- Chamizal dispute
-
The Chamizal dispute was a border conflict over about 600 acres (2.4 km2) on the U.S.-Mexico border between El Paso, Texas, and Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua. It was caused by differences between the bed of the Rio Grande (in Spanish: Río Bravo del Norte) as surveyed in 1852 and the present channel of the river.[1]
The Spanish word chamizal comes from chamizo, the common name for the four-wing saltbush (Atriplex canescens) which covered the disputed land near the present-day park.
Contents
Origins (1848–1895)
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (which officially ended the Mexican-American War) and the Treaty of 1884 were the agreements originally responsible for the settlement of the international border, both of which specified that the middle of Rio Grande was the border – irrespective of any alterations in the channels or banks. The Treaty of 1884 went on to maintain that the alterations had to result from such gradual natural causes. This provision followed the long-established doctrine of international law that when changes in the course of a boundary river are caused by a deposit of alluvium, the boundary changes with the river, but when changes are due to avulsion, the old channel remains the boundary.
The river continually shifted south between 1852 and 1868, with the most radical shift in the river occurring after a flood in 1864. By 1873 the river had moved approximately 600 acres (2.4 km2), cutting off land that was in effect made United States territory. The newly exposed land came to be known as El Chamizal, and eventually the land was settled and incorporated as part of El Paso. Both Mexico and the United States claimed the land. In 1895, Mexican citizens filed suit in the Juárez Primary Court of Claims to reclaim the land.
Disputes and controversy (1895–1963)
 U.S. Ambassador to Mexico, Thomas C. Mann (left) and the Mexican Secretary of Foreign Affairs, Manuel Tello Baurraud (right) sign the Chamizal Convention in Mexico City on 29 August 1963.
U.S. Ambassador to Mexico, Thomas C. Mann (left) and the Mexican Secretary of Foreign Affairs, Manuel Tello Baurraud (right) sign the Chamizal Convention in Mexico City on 29 August 1963.
In 1910 Mexico and the United States agreed to have the dispute settled by the International Boundary Commission,[1] and a tribunal was established comprising a representative from each country and a Canadian jurist, Eugene Lafleur, as presiding officer to investigate and deliberate over whether the change in the river's course had been gradual, whether the boundaries set by treaties were fixed, and whether the 1884 treaty applied.[2] Mexico claimed that the boundary had never changed and therefore that the Chamizal was technically Mexican territory, while the United States claimed that the 1884 convention applied, that the boundary was the result of gradual erosion, and that the property therefore belonged to the United States.
The tribunal recommended that year that part of the disputed tract lying between the riverbed, as surveyed in 1852, and the middle of the river in 1864 would become United States territory and the remainder of the tract become part of Mexico. The United States rejected the proposal on grounds that it did not conform to the agreements of the arbitration – fuelling a dispute between the two governments and fostering ill-will.
During this period of indecision, part of the land located in the middle of the river came to be known as Cordova Island. In a sense it was an island belonging to Mexico inside U.S. territory; thus, there was little or no control by the local authorities, which created a haven for crime and opportunities for illegal crossings.
Between 1911 and 1963 several more attempts were made by various presidents to solve the problem. Amongst the suggested compromises were forgiving debt, exchange of other territory along the Rio Grande, direct purchase of the tract, and inclusion of the Chamizal in the Rio Grande Rectification Project. The dispute continued to affect Mexico–United States relations adversely until President John F. Kennedy agreed to settle it on the basis of the 1911 arbitration award.[3] It was hoped that settlement of the dispute would strengthen the Alliance for Progress and solidify the Organization of American States.
Resolution
 U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson (left) and Mexican President Adolfo López Mateos (right) unveil the new boundary marker signaling the peaceful end of the Chamizal dispute on 25 September 1964.
U.S. President Lyndon B. Johnson (left) and Mexican President Adolfo López Mateos (right) unveil the new boundary marker signaling the peaceful end of the Chamizal dispute on 25 September 1964.
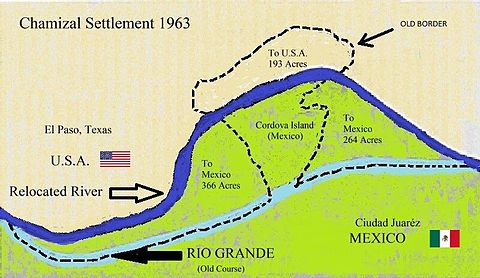
The dispute was formally settled on 14 January 1963, when the United States and Mexico ratified a treaty that generally followed the 1911 arbitration recommendations. The agreement awarded to Mexico 366 acres (1.48 km2) of the Chamizal area and 71 acres (0.29 km2) east of the adjacent Cordova Island. Although no payments were made between the two governments, the United States received compensation from a private Mexican bank for 382 structures included in the transfer. The United States also received 193 acres (0.78 km2) of Cordova Island from Mexico, and the two nations agreed to share equally in the cost of rechanneling the river. In 1964 Presidents Adolfo López Mateos and Lyndon B. Johnson met on the border to end the dispute officially. On 17 September 1963, the U.S. Congress introduced the American–Mexican Chamizal Convention Act of 1964, which finally settled the matter. In October 1967, President Johnson met with President Gustavo Díaz Ordaz on the border and formally proclaimed the settlement.[3]
One of the aims of the Chamizal Convention was to build a man-made channel to prevent the Rio Grande from blurring the international boundary in the future. The channel was constructed of concrete, 167 feet (51 m) in width at the top and 15 feet (4.6 m) deep.[4] The two governments shared the cost of the channel, along with the cost of three new bridges. Chamizal National Memorial was established in 1974 as a museum to increase visitor awareness of cooperation, diplomacy and cultural values as a basic means to conflict resolution.[5]
See also
References
- ^ a b Los Angeles Times (Dec 22, 1963) "End to the El Chamizal Affair"
- ^ Los Angeles Times ( Mar 13, 1963) Ruben Salazar, "Texas Due to Return 450 Acres to Mexico"
- ^ a b Los Angeles Times (December 21, 1963) Don Irwin, "Johnson Signs Treaty on Chamizal Turnover"
- ^ Los Angeles Times (Jul 21, 1963) "Curtain on El Chamizal"
- ^ Los Angeles Times (Jul 20, 1963) "Juarez Victors Cheer El Paso Deal Feebly"
External links
- Reports of International Arbitral Awards – The Chamizal Case
- Handbook of Texas Online: Chamizal Dispute
Coordinates: 31°45′30″N 106°27′30″W / 31.75833°N 106.45833°W
Categories:- History of the foreign relations of the United States
- 1963 in Mexico
- International territorial disputes of the United States
- Mexico–United States border
- Territorial disputes of Mexico
- Arbitration cases
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.