RNAP to bind to the promoter and transcribe the lac operon. In the presence of lactose, the repressor changes conformation and falls off the operator and RNAP is able to bind to the promoter.
The catabolite activator protein (CAP) is an example of an activator for this operon, present in prokaryotic systems. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is present in low levels of glucose, and binds to CAP which changes to an active conformation. Only then, can CAP act as an activator and help recruit RNAP to its binding site.
In other words, for maximum expression of the lac genes, there needs to be a high level of lactose (for the repressor to fall off) and a low level of glucose (for CAP to recruit RNAP) in the cell. Otherwise, either the repressor will bind to the operator (no genes transcribed), or there is no cooperative binding by CAP thus depending on a spontaneous binding of RNAP (low levels of genes transcribed).
See also
Categories:- Gene expression
- Proteins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.