- Malonic ester synthesis
-
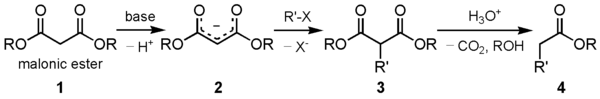
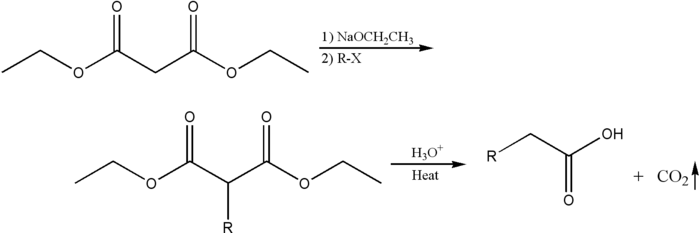
The malonic ester synthesis is a chemical reaction where diethyl malonate or another ester of malonic acid is alkylated at the carbon alpha (directly adjacent) to both carbonyl groups, and then converted to a substituted acetic acid.[1] The major drawback of malonic ester synthesis is that the alkylation stage can also produce dialkylated structures. This makes separation of products difficult and yields lower.[2]
Contents
Mechanism
A strong base is required to deprotonate the center proton. The protons alpha to carbonyl groups are easily deprotonated. The malonic ester is especially so by virtue of being adjacent to two carbonyl groups. The carbanion formed can undergo nucleophilic substitution on the alkyl halide, to give the alkylated compound. On heating, the di-ester undergoes thermal decarboxylation, yielding an acetic acid substituted by the appropriate R group.[3] Thus, the malonic ester can be thought of being equivalent to the -CH2COOH synthon.
The esters chosen are usually the same as the base used, i.e. ethyl esters with sodium ethoxide. This is to prevent scrambling by transesterification.
Variations
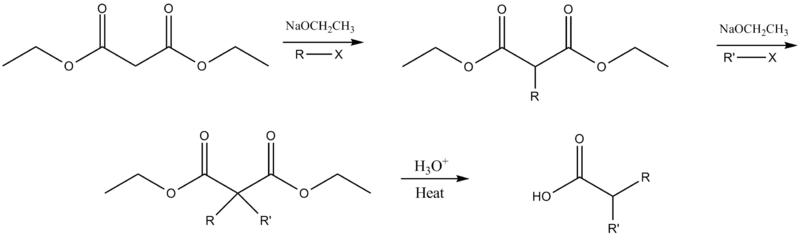
Dialkylation
The ester may be dialkylated if deprotonation and alkylation are repeated before the addition of aqueous acid.
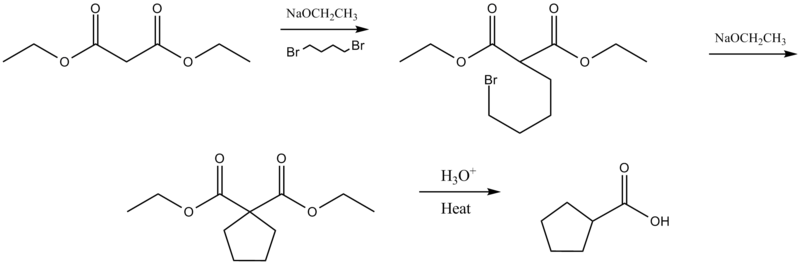
Cycloalkylcarboxylic acid synthesis
Intramolecular malonic ester synthesis occurs when reacted with a dihalide.[4][5]. This reaction is also called the Perkin alicyclic synthesis (see: alicyclic compound) after investigator William Henry Perkin, Jr. [6]
See also
References
- ^ House, Herbert O. (1972). Modern Synthetic Reactions. Menlo Park, CA.: W. A. Benjamin. ISBN 0-8053-4501-9.
- ^ Malonic Ester Synthesis - Alkylation of Enolates
- ^ "Malonic Ester Synthesis". Organic Chemistry Portal. http://www.organic-chemistry.org/namedreactions/malonic-ester-synthesis.shtm. Retrieved 2007-10-26.
- ^ Smith, Janice Gorzynski. Organic Chemistry: Second Ed. 2008. pp 905-906
- ^ Using the non-selective nature of malonic ester synthesis to produce cyclic compounds
- ^ Ueber die Einwirkung von Trimethylenbromid auf Acetessigäther, Benzoylessigäther und Malonsäureäther W. H. Perkin Jun. Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft Volume 16 Issue 2, Pages 1787 - 1797 1883 doi:10.1002/cber.18830160259
Categories:- Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions
- Substitution reactions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.