- Brewster's angle
-
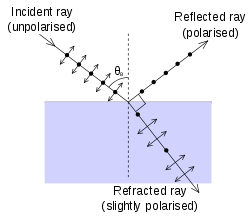
Brewster's angle (also known as the polarization angle) is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with no reflection. When unpolarized light is incident at this angle, the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized. This special angle of incidence is named after the Scottish physicist, Sir David Brewster (1781–1868).
Contents
Explanation
When light encounters a boundary between two media with different refractive indices, some of it is usually reflected as shown in the figure above. The fraction that is reflected is described by the Fresnel equations, and is dependent upon the incoming light's polarization and angle of incidence.
The Fresnel equations predict that light with the p polarization (electric field polarized in the same plane as the incident ray and the surface normal) will not be reflected if the angle of incidence is
where n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the two media. This equation is known as Brewster's law, and the angle defined by it is Brewster's angle.
The physical mechanism for this can be qualitatively understood from the manner in which electric dipoles in the media respond to p-polarized light. One can imagine that light incident on the surface is absorbed, and then reradiated by oscillating electric dipoles at the interface between the two media. The polarization of freely propagating light is always perpendicular to the direction in which the light is travelling. The dipoles that produce the transmitted (refracted) light oscillate in the polarization direction of that light. These same oscillating dipoles also generate the reflected light. However, dipoles do not radiate any energy in the direction of the dipole moment. Consequently, if the direction of the refracted light is perpendicular to the direction in which the light is predicted to be specularly reflected, the dipoles cannot create any reflected light.
With simple geometry this condition can be expressed as:
where θ1 is the angle of incidence and θ2 is the angle of refraction.
Using Snell's law,
one can calculate the incident angle θ1 = θB at which no light is reflected:
Solving for θB gives:
For a glass medium (n2 ≈ 1.5) in air (n1 ≈ 1), Brewster's angle for visible light is approximately 56°, while for an air-water interface (n2 ≈ 1.33), it is approximately 53°. Since the refractive index for a given medium changes depending on the wavelength of light, Brewster's angle will also vary with wavelength.
The phenomenon of light being polarized by reflection from a surface at a particular angle was first observed by Etienne-Louis Malus in 1808. He attempted to relate the polarizing angle to the refractive index of the material, but was frustrated by the inconsistent quality of glasses available at that time. In 1815, Brewster experimented with higher-quality materials and showed that this angle was a function of the refractive index, defining Brewster's law.
Brewster's angle is often referred to as the "polarizing angle", because light that reflects from a surface at this angle is entirely polarized perpendicular to the incident plane ("s-polarized") A glass plate or a stack of plates placed at Brewster's angle in a light beam can thus be used as a polarizer. The concept of a polarizing angle can be extended to the concept of a Brewster wavenumber to cover planar interfaces between two linear bianisotropic materials.
Applications
Polarized sunglasses use the principle of Brewster's angle to reduce glare from the sun reflecting off horizontal surfaces such as water or road. In a large range of angles around Brewster's angle the reflection of p-polarized light is lower than s-polarized light. Thus, if the sun is low in the sky reflected light is mostly s-polarized. Polarizing sunglasses use a polarizing material such as polaroid film to block horizontally-polarized light, preferentially blocking reflections from horizontal surfaces. The effect is strongest with smooth surfaces such as water, but reflections from road and the ground are also reduced.
Photographers use the same principle to remove reflections from water so that they can photograph objects beneath the surface. In this case, the polarizing filter camera attachment can be rotated to be at the correct angle (see figure).
 Photograph taken of a window with a camera polarizer filter rotated to two different angles. In the picture at left, the polarizer is aligned with the polarization angle of the window reflection. In the picture at right, the polarizer has been rotated 90° eliminating the heavily polarized reflected sunlight.
Photograph taken of a window with a camera polarizer filter rotated to two different angles. In the picture at left, the polarizer is aligned with the polarization angle of the window reflection. In the picture at right, the polarizer has been rotated 90° eliminating the heavily polarized reflected sunlight.Brewster windows
Gas lasers typically use a window tilted at Brewster's angle to allow the beam to leave the laser tube. Since the window reflects some s-polarized light but no p-polarized light, the gain for the s polarization is reduced but that for the p polarization is not affected. This causes the laser's output to be p polarized, and allows lasing with no loss due to the window.[1]
Notes
- ^ Optics, 3rd edition, Hecht, ISBN 0-201-30425-2
References
- A. Lakhtakia, "Would Brewster recognize today's Brewster angle?" OSA Optics News, Vol. 15, No. 6, pp. 14–18 (1989).
- A. Lakhtakia, "General schema for the Brewster conditions," Optik, Vol. 90, pp. 184–186 (1992).
External links
- Brewster's Angle Extraction from Wolfram Research
- Brewster window at RP-photonics.com
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.